Abstract
Objective
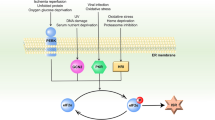
The exposure of organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus (GA), and lysosomes, to stress activates death mechanisms. Recently, telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) has been shown to be involved in cell survival. However, the relationship between TERT and the stress responses is still unclear. Here, we aimed to clarify the possible mechanisms of action through which TERT promotes cell survival by studying its effect on the stresses faced by multiple organelles in human fibroblasts.
Results
We found that TERT enhanced the survival rate of cells under ER stress, regardless of ER stress inducers such as tunicamycin (protein glycosylation inhibitor), thapsigargin (Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor), brefeldin A (protein transport inhibitor), or dithiothreitol (disulfide bond formation inhibitor). We also found that TERT enhanced the survival rate of cells under GA and lysosomal stresses.
Conclusion
Collectively, these results suggest that TERT suppresses cell stress and promotes cell survival via different mechanisms. These findings may offer new insights into the implications of TERT in the treatment of stress-induced conditions such as aging, obesity, and neurodegenerative diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Artandi SE, DePinho RA (2009) Telomeres and telomerase in cancer. Carcinogenesis 31:9–18
Barzilay E, Ben-Califa N, Hirschberg K, Neumann D (2005) Uncoupling of brefeldin a-mediated coatomer protein complex-I dissociation from Golgi redistribution. Traffic 6:794–802
Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB, Harley CB, Shay JW, Lichtsteiner S, Wright WE (1998) Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science 279:349–352
Braakman I, Hebert DN (2013) Protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5:a013201
Brown MK, Naidoo N (2012) The endoplasmic reticulum stress response in aging and age-related diseases. Front Physiol 16:3–263
Cao Y, Li H, Deb S, Liu J-P (2002) TERT regulates cell survival independent of telomerase enzymatic activity. Oncogene 21:3130–3138
Cong Y-S, Wright WE, Shay JW (2002) Human telomerase and its regulation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:407–425
Dinter A, Berger E (1998) Golgi-disturbing agents. Histochem Cell Biol 109:571–590
Fan J, Hu Z, Zeng L, Lu W, Tang X, Zhang J, Li T (2008) Golgi apparatus and neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Dev Neurosci 26:523–534
Fulda S, Gorman AM, Hori O, Samali A (2010) Cellular stress responses: cell survival and cell death. Int J cell Biol 2010:214074
Halperin L, Jung J, Michalak M (2014) The many functions of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperones and folding enzymes. IUBMB Life 66:318–326
Hosoi T, Inoue Y, Nakatsu K, Matsushima N, Kiyose N, Shimamoto A, Tahara H, Ozawa K (2014) TERT attenuated ER stress-induced cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 447:378–382
Hosoi T, Nakatsu K, Shimamoto A, Tahara H, Ozawa K (2016) Inhibition of telomerase causes vulnerability to endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal cell death. Neurosci Lett 629:241–244
Jadot M, Colmant C, Wattiaux-De Coninck S, Wattiaux R (1984) Intralysosomal hydrolysis of glycyl-l-phenylalanine 2-naphthylamide. Biochem J 219:965–970
Katayama T, Imaizumi K, Manabe T, Hitomi J, Kudo T, Tohyama M (2004) Induction of neuronal death by ER stress in Alzheimer’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat 28:67–78
Kirkegaard T, Jäättelä M (2009) Lysosomal involvement in cell death and cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular. Cell Res 1793:746–754
Kurz T, Terman A, Gustafsson B, Brunk UT (2008) Lysosomes and oxidative stress in aging and apoptosis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 1780:1291–1303
Lee J, Sung YH, Cheong C, Choi YS, Jeon HK, Sun W, Hahn WC, Ishikawa F, Lee HW (2008) TERT promotes cellular and organismal survival independently of telomerase activity. Oncogene 27:3754–3760
Lin JH, Walter P, Yen TB (2008) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease pathogenesis. Annu Rev pathmechdis Mech Dis 3:399–425
Machamer CE (2015) The Golgi complex in stress and death. Front Neurosci 6:9–421
Mattson MP, Zhang P, Fu W (2013) Roles for TERT and Telomerase in Cell Differentiation and Apoptosis. in: Madame Curie Bioscience Database [Internet]. Austin (TX): Landes Bioscience. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK6129/ 2000–2013
Milisav I (2011) Cellular stress responses. In: advances in regenerative medicine. InTech, https://doi.org/10.5772/26118, https://www.intechopen.com/books/advances-in-regenerative-medicine/cellular-stress-responses 2011
Oh H, Taffet GE, Youker KA, Entman ML, Overbeek PA, Michael LH, Schneider MD (2001) Telomerase reverse transcriptase promotes cardiac muscle cell proliferation, hypertrophy, and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:10308–10313
Orr ME, Oddo S (2013) Autophagic/lysosomal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res Ther 5:53
Oslowski CM, Urano F (2011) Measuring ER stress and the unfolded protein response using mammalian tissue culture system. Methods Enzymol 490:71–92
Park WH, Lee MS, Park K, Kim ES, Kim BK, Lee YY (2002) Monensin-mediated growth inhibition in acute myelogenous leukemia cells via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Int J Cancer 101:235–242
Park WH, Kim ES, Kim BK, Lee YY (2003) Monensin-mediated growth inhibition in NCI-H929 myeloma cells via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Int J Oncol 23:197–204
Pizzey J, Witkowski J, Jones G (1984) Monensin-induced inhibition of cell spreading in normal and dystrophic human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci 81:4960–4964
Qureshi MA, Haynes CM, Pellegrino MW (2017) The mitochondrial unfolded protein response: signaling from the powerhouse. J Biol Chem 292:13500–13506
Rosenberger S, Thorey IS, Werner S, Boukamp P (2007) A novel regulator of telomerase S100A8 mediates differentiation-dependent and calcium-induced inhibition of telomerase activity in the human epidermal keratinocyte line HaCaT. J Biol Chem 282:6126–6135
Santaguida S, Amon A (2015) Aneuploidy triggers a TFEB-mediated lysosomal stress response. Autophagy 11:2383–2384
Sasaki K, Yoshida H (2015) Organelle autoregulation—stress responses in the ER, Golgi, mitochondria and lysosome. J Biochem 157:185–195
Schröder M, Kaufman RJ (2005) ER stress and the unfolded protein response. Mutat Res/Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 569:29–63
Suomalainen A, Battersby BJ (2017) Mitochondrial diseases: the contribution of organelle stress responses to pathology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19(2):77
Taniguchi M, Yoshida H (2017) TFE3, HSP47, and CREB3 pathways of the mammalian Golgi stress response. Cell Struct Funct 42:27–36
Wai LK (2004) Telomeres, telomerase, and tumorigenesis–a review Medscape. Gen Med 6:3
Yadav RK, Chae S-W, Kim H-R, Chae HJ (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and cancer. J cancer Prev 19:75–88
Zhang GF, Driouich A, Staehelin LA (1993) Effect of monensin on plant Golgi: re-examination of the monensin-induced changes in cisternal architecture and functional activities of the Golgi apparatus of sycamore suspension-cultured cells. J Cell Sci 104:819–831
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the JSPS KAKENHI and Takeda Science Foundations.
Supporting information
Supplementary Fig. 1—Overexpression of TERT in the TIG-3-TERT cell line.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical statement
The authors declare that there are no studies conducted with human participants or animals.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abd El-Hafeez, A.A., Hosoi, T., Nakatsu, K. et al. TERT enhances the survival rate of human fibroblasts under endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomal stresses. Biotechnol Lett 40, 915–922 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2544-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2544-1