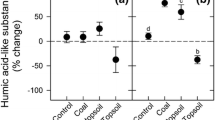
Abstract
This review focuses on ligninolytic fungi, soil bacteria, plants and root exudates in the degradation and solubilisation of low grade and waste coal and the interaction between these mutualistic biocatalysts. Coal represents a considerable portion of the total global fossil fuel reserve and continued demand for, and supply of this resource generates vast quantities of spoil and low grade waste. Large scale bioremediation technologies for the beneficiation of waste coal have unfortunately not yet been realised despite the many discoveries of microorganisms capable of lignite, lignin, and humic acid breakdown. Even so, solubilisation and depolymerization of low grade coal appears to involve either ligninolytic enzyme action or the production of alkaline substances or both. While the precise mechanism of coal biosolubilisation is unclear, a model for the phyto-biodegradation of low rank coal by mutualistic interaction between ligninolytic microorganisms and higher plants is proposed. Based on accumulated evidence this model suggests that solubilisation and degradation of lignite and waste coals commences upon plant root exudate and ligninolytic microorganism interaction, which is mutualistic, and includes soil bacteria and both mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal fungi. It is envisaged that this model and its further elaboration will aid in the development of functional technologies for commercial bioremediation of coal mine spoils, contribute to soil formation, and the overall biogeochemistry of organic carbon in the global ecosystem.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achi OK (1994) Growth and coal-solubilizing activity of Penicillium simplicissimum on coal-related aromatic compounds. Bioresource Technol 48:53–57
Ahmad M, Roberts JN, Hardiman EM, Singh R, Eltis LD, Bugg TDH (2011) Identification of DypB from Rhodococcus jostii RHA1 as a lignin peroxidase. Biochemistry 50:5096–5107
Almendros G, Dorado J (1999) Molecular characteristics related to the biodegradability of humic acid preparations. Eur J Soil Sci 50:227–236
Bais HP, Park SW, Weir TL, Callaway RM, Vivanco JM (2004) How plants communicate using the underground information superhighway. Trends Plant Sci 9:26–32
Bais HP, Weir TL, Perry LG, Gilroy S, Vivanco JM (2006) The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:233–266
Bandounas L, Wierckx NJP, de Winde JH, Ruijssenaars HJ (2011) Isolation and characterization of novel bacterial strains exhibiting ligninolytic potential. BMC Biotechnol 11:94–105
Boersma FGH, Warmink JA, Andreote FA, van Elsas JD (2009) Selection of Sphingomonadaceae at the base of Laccaria proxima and Russula exalbicans fruiting bodies. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:1979–1989
Brunetti G, Plaza C, Clapp CE, Senesi N (2007) Compositional and functional features of humic acids from organic amendments and amended soils in Minnesota, USA. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1355–1365
Campitelli PA, Velasco MI, Ceppi SB (2006) Chemical and physicochemical characteristics of humic acids extracted from compost, soil and amended soil. Talanta 69:1234–1239
Carlson CC, Adriano DC (1993) Environmental impacts of coal combustion residues. J Environ Qual 22:227–247
Catcheside DEA, Ralph JP (1999) Biological processing of coal. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:16–24
Coates JD, Cole KA, Chakraborty R, O’Connor SM, Achenbach LA (2002) Diversity and ubiquity of bacteria capable of utilizing humic substances as electron donors for anaerobic respiration. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2445–2452
Cohen MS, Gabriele PD (1982) Degradation of coal by the fungi Polyporus versicolor and Poria monticola. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:23–27
Cohen MS, Feldmann KA, Brown CS, Grey ET (1990) Isolation and identification of the coal solubilizing agent produced by Trametes versicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3285–3290
Conesa A, Punt PJ, van den Hondel CAMJJ (2002) Fungal peroxidases: molecular aspects and applications. J Biotechnol 93:143–158
Crawford D, Pometto A III, Crawford R (1983) Lignin degradation by Streptomyces viridosporus: isolation and characterization of a new polymeric lignin degradation intermediate. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:898–904
Dakora FD, Phillips DA (2002) Root exudates as mediators of mineral acquisition in low-nutrient environments. Plant Soil 245:35–47
Del Rio JC, González-Villa FM, Verdejo T (1994) Characterization of humic acids from low rank coals by 13C-NMR and pyrolysis-methylation. Formation of benzenecarboxylic acid moieties during the coalification process. Org Geochem 22:885–891
Demirbas A, Kar Y, Deveci H (2006) Humic substances and nitrogen-containing compounds from low rank brown coals. Energy Sources Part A 28:341–351
Ekka NJ, Behera N (2010) A study of the mycorrhizal association with vegetation on coal mines spoil. Bioscan 5:369–372
el Zahar Haichar F, Marol C, Berge O, Rangel-Castro JI, Prosser JI, Balesdent J, Heulin T, Achouak W (2008) Plant host habitat and root exudates shape soil bacterial community structure. ISME J 2:1221–1230
Fakoussa RM (1988) Production of water-soluble coal-substances by partial microbial liquefaction of untreated hard coal. Resour Conser Recycl 1:251–260
Fakoussa RM, Frost PJ (1999) In vivo-decolorization of coal-derived humic acids by laccase-excreting fungus Trametes versicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:60–65
Fakoussa RM, Hofrichter M (1999) Biotechnology and microbiology of coal degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:25–40
Fong SS, Seng L, Chong WN, Asing J, Faizal M, Nor M, Satirawaty M, Pauzan A (2006) Characterization of the coal derived humic acids from Mukah, Sarawak as soil conditioner. J Braz Chem Soc 17:582–587
Fredrickson JK, Balkwill DL, Romine MF, Shi T (1999) Ecology, physiology, and phylogeny of deep subsurface Sphingomonas sp. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23:273–283
Gotz GKE, Fakoussa RM (1999) Fungal biosolubilization of Rhenish brown coal monitored by Curie point pyrolysis/gas chromatography/mass spectrometry using tetraethylammonium hydroxide. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:41–48
Gramss G, Rudeschko O (1998) Activities of oxidoreductase enzymes in tissue extracts and sterile root exudates of three crop plants, and some properties of the peroxidase component. New Phytol 138:401–409
Grinhut T, Hadar Y, Chen Y (2007) Degradation and transformation of humic substances by saprotrophic fungi: processes and mechanisms. Fungal Biol Rev 21:179–189
Gutierrez-Zamora M-L, Manefield M (2010) An appraisal of methods for linking environmental processes to specific microbial taxa. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 9:153–185
Hammel KE (1996) Extracellular free radical biochemistry of ligninolytic fungi. New J Chem 20:195–198
Hammel KE, Moen MA (1991) Depolymerization of a synthetic lignin in vitro by lignin peroxidase. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:15–18
Harvey PJ, Thurston CF (2001) The biochemistry of ligninolytic fungi. In: Gadd GM (ed) Fungi in bioremediation. British Mycological Society Symposia, pp 27–51
Hatakka A (1994) Lignin-modifying enzymes from selected white-rot fungi: production and role in lignin degradation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:125–135
Hatcher PG, Breger IA, Szeverenyi N, Maciel GE (1982) Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of ancient buried wood-II. Observations on the origin of coal from lignite to bituminous coal. Org Geochem 4:9–18
Hayatsu R, Winans RE, McBeth RL, Scott RG, Moore LP, Studier MH (1979) Lignin like polymers in coals. Nature 278:41–43
Henning K, Steffes H, Fakoussa RM (1997) Effects on the molecular weight distribution of coal derived humic acids studied by ultrafiltration. Fuel Process Technol 52:225–237
Hodek W (1994) The structure of coal in regard of microbiological degradation. Fuel Process Technol 40:369–378
Hofrichter M (2002) Review: lignin conversion by manganese peroxidase (MnP). Enzyme Microbiol Technol 30:454–466
Hofrichter M, Fakoussa R (2001) Microbial degradation and modification of coal. In: Steinbuchel A, Hofrichter M (eds) Lignin, humic substances and coal, vol 1. Wiley–VCH, Weinheim, pp 393–427
Hofrichter M, Fritsche W (1997) Depolymerization of low-rank coal by extracellular fungal enzyme systems. 2. The ligninolytic enzymes of the coal-humic acid depolymerizing fungus Nematoloma forwardii b19. Fuel Energy Abstr 38:296
Hofrichter M, Bublitz F, Fritsche W (1997) Fungal attack on coal II. Solubilization of low-rank coal by filamentous fungi. Fuel Process Technol 52:55–64
Hofrichter M, Ziegenhagen D, Sorge S, Ullrich R, Bublitz F, Fritsche W (1999) Degradation of lignite (low-rank coal) by ligninolytic basidiomycetes and their manganese peroxidase system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:78–84
Hölker U, Höfer M (2002) Solid substrate fermentation of lignite by the coal-solubilizing mould, Trichoderma atroviride, in a new type of bioreactor. Biotechnol Lett 24:1643–1645
Hölker U, Ludwig S, Scheel T, Höfer M (1999) Mechanisms of coal solubilization by the deuteromycetes Trichoderma atroviride and Fusarium oxysporum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:57–59
Hölker U, Schmiers H, Grobe S, Winkelhofer M, Polsakiewicz M, Ludwig S, Dohse J, Höfer M (2002) Solubilization of low-rank coal by Trichoderma atroviride: evidence for the involvement of hydrolytic and oxidative enzymes by using 14C-labelled lignite. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 28:207–212
Igbinigie EE, Aktins S, van Breugel Y, van Dyke S, Davies-Coleman MT, Rose PD (2008) Fungal biodegradation of hard coal by a newly reported isolate, Neosartorya fischeri. Biotechnol J 3:1407–1416
Igbinigie EE, Mutambanengwe CZ, Rose PD (2010) Phyto-bioconversion of hard coal in the Cynodon dactylon/coal rhizosphere. Biotechnol J 5:292–303
Jeon CO, Park W, Padmanabhan P, DeRito C, Snape JR, Madsen EL (2003) Discovery of a bacterium, with distinctive dioxygenase, that is responsible for in situ biodegradation in contaminated sediment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13591–13596
Juwarkar AA, Jambhulkar HP (2008a) Phytoremediation of coal mine spoil dump through integrated biotechnological approach. Bioresource Technol 99:4732–4741
Juwarkar AA, Jambhulkar HP (2008b) Restoration of fly ash dump through biological interventions. Environ Monit Assess 139:355–365
Katayama Y, Nishikawa S, Murayama A, Yamasaki M, Morohoshi N, Haraguchi T (1988) The metabolism of biphenyl structures in lignin by the soil bacterium Pseudomonas paucimobilis Syk-6. FEBS Lett 233:129–133
Keck A, Conradt D, Mahler A, Stolz A, Mattes R, Klein J (2006) Identification and functional analysis of the genes for naphthalenesulfonate catabolism by Sphingomonas xenophaga BN6. Microbiology 152:1929–1940
Kersten P, Cullen D (2007) Extracellular oxidative systems of the lignin degrading Basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Fungal Genet Biol 44:77–87
Kim S-J, Kwon KK (2010) Marine, hydrocarbon degrading alphaproteobacteria. In: Timmis KN (ed) Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 1707–1714
Klein J, Catcheside DEA, Fakoussa R, Gazso L, Fritsche W, Höfer M, Laborda F, Margarit I, Rehm H-J, Reich-Walber M, Sand W, Schacht S, Schmiers H, Setti L, Steinbüchel A (1999) Biological processing of fossil fuels—résumé of the bioconversion session of ICCS 97. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:2–15
Kögel-Knabner I (2000) Analytical approaches for characterizing soil organic matter. Organic Geochem 31:609–625
Kuiper I, Lagendijk EL, Bloemberg GV, Lugtenberg BJJ (2004) Rhizoremediation: a beneficial plant-microbe interaction. MPMI 17:6–15
Kulikova NA, Stepanova EV, Koroleva OV (2005) Mitigating Activity of humic substances: direct influence on biota. In: Perminova IV, Hatfield K, Hertkorn N (eds) Use of humic substances to remediate polluted environments: from theory to practice. NATO Science Series: IV. Earth Environ Sci 52:285–309
Laborda F, Monistrol IF, Luna N, Fernández M (1999) Processes of liquefaction/solubilization of Spanish coals by microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:49–56
Leung HM, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2007) Survival strategies of plants associated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on toxic mine tailings. Chemosphere 66:905–915
Leys NM, Ryngaert A, Bastiaens L, Verstraete W, Top EM, Springael D (2004) Occurrence and phylogenetic diversity of Sphingomonas strains in soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1944–1955
Machnikowska H, Pawelec K, Podgórska A (2002) Microbial degradation of low rank coals. Fuel Process Technol 77(78):17–23
Maka A, Srivastava VJ, Kilbane JJ II, Akin C (1989) Biological solubilisation of untreated North Dakota lignite by a mixed bacterial and bacterial/fungal culture. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 20(21):715–729
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London
Marzec A (2002) Towards an understanding of the coal structure: a review. Fuel Process Technol 77(78):25–32
Meharg AA (2003) The mechanistic basis of interactions between mycorrhizal associations and toxic metal cations. Mycol Res 107:1253–1265
Mester T, Tien M (2000) Oxidation mechanism of ligninolytic enzymes involved in the degradation of environmental pollutants. Int Biodeter Biodeg 46:51–59
Millard P, Singh BK (2010) Does grassland vegetation drive soil microbial diversity? Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 88:147–158
Mukasa-Mugerwa TT, Dames JF, Rose PD (2011) The role of a plant/fungal consortium in the degradation of bituminous hard coal. Biodegradation 22:129–141
Mukhopadhyay S, Maiti SK (2009) Reclamation of mine spoils with vesicular arbuscular mycorrhiza (VAM) fungi—a review. Environ Ecol 27:642–646
Novotný C, Svobodová K, Erbanová P, Cajthaml T, Kasinath A, Lang E, Šašek V (2004) Ligninolytic fungi in bioremediation: extracellular enzyme production and degradation rate. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1545–1551
Orth AB, Tien M (1995) Biotechnology of lignin degradation. In: Esser K, Lemke PA (eds) The mycota II. Genetics and biotechnology. Springer, Berlin, pp 287–302
Orth BA, Royse D, Tien M (1993) Ubiquity of lignin-degrading peroxidases among various wood degrading fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:4017–4023
Paterson E, Gebbing T, Abel C, Sim A, Telfer G (2007) Rhizodeposition shapes rhizosphere microbial community structure in organic soil. New Phytol 173:600–610
Penã-Castro JM, Barrera-Figueroa BE, Fernández-Linares L, Ruiz-Medrano R, Xoconostle-Cázares B (2006) Isolation and identification of up-regulated genes in bermudagrass roots (Cynodon dactylon L.) grown under petroleum hydrocarbon stress. Plant Sci 170:724–731
Perez J, Munoz-Dorado J, de la Rubia T, Martinez T (2002) Biodegrdation and biological treatments of cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin: an overview. Int Microbiol 5:53–63
Pilon-Smits E (2005) Phytoremediation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:15–39
Polman JK, Stoner DL, Delezene-Briggs KM (1994) Bioconversion of coal, lignin and dimethoxybenzyl alcohol by Penicillium citrinum. J Ind Microbiol 13:292–299
Quigley DR, Wey JE, Breckenridge CR, Stoner DL (1988) The influence of pH on biological solubilisation of oxidized, low-rank coal. Resour Conserv Recycl 1:163–174
Quigley DR, Ward B, Crawford DL, Hatcher HJ, Dugan PR (1989) Evidence that microbially produced alkaline materials are involved in coal biosolubilization. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 20(21):753–763
Ralph JP, Catcheside DEA (1996) Size-exclusion chromatography of solubilised low-rank coal. J Chromatogr A 724:97–105
Ralph JP, Catcheside DEA (1997) Transformations of low rank coal by Phanerochaete chrysosporium and other wood-rot fungi. Fuel Process Technol 52:79–93
Ralph JP, Catcheside DEA (1999) Transformation of macromolecules from a brown-coal by lignin peroxidase. Appl Microb Biotechnol 52:70–77
Ram LC, Srivastava NK, Jha SK, Sinha AK, Masto RE, Selvi VA (2007) Management of lignite fly ash for improving soil fertility and crop productivity. Environ Manag 40:438–452
Ramachandra M, Crawford D, Hertel G (1988) Characterization of an extracellular lignin peroxidase of the lignocellulolytic actinomycete Streptomyces viridosporus. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:3057–3063
Ramachandran TV, Lalit BY, Mishra UC (1990) Modifications in natural radioactivity content of soil samples around thermal power stations in India. Indian J Environ Health 32:13–19
Roberts JN, Singh R, Grigg JC, Murphy MEP, Bugg TDH, Eltis Ld (2011) Characterization of dye-decolorizing peroxidases from Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. Biochemistry 50:5108–5119
Ronchel M, Ramos JL (2001) Dual system to reinforce biological containment of recombinant bacteria designed for rhizoremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2649–2656
Schmöger MEV, Oven M, Grill E (2000) Detoxification of arsenic by phytochelatins in plants. Plant Physiol 122:793–801
Semple KT, Cain RB, Schmidt S (1999) Biodegradation of aromatic compounds by microalgae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 170:291–300
Shukla SK, Singh K, Singh B, Gautam NN (2011) Biomass productivity and nutrient availability of Cyanodon dactylon (L.) Pers. growing on soils of different sodicity stress. Biomass Bioenergy 35:3440–3447
Singh BK, Nunan N, Ridgway KP, McNicol J, Young JPW, Daniell TJ, Prosser JI, Millard P (2008) Relationship between assemblages of mycorrhizal fungi and bacteria on grass roots. Environ Microbiol 10:534–541
Steffen KT, Hatakka A, Hofrichter M (2002) Degradation of humic acids by the litter-decomposing Basidiomycete Collybia dryophila. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3442–3448
Stout SA, Boon JJ, Spackman W (1988) Molecular aspects of the peatification and early coalification of angiosperm and gymnosperm woods. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:405–414
Strandberg GW, Lewis SN (1987) The Solubilization of coal by an extracellular product from Streptomyces setonii 75Vi2. J Ind Microbiol 1:371–375
Tao XX, Chen H, Shi KY, Lv ZP (2010) Identification and biological characteristics of a newly isolated fungus Hypocrea lixii and its role in lignite bioconversion. Afr J Microbiol Res 4:1842–1847
Temp U, Meyrahn H, Eggert C (1999) Extracellular phenol oxidase patterns during depolymerization of low-rank coal by three basidiomycetes. Biotechnol Lett 21:281–287
Thurston CF (1994) The structure and function of fungal laccases. Microbiology 140:19–26
Torzilli AP, Isbister JD (1994) Comparison of coal solubilisation by bacteria and fungi. Biodegradation 5:55–62
Tripathi RC, Jain VK, Tripathi PSM (2010) Fungal biosolubilization of Neyveli lignite Into humic acid. Energy Sources A 32:72–82
Uroz S, Calvaruso C, Turpault MP, Pierrat JC, Mustin C, Frey-Klett P (2007) Effect of the mycorrhizosphere on the genotypic and metabolic diversity of the bacterial communities involved in mineral weathering in a forest soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3019–3027
Vacca DJ, Bleam WF, Hickey WJ (2005) Isolation of soil bacteria adapted to degrade humic acid-sorbed phenanthrene. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3797–3805
Valdrighi MM, Pera A, Agnolucci M, Frassinetti S, Lunardi D, Vallini G (1996) Effects of compost derived humic acids on vegetable biomass production and microbial growth within a plant (Cichorium intybus)— soil system: comparative study. Agric Ecosys Environ 58:133–144
Van Trump JI, Wrighton KC, Thrash JC, Weber KA, Andersen GL, Coates JD (2011) Humic acid-oxidizing, nitrate-reducing bacteria in agricultural soils. mBio 2(4):e00044-11. doi:10.1128/mBio.00044-11
Vicuna R (1988) Bacterial degradation of lignin. Enzyme Microb Technol 10:646–655
Visser SA (1985a) Physiological action of humic substances on microbial cells. Soil Biol Biochem 17:457–462
Visser SA (1985b) Effects of humic acids on numbers and activities of micro-organisms within physiological groups. Org Geochem 8:81–85
Wariishi H, Valli K, Gold MH (1991) Depolymerization of lignin by manganese peroxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 176:269–275
Warshawsky D, LaDow K, Schneider J (2007) Enhanced degradation of benzo[a]pyrene by Mycobacterium sp. in conjunction with green alga. Chemosphere 69:500–506
Yin S, Tao X, Shi K (2011) The role of surfactants in coal bio-solubilisation. Fuel Process Technol 92:1554–1559
Yuan H-L, Toyota K, Kimura M (1995) Observation with scanning electron microscope of microbial succession on lignite along with weathering. Bull Jpn Soc Microbiol Ecol 10:53–58
Yuan H-L, Yang JS, Wang FQ, Chen WX (2006) Degradation and solubilization of Chinese lignite by Penicillium sp. P6. Appl Biochem Microbiol 42:52–55
Zavarzina AG, Leontievsky AA, Golovleva LA, Trofimov SY (2004) Biotransformation of soil humic acids by blue laccase of Panus tigrinus 8/18: an in vitro study. Soil Biol Biochem 36:359–369
Zimmermann W (1990) Degradation of lignin by bacteria. J Biotechnol 13:119–130
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support provided by Anglo Thermal Coal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekhohola, L.M., Igbinigie, E.E. & Cowan, A.K. Biological degradation and solubilisation of coal. Biodegradation 24, 305–318 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9594-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9594-1