Abstract
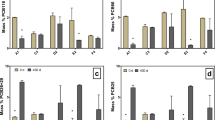
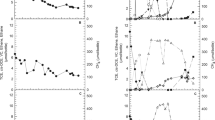
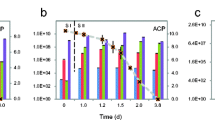
The potential for extracellular electron shuttles to stimulate RDX biodegradation was investigated with RDX-contaminated aquifer material. Electron shuttling compounds including anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) and soluble humic substances stimulated RDX mineralization in aquifer sediment. RDX mass-loss was similar in electron shuttle amended and donor-alone treatments; however, the concentrations of nitroso metabolites, in particular TNX, and ring cleavage products (e.g., HCHO, MEDINA, NDAB, and NH4 +) were different in shuttle-amended incubations. Nitroso metabolites accumulated in the absence of electron shuttles (i.e., acetate alone). Most notably, 40–50% of [14C]-RDX was mineralized to 14CO2 in shuttle-amended incubations. Mineralization in acetate amended or unamended incubations was less than 12% within the same time frame. The primary differences in the presence of electron shuttles were the increased production of NDAB and formaldehyde. NDAB did not further degrade, but formaldehyde was not present at final time points, suggesting that it was the mineralization precursor for Fe(III)-reducing microorganisms. RDX was reduced concurrently with Fe(III) reduction rather than nitrate or sulfate reduction. Amplified 16S rDNA restriction analysis (ARDRA) indicated that unique Fe(III)-reducing microbial communities (β- and γ-proteobacteria) predominated in shuttle-amended incubations. These results demonstrate that indigenous Fe(III)-reducing microorganisms in RDX-contaminated environments utilize extracellular electron shuttles to enhance RDX mineralization. Electron shuttle-mediated RDX mineralization may become an effective in situ option for contaminated environments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian NR, Arnett CM (2004) Anaerobic biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) by Acetobacterium malicum strain HAAP-1 isolated from a methanogenic mixed culture. Curr Microbiol 48(5):332–340
Adrian NR, Arnett CM, Hickey RF (2003) Stimulating the anaerobic biodegradation of explosives by the addition of hydrogen or electron donors that produce hydrogen. Water Res 37(14):3499–3507
Akob DM, Mills HJ, Kostka JE (2007) Metabolically active microbial communities in uranium-contaminated subsurface sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59(1):95–107
Akob DM, Mills HJ, Gihring TM, Kerkhof L, Stucki JW, Anastacio AS, Chin K-J, Kusel K, Palumbo AV, Watson DB, Kostka JE (2008) Functional diversity and electron donor dependence of microbial populations capable of U(VI) reduction in radionuclide-contaminated subsurface sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(10):3159–3170
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59(1):143–169
Balakrishnan VK, Halasz A, Hawari J (2003) Alkaline hydrolysis of the cyclic nitramine explosives RDX, HMX, and CL-20: new insights into degradation pathways obtained by the observation of novel intermediates. Environ Sci Technol 37(9):1838–1843
Bhushan B, Trott S, Spain JC, Halasz A, Paquet L, Hawari J (2003) Biotransformation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) by a rabbit liver cytochrome P450: insight into the mechanism of RDX biodegradation by Rhodococcus sp. strain DN22. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(3):1347–1351
Bhushan B, Halasz A, Hawari J (2006) Effect of iron(III), humic acids and anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate on biodegradation of cyclic nitramines by Clostridium sp. EDB2. J Appl Microbiol 100(3):555–563
Boopathy R, Gurgas M, Ullian J, Manning JF (1998) Metabolism of explosive compounds by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Curr Microbiol 37(2):127–131
Borch T, Inskeep WP, Harwood JA, Gerlach R (2005) Impact of ferrihydrite and anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate on the reductive transformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by a gram-positive fermenting bacterium. Environ Sci Technol 39(18):7126–7133
Bradley PM, Dinicola RS (2005) RDX (hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine) biodegradation in aquifer sediments under manganese-reducing conditions. Bioremediat J 9(1):1–8
Coates JD, Ellis DJ, Blunt-Harris EL, Gaw CV, Roden EE, Lovley DR (1998) Recovery of humic reducing bacteria from a diversity of environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(4):1504–1509
Crocker FH, Thompson KT, Szecsody JE, Fredrickson HL (2005) Biotic and abiotic degradation of CL-20 and RDX in soils. J Environ Qual 34(6):2208–2216
Finneran KT, Lovley DR (2001) Anaerobic degradation of Methyl tert-Butyl Ether (MTBE) and tert-Butyl Alcohol (TBA). Environ Sci Technol 35(9):1785–1790
Fournier D, Halasz A, Spain J, Firuasek P, Hawari J (2002) Determination of key metabolites during biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-triazine with Rhodococcus sp. strain DN22. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(1):166–172
Fournier D, Halasz A, Spain J, Spanggord RJ, Bottaro JC, Hawari J (2004) Biodegradation of the hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine ring cleavage product 4-nitro-2,4-diazabutanal by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(2):1123–1128
Fournier D, Trott S, Hawari J, Spain J (2005) Metabolism of the aliphatic nitramine 4-nitro-2,4-diazabutanal by Methylobacterium sp. strain JS178. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(8):4199–4202
Fredrickson JK, Kostandarithes HM, Li SW, Plymale AE, Daly MJ (2000) Reduction of Fe(III), Cr(VI), U(VI), and Tc(VII) by Deinococcus radiodurans R1. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(5):2006–2011
Freedman DL, Sutherland KW (1998) Biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) under nitrate-reducing conditions. Water Sci Technol 38(7):33–40
Gregory KB, Larese-Casanova P, Parkin GF, Scherer MM (2004) Abiotic transformation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine by Fe(II) bound to magnetite. Environ Sci Technol 38(5):1408–1414
Hawari J (2000) Biodegradation of RDX and HMX: from basic research to field application. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fl, pp 277–310
Hawari J, Halasz A, Groom C, Deschamps S, Paquet L, Beaulieu C, Corriveau A (2002) Photodegradation of RDX in aqueous solution: a mechanistic probe for biodegradation with Rhodococcus sp. Environ Sci Technol 36(23):5117–5123
Hofstetter TB, Heijman CG, Haderlein SB, Holliger C, Schwarzenbach RP (1999) Complete reduction of TNT and other (poly)nitroaromatic compounds under iron reducing subsurface conditions. Environ Sci Technol 33(9):1479–1487
Holmes DE, Finneran KT, O’Neil RA, Lovley DR (2002) Enrichment of members of the family Geobacteraceae associated with stimulation of dissimilatory metal reduction in uranium-contaminated aquifer sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(5):2300–2306
Jackson RG, Rylott EL, Fournier D, Hawari J, Bruce NC (2007) Exploring the biochemical properties and remediation applications of the unusual explosive-degrading P450 system XplA/B. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(43):16822–16827
Just CL, Schnoor JL (2004) Phytophotolysis of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) in leaves of reed canary grass. Environ Sci Technol 38(1):290–295
Kim D, Strathmann TJ (2007) Role of organically complexed iron(II) species in the reductive transformation of RDX in anoxic environments. Environ Sci Technol 41:1257–1264
Kostka JE, Roychoudhury A, Van Cappellen P (2002) Rates and controls of anaerobic microbial respiration across spatial and temporal gradients in saltmarsh sediments. Biogeochemistry 60:49–76
Kwon MJ, Finneran KT (2006) Microbially mediated biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine by extracellular electron shuttling compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(9):5933–5941
Kwon MJ, Finneran KT (2008a) Biotransformation products and mineralization potential for hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) in abiotic versus biological degradation pathways with anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) and Geobacter metallireducens. Biodegradation 19(5):705–715
Kwon MJ, Finneran KT (2008b) Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) and octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine (HMX) biodegradation kinetics amongst several Fe(III)-reducing genera. Soil Sediment Contam 17(2):189–203
Kwon MJ, Finneran KT (2008c) Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) reduction is concurrently mediated by direct electron transfer from hydroquinones and the resulting biogenic Fe(II) formed during electron shuttle-amended biodegradation. Environ Eng Sci 26(5):961–971
Lane DJ, Pace B, Olsen GJ, Stahl DA, Sogin ML, Pace NR (1985) Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82(20):6955–6959
Larese-Casanova P, Scherer MM (2008) Abiotic transformation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) by green rusts. Environ Sci Technol 42(11):3975–3981
Li X, Krumholz LR (2008) Influence of nitrate on microbial reduction of pertechnetate. Environ Sci Technol 42(6):1910–1915
Lovley DR (1995) Bioremediation of organic and metal contaminants with dissimilatory metal reduction. J Ind Microbiol 14:85–93
Lovley DR (1997) Microbial Fe(III) reduction in subsurface environments. FEMS Microbiol Rev 20:305–313
Lovley DR (2000) Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. In: Lovley DR (ed) Environmental metal–microbe interactions. ASM Press, Washington, DC
Lovley DR, Phillips EJP (1987) Competitive mechanisms for inhibition of sulfate reduction and methane production in the zone of ferric iron reduction in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 53(11):2636–2641
Lovley DR, Fraga JL, Blunt-Harris EL, Hayes LA, Phillips EJP, Coates JD (1998) Humic substances as a mediator for microbially catalyzed metal reduction. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 26(3):152–157
Lu WJ, Wang HT, Huang CY, Reichardt W (2002) Communities of iron(III)-reducing bacteria in irrigated tropical rice fields. Microbes Environ 17(4):170–178
Männistö MK, Tiirola MA, Puhakka JA (2001) Degradation of 2,3,4,6-tetrachlorophenol at low temperature and low dioxygen concentrations by phylogenetically different groundwater and bioreactor bacteria. Biodegradation 12(5):291–301
McCormick NG, Cornell JH, Kaplan HS (1981) Biodegradation of hexadro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine. Appl Environ Microbiol 42(5):817–823
Meyer SA, Marchand AJ, Hight JL, Roberts GH, Escalon LB, Inouye LS, MacMillan DK (2005) Up-and-down procedure (UDP) determinations of acute oral toxicity of nitroso degradation products of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX). J Appl Toxicol 25(5):427–434
Meyers SK, Deng SP, Basta NT, Clarkson WW, Wilber GG (2007) Long-term explosive contamination in soil: effects on soil microbial community and bioremediation. Soil & Sediment Contamination 16(1):61–77
Naja G, Halasz A, Thiboutot S, Ampleman G, Hawari J (2008) Degradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) using zero valent iron nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 42(12):4364–4370
Oh BT, Just CL, Alvarez PJJ (2001) Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine mineralization by zero valent iron and mixed anaerobic cultures. Environ Sci Technol 35(21):4341–4346
Pitot HCI, Dragan YP (1996) Chemical carcinogens. McGraw-Hill, NY
Reardon CL, Cummings DE, Petzke LM, Kinsall BL, Watson DB, Peyton BM, Geesey GG (2004) Composition and diversity of microbial communities recovered from surrogate minerals incubated in an acidic uranium-contaminated aquifer. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(10):6037–6046
Rhine ED, Sims GK, Mulvaney RL, Pratt EJ (1998) Improving the Berthelot reaction for determining ammonium in soil extracts and water. J Soil Sci Soc Am 62(2):473–480
Roden EE, Urrutia MM, Mann CJ (2000) Bacterial reductive dissolution of crystalline Fe(III) oxide in continuous-flow column reactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(3):1062–1065
Schwarzenbach RP, Stierli R, Lanz K, Zeyer J (1990) Quinone and iron porphyrin mediated reduction of nitroaromatic compounds in homogeneous aqueous solution. Environ Sci Technol 24(10):1566–1574
Seth-Smith HMB, Rosser SJ, Basran A, Travis ER, Dabbs ER, Nicklin S, Bruce NC (2002) Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of the hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine degradation gene cluster from Rhodococcus rhodochrous. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(10):4764–4771
Sherburne LA, Shrout JD, Alvarez PJJ (2005) Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) degradation by Acetobacterium paludosum. Biodegradation 16(6):539–547
Sheremata TW, Halasz A, Paquet L, Thiboutot S, Ampleman G, Hawari J (2001) The fate of the cyclic nitramine explosive RDX in natural soil. Environ Sci Technol 35(6):1037–1040
Snoeyenbos-West OL, Nevin KP, Anderson RT, Lovley DR (2000) Enrichment of Geobacter species in response to stimulation of Fe(III) reduction in sandy aquifer sediments. Microbial Ecol 39:153–167
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl Acids Res 22(22):4673–4680
Thompson KT, Crocker FH, Fredrickson HL (2005) Mineralization of the cyclic nitramine explosive hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine by Gordonia and Williamsia spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8265–8272
Weber KA, Urrutia MM, Churchill PF, Kukkadapu RK, Roden EE (2006) Anaerobic redox cycling of iron by freshwater sediment microorganisms. Environ Microbiol 8(1):100–113
Zachara JM, Fredrickson JK, Smith SC, Gassman PL (2001) Solubilization of Fe(III) oxide-bound trace metals by a dissimilatory Fe(III) reducing bacterium. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:75–93
Zhao JS, Paquet L, Halasz A, Hawari J (2003) Metabolism of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine through initial reduction to hexahydro-1-nitroso-3,5-dinitro-1,3,5-triazine followed by denitration in Clostridium bifermentans HAW-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63(2):187–193
Zuo Y, Xing D, Regan JM, Logan BE (2008) Isolation of the exoelectrogenic bacterium Ochrobactrum anthropi YZ-1 by using a U-tube microbial fuel cell. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(10):3130–3137
Acknowledgments
We thank Scott R. Drew of GeoSyntec Consultants for technical assistance and logistical management for field sampling and acquisition and for thoughtful discussions. We acknowledge Pam Sheehan of the Picatinny Arsenal and Paul Hatzinger of Shaw Group for aquifer material sampling and preservation. This work was supported by the Department of Defense Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (SERDP) project number ER-1377.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, M.J., Finneran, K.T. Electron shuttle-stimulated RDX mineralization and biological production of 4-nitro-2,4-diazabutanal (NDAB) in RDX-contaminated aquifer material. Biodegradation 21, 923–937 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9352-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9352-1