Abstract
Objectives
Decaying wood samples were collected, and actinomycetes were isolated and screened for laccase production. The identity of the efficient laccase-producing isolate was confirmed by using a molecular approach. Fermentation conditions for laccase production were optimized, and laccase biochemical properties were studied.
Results
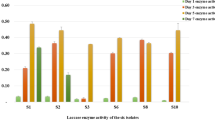
Based on the 16S rRNA gene sequencing and phylogenetic analysis, the isolate coded as HWP3 was identified as Streptomyces sp. LAO. The time-course study showed that the isolate optimally produced laccase at 84 h with 40.58 ± 2.35 U/mL activity. The optimized physicochemical conditions consisted of pH 5.0, ferulic acid (0.04%; v/v), pine back (0.2 g/L), urea (1.0 g/L), and lactose (1 g/L). Streptomyces sp. LAO laccase was optimally active at pH and temperature of 8.0 and 90 °C, respectively, with remarkable pH and thermal stability. Furthermore, the enzyme had a sufficient tolerance for organic solvents after 16 h of preincubation, with laccase activity > 70%. Additionally, the laccase maintained considerable residual activity after pretreatment with 100 mM of chemical agents, including sodium dodecyl sulphate (69.93 ± 0.89%), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (93.1 ± 7.85%), NaN3 (96.28 ± 3.34%) and urea (106.03 ± 10.72%).
Conclusion
The laccase's pH and thermal stability; and robust catalytic efficiency in the presence of organic solvents suggest its industrial and biotechnological application potentials for the sustainable development of green chemistry.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed in the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The nucleotide sequence of the Streptomyces sp. LAO was deposited in NCBI GenBank and could be accessed through the accession number MK290990.
References
Ademakinwa AN, Agboola FK (2016) Biochemical characterization and kinetic studies on a purified yellow laccase from newly isolated Aureobasidium pullulans NAC8 obtained from soil containing decayed plant matter. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 14:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2016.05.004
Afreen S, Anwer R, Singh RK, Fatma T (2018) Extracellular laccase production and its optimization from Arthrospira maxima catalyzed decolorization of synthetic dyes. Saudi J Biol Sci 25:1446–1453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.01.015
Arias ME, Arenas M, Rodríguez J, Soliveri J, Ball AS, Hernández M (2003) Kraft pulp biobleaching and mediated oxidation of a nonphenolic substrate by laccase from Streptomyces cyaneus CECT 3335. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1953–1958. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.4.1953-1958.2003
Arias ME, Blánquez A, Hernández M, Rodríguez J, Ball AS, Jiménez-Morillo NT, González-Vila FJ, González-Pérez JA (2016) Role of a thermostable laccase produced by Streptomyces ipomoeae in the degradation of wheat straw lignin in solid state fermentation. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 122:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2016.09.023
Atalla MM, Zeinab HK, Eman RH, Amani AY, Abeer AAEA (2013) Characterization and kinetic properties of the purified Trematosphaeria mangrovei laccase enzyme. Saudi J Biol Sci 20:373–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2013.04.001
Blánquez A, Ball AS, González-Pérez JA, Jiménez-Morillo NT, González-Vila F, Hernández AME, M, (2017) Laccase SilA from Streptomyces ipomoeae CECT 3341, a key enzyme for the degradation of lignin from agricultural residues. PLoS ONE 12:e0187649. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187649
de Cassia PJ, Giese EC, de Souza Moretti MM, dos Santos Gomes AC, Perrone OM, Boscolo M, da Silva R, Gomes E, Martins DAB (2017) Effect of metal ions, chemical agents and organic compounds on lignocellulolytic enzymes activities. Enzyme Inhibitors and Activators, Murat Senturk, IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/65934
de Gonzalo G, Colpa DI, Habib MH, Fraaije MW (2016) Bacterial enzymes involved in lignin degradation. J Biotechnol 236:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.08.011
de Lima Procópio RE, da Silva IR, Martins MK, de Azevedo JL, de Araújo JM (2012) Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces. Braz J Infect Dis 16:466–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjid.2012.08.014
Deepa T, Gangwane A, Sayyed RZ, Jadhav HP, Mehjabeen, (2020) Optimization and scale-up of laccase production by Bacillus sp. BAB-4151 isolated from the waste of the soap industry. Environ Sustain 3:471–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-020-00135-9
El-Bendary MA, Ezzat SM, Ewais EA, Al-Zalama MA (2020) Optimization of spore laccase production by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens isolated from wastewater and its potential in green biodecolorization of synthetic textile dyes. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2020.1786698
Fernandes TAR, da Silveira WB, Passos FML, Zucchi TD (2014) Characterization of a thermotolerant laccase produced by Streptomyces sp. SB086. Ann Microbiol 64:1363–1369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0781-z
Fernandez-Fernandez M, Moldes SMÁ, D, (2013) Recent developments and applications of immobilized laccase. Biotechnol Adv 31:1808–1825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.02.013
Huang WT, Tai R, Hseu RS, Huang CT (2011) Overexpression and characterization of a thermostable, pH-stable and organic solvent-tolerant Ganoderma fornicatum laccase in Pichia pastoris. Process Biochem 46:1469–1474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.03.020
Jing D (2010) Improving the simultaneous production of laccase and lignin peroxidase from Streptomyces lavendulae by medium optimization. Bioresour Technol 101:7592–7597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.087
Kuddus M, Joseph B, Ramteke PW (2013) Production of laccase from newly isolated Pseudomonas putida and its application in bioremediation of synthetic dyes and industrial effluents. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 2:333–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2013.06.002
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Liu Y, Huang L, Guo W, Jia L, Fu Y, Gui S, Lu F (2017) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a thermostable and pH-stable laccase from Klebsiella pneumoniae and its application to dye decolorization. Process Biochem 53:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.11.015
Lu L, Zhao M, Wang TN, Zhao LY, Du MH, Li TL, Li DB (2012) Characterization and dye decolorization ability of an alkaline resistant and organic solvents tolerant laccase from Bacillus licheniformis LS04. Bioresour Technol 115:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.111
Lu L, Zeng G, Fan C, Ren X, Wang C, Zhao Q, Zhang J, Chen M, Chen A, Jiang M (2013) Characterization of a laccase-like multicopper oxidase from newly isolated Streptomyces sp. C1 in agricultural waste compost and enzymatic decolorization of azo dyes. Biochem Eng J 72:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.01.004
Ma X, Liu L, Li Q, Liu Y, Yi L, Ma L, Zhai C (2017) High-level expression of a bacterial laccase, CueO from Escherichia coli K12 in Pichia pastoris GS115 and its application on the decolorization of synthetic dyes. Enzyme Microb Technol 103:4–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2017.04.004
Moya R, Hernández M, García-Martín AB, Ball AS, Arias ME (2010) Contributions to a better comprehension of redox-mediated decolouration and detoxification of azo dyes by a laccase produced by Streptomyces cyaneus CECT 3335. Bioresour Technol 101:2224–2229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.061
Niladevi KN, Jacob N, Prema P (2008) Evidence for a halotolerant-alkaline laccase in Streptomyces psammoticus: purification and characterization. Process Biochem 43:654–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2008.02.002
Niladevi KN, Sukumaran RK, Jacob N, Anisha GS, Prema P (2009) Optimization of laccase production from a novel strain—Streptomyces psammoticus using response surface methodology. Microbiol Res 164:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2006.10.006
Olajuyigbe FM, Fatokun CO (2017) Biochemical characterization of an extremely stable pH-versatile laccase from Sporothrix carnis CPF-05. Int J Biol Macromol 94:535–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.037
Omeje KO, Nnolim NE, Ezema BO, Ozioko JN, Eze SOO (2020) Synthetic dyes decolorization potential of agroindustrial waste-derived thermo-active laccase from Aspergillus species. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 29:101800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101800
Pawlik A, Wójcik M, Rułka K, Motyl-Gorzel K, Osińska-Jaroszuk M, Wielbo J, Marek-Kozaczuk M, Skorupska A, Rogalski J, Janusz G (2016) Purification and characterization of laccase from Sinorhizobium meliloti and analysis of the lacc gene. Int J Biol Macromol 92:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.012
Sharma V, Ayothiraman S, Dhakshinamoorthy V (2019) Production of highly thermo-tolerant laccase from novel thermophilic bacterium Bacillus sp. PC-3 and its application in functionalization of chitosan film. J Biosci Bioeng 127:672–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.11.008
Stepankova V, Bidmanova S, Koudelakova T, Prokop Z, Chaloupkova R, Damborsky J (2013) Strategies for stabilization of enzymes in organic solvents. Acs Catal 3:2823–2836. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs400684x
Sun J, Zheng M, Lu Z, Lu F, Zhang C (2017) Heterologous production of a temperature and pH-stable laccase from Bacillus vallismortis fmb-103 in Escherichia coli and its application. Process Biochem 55:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.01.030
Trubitsina LI, Tishchenko SV, Gabdulkhakov AG, Lisov AV, Zakharova MV, Leontievsky AA (2015) Structural and functional characterization of two-domain laccase from Streptomyces viridochromogenes. Biochimie 112:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2015.03.005
Unuofin JO, Moubasher HA, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2019a) Production of polyextremotolerant laccase by Achromobacter xylosoxidans HWN16 and Citrobacter freundii LLJ16. Biotechnol Rep 22:e00337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00337
Unuofin JO, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2019b) Recovery of laccase-producing gammaproteobacteria from wastewater. Biotechnol Rep 21:e00320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00320
Unuofin JO, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2019c) Utilization of agroindustrial wastes for the production of laccase by Achromobacter xylosoxidans HWN16 and Bordetella bronchiseptica HSO16. J Environ Manage 231:222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.016
Wu MH, Lin MC, Lee CC, Yu SM, Wang AHJ, Ho THD (2019) Enhancement of laccase activity by preincubation with organic solvents. Sci Rep 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45118-x
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the South African Medical Research Council (SAMRC) for financial support.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: UN; Methodology: AG and NN; Formal analysis and investigation: NN and TD; Writing—original draft preparation: AG and NN; Writing—review and editing: UN; Resources and Supervision: UN and AO. The authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animal experiments.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gogotya, A., Nnolim, N.E., Digban, T.O. et al. Characterization of a thermostable and solvent-tolerant laccase produced by Streptomyces sp. LAO. Biotechnol Lett 43, 1429–1442 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03131-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03131-z