Abstract
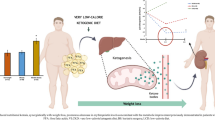
Some studies have demonstrated the participation of leptin in magnesium metabolism. On the other hand, there is evidence of the role of magnesium in the leptin intracellular signaling pathway. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the existence of a relationship between serum leptin concentrations and magnesium biomarkers in women with obesity. Case–control study involving 108 women aged between 20 and 50 years, divided into two groups: obese (n = 52) and control (n = 56). Body weight, height and waist circumference, body mass index, dietary magnesium intake, magnesium biomarkers and serum leptin concentrations were measured. Serum leptin concentrations showed a statistically significant difference between groups (p < 0.001). Mean values of magnesium intake were lower than intake recommended, and with no statistically significant difference between two groups (p > 0.05). Women with obesity had lower plasma and erythrocyte magnesium concentrations than control group did (p < 0.001). Magnesium concentrations found in the urine of women with obesity were higher than the control group was, with a statistically significant difference (p < 0.001). There was a correlation between serum leptin and magnesium biomarkers (p < 0.001). Women with obesity show an inadequate magnesium nutritional status characterized by low plasma and erythrocyte concentrations and high concentrations in urine, and they also have high serum leptin concentrations. Thus, it was possible to observe a correlation between hyperleptinemia and magnesium biomarkers, requiring further studies to determine whether the dysfunction of this hormone can influence the compartmentalization of the mineral in obese organisms.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting the results of this study will be de-identified upon request to the corresponding author [DNM]. The data are not publicly available due to containing information such as socioeconomic data, name, email, telephone and address of the participants. Study data will be available upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Anção MS, Cuppari L, Draine AS, Singulem D (2002) Programa de apoio à nutrição Nutwin: versão.1.5. Departamento de Informática em Saúde, São Paulo
Atabek ME, Kurtoglu S, Pirgon O (2006) Possible effect of leptina on renal magnesium excretion in adolescente patients with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Int 48(4):393–397. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-200X.2006.02227.x
Ayina CAN, Noubiap JJN, Ngoa LSE, Boudou P, Gautier F, Mengno MK, Mbanya JC, Sobngwi E (2016) Association of serum leptin andadiponectin with anthropomorphic índices of obesity, blood lipids and insulin resistance in a sub-saharan African population. Lipids Health Dis 15(96):96–107. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-016-0264-x
Baaij JHF, Hoenderop GJJ, Bindels RJM (2015) Magnesium in man: implications for health and disease. Physiol Rev 95:1–46. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00012.2014
Brooks AJ, Daí W, O’mara ML et al (2014) Mechanism of activation of protein kinase JAK2 by the growth hormone receptor. Science 344(6185). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1249783
Cabral MJ, Vieira KA, Sawaya AL, Florencia TMMT (2013) Perfil socioeconômico nutricional e de ingestão alimentar de beneficiários do Programa Bolsa Família. Estud av 27(78): 71–87. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-40142013000200006
Cruz KJ, Oliveira AR, Pinto DP, Morais JBS, Lima FS, Colli C, Torres-Leal FL, Marreiro DN (2014) Influence of magnesium on insulin resistance in obese women. Biol Trace Elem Res 160(3):305–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0044-2
Elin RJ (1987) Assessment of magnesium status. Clin Chem 33(11):1965–1970
Esteban NR, Ferre MG, Alonso PH, Salvadó JS (2018) Dietary magnesium and cardiovascular disease: a review with emphasis in epidemiological. Nutrients 10(2):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020168
Gruzdeva O, Borodkina D, Uchasova E, Dyleva Y, Barbarash O (2019) Leptin resistance: underlying mechanisms and diagnosis. Diab Metab Syndr Obes 12(1):191–198. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-52732006000100009
Hwang M, Go Y, Park JH, Shin SK, Song SE, Oh BC, Im SS, Hwang I, Jeon YH, Lee IK, Seino S, Song DK (2016) Epac2a-null mice exhibit obesity-prone nature more susceptible to leptin resistance. Int J Obes 41(2):279–288. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2016.208
Institute Of Medicine (1997) Food And nutrition board. dietary reference intakes for calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin d and fluoride. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Jastrzębska-Mierzyńska M, Ostrowska L, Hady HR, Dadan J (2012) Assessment of dietary habits, nutritional status and blood biochemical parameters in patients prepared for bariatric surgery: a preliminary study. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne 7(3):156–165. https://doi.org/10.5114/wiitm.2011.27581
Kasper P, Vohlen C, Dinger K, Mohr J, Hucklenbruch-Rother E, Janoschek R, Koth J, Matthes J, Appel S, Dotsch J (2017) Renal metabolic programming is linked to the dynamic regulation of a leptin-Klf15 axis and Akt/AMPKα signaling in male offspring of obese dams. Endocrinology 10(10):1–30. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2017-00489
Lecube A, Baena-Fustegueras JA, Fort JM, Pelegrí D, Hernández C, Simó R (2012) Diabetes is the main factor accounting for hypomagnesemia in obese subjects. PLoS ONE 7(1):30599. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030599
López-Jaramillo P, Gómez-Arbeláez D, López-López J, López-López C, Martínez-Ortega J, Gómez-Rodríguez A, Triana-Cubillos S (2014) The role of leptin/adiponectin ratio in metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig 18(1):37–45. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2013-0053
Lourenço BH, Vieira LP, Macedo A, Nakasato M, Marucci MFN, Bocchi EA (2009) Estado nutricional e adequação da ingestão de energia e nutrientes em pacientes com insuficiência cardíaca. Arq Bras Cardiol 93(5):541–548. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0066-782X2009001100016
Ma J, Zhao N, Zhu D (2016) Biphasic responses of human vascular smooth muscle cells to magnesium ion. J Biomed Mater Res A 104(2):347–356. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.35570
Mackenzie SM, Kralingen CJV, Davies E (2019) Regulation of aldosterone secretion. Vitam Horm 109:241–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2018.07.001
Martins MC, Faleiro LL, Fonseca A (2012) Relationship between leptin and body mass and metabolic syndrome in an adult population. Rev Port Cardiol 31(11):711–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repc.2012.08.002
Mayan H, Farfel Z, Karlish SJD (2018) Renal Mg handling, FXYD2 and the central role of the Na,K-ATPase. Physiol Rep 6(17):e13843. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13843
Morais JB, Severo JS, Santos LR, Melo SRS, Santos RO, Oliveira ARS, Cruz KJC, Marreiro DN (2016) Role of magnesium in oxidative stress in individuals with obesity. Biol Trace Elem Res 176(1):20–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0793-1
Nielsen FH (2010) Magnesium, inflammation, and obesity in chronic disease. Nutrit Reviw 68(6):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00293.x
Nielsen FH, Johnson LAK (2017) Data from controlled metabolicward studies provide guidance for the determination of status indicators and dietary requirements for magnesium. Biol Trace Elem Res 177(1):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0873-2
Oliveira ARS, Cruz KJC, Severo JS, Morais JBS, Freitas TE, Araújo RS, Marreiro DN (2015) Magnesium status and its relationship with C-reactive protein in obese women. Biol Trace Elem Res 168(2):296–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0358-8
Pretz D, Foll CL, Rizwan MZ, Lutz TA, Tups A (2020) Hyperleptinemia as a contributing factor for the impairment of glucose intolerance in obesity. Faseb J 35(2):e21216. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202001147R
Romani AMP (2011) Cellular magnesium homeostasis. Arch Biochem Biophys 512(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2011.05.010
Romero ABR, Lima FS, Colli C (2017) Mg status in inflammation, insulin resistance, and associated conditions. Nutrire 42(6):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41110-017-0031-4
Santos LR, Melo SRS, Severo JS, Morais JBS, Beserra JB, Fontenelle LC, Oliveira ARS, Cruz KJC, Sousa MP, Oliveira FE, Sousa GS, Henriques GS, Marreiro DN (2021) Magnesium parameters and their association with lipid metabolism markers in obese women. Rev Chil Nutr 48:80–88. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-75182021000100080
Tietz NW (1995) Clinical guide to laboratory test, 3rd edn. Saunders Company, Philadelphia
Tsai JP (2017) The association of serum leptin levels with metabolic diseases. Tzu Chi Med J 29(4):192–196. https://doi.org/10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_123_17
Whitehouse RC, Prasad AS, Rabbani PI, Cossack ZT (1982) Zinc in plasma, neutrophils, lymphocytes, and erythrocytes as determined by flameless atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Clin Chem 28(3):475–80
World Health Organization (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. techincal report series. WHO, Geneva, p 894
World Health Organization (2008) Waist circumference and waist-hip ratio: report of a who expert consultation. WHO, Geneva
Zaakouk AM, Hassan MA, Tolba OA (2016) Serum magnesium status among obese children and adolescents. Egypt Pediatr Ass Gazette 64(1):32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epag.2015.11.002
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SRM and DNM conceived the ideia of study, SRSM, LRS JBSM, KJCC, ARSO, NCS and GSS collection of biological material, data tabulation and drafted the manuscript, SRSM, KJCC and DNM manuscript review, statistical analysis and construction of graphic schemes, TBP, GM, SB and GSH biochemical analyses.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by Research Ethics Committee of the Federal University of Piaui, protocol number 13489613.5.0000.5214, and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients signed a consent form.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Sousa Melo, S.R., dos Santos, L.R., Morais, J.B.S. et al. Leptin and its relationship with magnesium biomarkers in women with obesity. Biometals 35, 689–697 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00393-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00393-6