Abstract
Objectives
To research the inherent properties of the co-expression of three types degumming-related enzymes and breed more powerful degumming strains.
Results
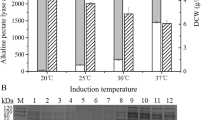
Six tandem multimers of the pectate lyase gene, the xylanase gene, and the endo-1,4-β-mannanase gene, which are essential for degumming process, were co-expressed and evaluated in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). The xyl91 gene had a synergistic effect with endo-1,4-β-mannanase and pectate lyase from DCE-01, when xyl gene was replaced with xyl91 in the multimer. The recombinant pET-pxm(91x) was selected and transformed into the original degumming strain DCE-01, which led to an enzymatic activity improvement. Furthermore, the weight loss, reducing sugar and COD value of the sample treated with the new engineered strain pET-pxm(91x)/DCE-01 increased to 22.5 %, 460 mg ml−1 and 4.9, respectively.
Conclusions
The co-expression of degumming-related enzyme genes may be applied in industrial tests and represents a novel direction for bio-degumming research.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu S, Saha MN, Chattopadhyay D, Chakrabarti K (2008) Large-scale degumming of ramie fibre using a newly isolated Bacillus pumilus DKS1 with high pectate lyase activity. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:239–245
Bera A, Ghosh A, Mukhopadhyay A, Chattopadhyay D, Chakrabarti K (2015) Improvement of degummed ramie fiber properties upon treatment with cellulase secreting immobilized A. larrymoorei A1. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38:341–351
Brühlmann F, Leupin M, Erismann KH, Fiechter A (2000) Enzymatic degumming of ramie bast fibers. J Biotechnol 76:43–50
Duan S, Liu Z, Feng X, Zheng K, Cheng L, Zheng X (2012) Diversity and characterization of ramie-degumming strains. Sci Agric 69:119–125
Kozlowski R, Batog J, Konczewicz W, Mackiewicz-Talarczyk M, Muzyczek M, Sedelnik N, Tanska B (2006) Enzymes in bast fibrous plant processing. Biotechnol Lett 28:761–765
Liu Z, Duan S, Sun Q, Peng Y, Feng X, Zheng K, Hu Z, Zhang Y (2012) A rapid process of ramie bio-degumming by Pectobacterium sp. CXJZU-120. Text Res J 82:1553–1559
Mukhopadhyay A, Dutta N, Chattopadhyay D, Chakrabarti K (2013) Degumming of ramie fiber and the production of reducing sugars from waste peels using nanoparticle supplemented pectate lyase. Bioresour Technol 137:202–208
Srivastava S, Bharti RK, Verma PK, shekhar Thakur I (2015) Cloning and expression of gamma carbonic anhydrase from Serratia sp. ISTD04 for sequestration of carbon dioxide and formation of calcite. Bioresour Technol 188:209–213
Wang F-J, Song H-L, Wang X-M, Zhang W-J, Wang B-L, Zhao J, Hu Z-B (2012) Tandem multimer expression and preparation of hypoglycemic peptide MC6 from Momordica charantia in Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:612–619
Zou M, Li X, Zhao J, Qu Y (2013) Characteristics of polygalacturonate lyase C from Bacillus subtilis 7-3-3 and its synergistic action with PelA in enzymatic degumming. PLoS One 8:e79357
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by grants from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2006AA02Z249), the China Agriculture Research System (No. CARS-19-E24), and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (CAAS-ASTIP-2015-IBFC), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (No. 2016jj3126).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Bacterial strains and plasmids used in the study.
Supplementary Table 2—The primer pairs used in the vector construction.
Supplementary Table 3—Comparison of key enzyme activity in recombinant degumming strain pET-pxm(91x)/DCE-01 and wild native degumming strain DCE-01.
Supplementary Fig. 1—Cloning of degumming related genes from DCE-01 and BE-91 by PCR.
Supplementary Fig. 2—Identification of recombinant plasmids by restriction analysis.
Supplementary Fig. 3—Single and double digestion of recombinant plasmid pET-pxm(91x) in DCE-01 after bio-degumming.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Liu, Z., Zeng, J. et al. Construction and co-expression of polycistronic plasmids encoding bio-degumming-related enzymes to improve the degumming process of ramie fibres. Biotechnol Lett 38, 2089–2096 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2204-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2204-2