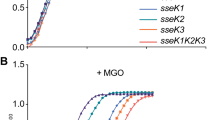
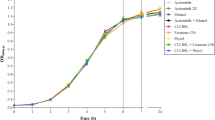
Abstract
Salmochelin is a C-glucosylated enterobactin produced by Salmonella species, uropathogenic and avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strains, and certain Klebsiella strains. It was the first glucosylated siderophore described. The glucosylation has been interpreted as a bacterial evasion mechanism against the mammalian catecholate siderophore-binding protein siderocalin (NGAL-lipocalin). The synthesis, excretion, and uptake of salmochelin requires five genes, iroBCDEN, and also the enterobactin biosynthesis and utilization system. Some salmochelin-producing strains also secrete microcins, which possess a C-terminal, linear glucosyl-enterobactin moiety. These microcins recognize the catecholate siderophore receptors IroN, Cir, Fiu, and FepA, and may inhibit the growth of competitors for catecholate siderophores.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bäumler AJ, Tsolis RM, van der Velden AW, Stojiljkovic I, Anic S, Heffron F (1996) Identification of a new iron regulated locus of Salmonella typhi. Gene 183:207–213. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(96)00560-4
Bister B, Bischoff D, Nicholson GJ, Valdebenito M, Schneider K, Winkelmann G, Hantke K, Süssmuth RD (2004) The structure of salmochelins: C-glucosylated enterobactins of Salmonella enterica. Biometals 17:471–481. doi:10.1023/B:BIOM.0000029432.69418.6a
Crouch ML, Castor M, Karlinsey JE, Kalhorn T, Fang FC (2008) Biosynthesis and IroC-dependent export of the siderophore salmochelin are essential for virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Mol Microbiol 67:971–983. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.06089.x
Feldmann F, Sorsa LJ, Hildinger K, Schubert S (2007) The salmochelin siderophore receptor IroN contributes to invasion of urothelial cells by extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli in vitro. Infect Immun 75:3183–3187. doi:10.1128/IAI.00656-06
Fischbach MA, Lin H, Liu DR, Walsh CT (2005) In vitro characterization of IroB, a pathogen-associated C-glycosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:571–576. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408463102
Fischbach MA, Lin H, Zhou L, Yu Y, Abergel RJ, Liu DR, Raymond KN, Wanner BL, Strong RK, Walsh CT, Aderem A, Smith KD (2006) The pathogen-associated iroA gene cluster mediates bacterial evasion of lipocalin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:16502–16507. doi:10.1073/pnas.0604636103
Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S, Rodriguez DJ, Holmes MA, Strong RK, Akira S, Aderem A (2004) Lipocalin 2 mediates an innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating iron. Nature 432:917–921. doi:10.1038/nature03104
Fu JM (1985) The structure elucidation of methyl pacifarinic acid. Thesis, University of Illinois at Chicago
Goetz DH, Holmes MA, Borregaard N, Bluhm ME, Raymond KN, Strong RK (2002) The neutrophil lipocalin NGAL is a bacteriostatic agent that interferes with siderophore-mediated iron acquisition. Mol Cell 10:1033–1043. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00708-6
Hantke K, Nicholson G, Rabsch W, Winkelmann G (2003) Salmochelins, siderophores of Salmonella enterica and uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains, are recognized by the outer membrane receptor IroN. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:3677–3682. doi:10.1073/pnas.0737682100
Kjeldsen L, Johnsen AH, Sengelov H, Borregaard N (1993) Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem 268:10425–10432
Lin H, Fischbach MA, Liu DR, Walsh CT (2005) In vitro characterization of salmochelin and enterobactin trilactone hydrolases IroD, IroE, and Fes. J Am Chem Soc 127:11075–11084. doi:10.1021/ja0522027
Mercado G, Tello M, Marin M, Monasterio O, Lagos R (2008) The production in vivo of microcin E492 with antibacterial activity depends on salmochelin and EntF. J Bacteriol 190:5464–5471. doi:10.1128/JB.00351-08
Patzer SI, Baquero MR, Bravo D, Moreno F, Hantke K (2003) The colicin G, H and X determinants encode microcins M and H47, which might utilize the catecholate siderophore receptors FepA, Cir, Fiu and IroN. Microbiology 149:2557–2570. doi:10.1099/mic.0.26396-0
Rabsch W, Methner U, Voigt W, Tschäpe H, Reissbrodt R, Williams PH (2003) Role of receptor proteins for enterobactin and 2, 3-dihydroxybenzoylserine in virulence of Salmonella enterica. Infect Immun 71:6953–6961. doi:10.1128/IAI.71.12.6953-6961.2003
Schneider HA (1967) Ecological ectocrines in experimental epidemiology. A new class, the “pacifarins,” is delineated in the nutritional ecology of mouse salmonellosis. Science 158:597–603. doi:10.1126/science.158.3801.597
Thomas X, Destoumieux-Garzon D, Peduzzi J, Afonso C, Blond A, Birlirakis N, Goulard C, Dubost L, Thai R, Tabet JC, Rebuffat S (2004) Siderophore peptide, a new type of post-translationally modified antibacterial peptide with potent activity. J Biol Chem 279:28233–28242. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400228200
Torkkell S, Kunnari T, Palmu K, Hakala J, Mantsala P, Ylihonko K (2000) Identification of a cyclase gene dictating the C-9 stereochemistry of anthracyclines from Streptomyces nogalater. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:396–399. doi:10.1128/AAC.44.2.396-399.2000
Valdebenito M, Müller SI, Hantke K (2007) Special conditions allow binding of the siderophore salmochelin to siderocalin (NGAL-lipocalin). FEMS Microbiol Lett 277:182–187. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00956.x
Wawszkiewicz EJ (1975) Riddle of pacifarins. In: Schlesinger MJ (ed) Microbiology—1974. ASM, Washington D.C., pp 299–305
Wawszkiewicz EJ, Schneider HA (1975) Control of salmonellosis pacifarin biosynthesis by iron. Infect Immun 11:69–72
Zhu M, Valdebenito M, Winkelmann G, Hantke K (2005) Functions of the siderophore esterases IroD and IroE in iron-salmochelin utilization. Microbiology 151:2363–2372. doi:10.1099/mic.0.27888-0
Acknowledgments
We thank Andreas Kulik for help with the illustrations, G. Winkelmann and the group of R. D. Süßmuth group for collaborations, and V. Braun and Karen Brune (Marburg) for comments on the manuscript and editing. Financial support by the DFG is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, S.I., Valdebenito, M. & Hantke, K. Salmochelin, the long-overlooked catecholate siderophore of Salmonella . Biometals 22, 691–695 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-009-9217-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-009-9217-4