Abstract
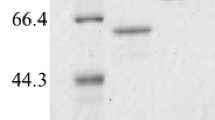
The end products from starch hydrolysis by amylases have important applications in various industries. Here, two amylases derived from two Streptomyces species that hydrolyze soluble starch from potato produced maltotriose as the primary maltooligosaccharide product. The genes, annotated as putative glycoside hydrolases, were cloned and expressed in Streptomyces lividans. These amylases displayed hydrolysis activity from pH 3 to 9.5 and were not affected by Ca2+. Optimal production of maltotriose was between 20 and 30 °C at pH 6.5. At the optimal temperature, both amylases produced maltotriose-rich end products rather than either maltose or maltotetraose.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doukyu N, Yamagishi W, Kuwahara H, Ogino H (2008) A maltooligosaccharide-forming amylase gene from Brachybacterium sp. strain LB25: cloning and expression in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72:2444–2447
Gupta R, Gigras P, Mohapatra H, Goswami VK, Chauhan B (2003) Microbial α-amylases: a biotechnological perspective. Proc Biochem 38:1599–1616
Hwang SY, Nakashima K, Okai N, Okazaki F, Miyake M, Harazono K, Ogino C, Kondo A (2013) Thermal stability and starch degradation profile of α-amylase from Streptomyces avermitilis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77:2449–2453
Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Shinose M, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sasaki Y, Hattori M, Omura S (2003) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biol 21:526–531
Kaneko T, Ohno T, Ohisa N (2005) Purification and characterization of a thermostable raw starch digesting amylase from a Streptomyces sp. isolated in a milling factory. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69:1073–1081
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical streptomyces genetics. John Innes Centre, Norwich
Kobayashi T, Kanai H, Aono R, Horikoshi K, Kudo T (1994) Cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of the α-amylase gene from the haloalkaliphilic archaeon Natronococcus sp. strain Ah-36. J Bacteriol 176:5131–5134
Ogino C, Kanemasu M, Hayashi Y, Kondo A, Shimizu N, Tokuyama S, Tahara Y, Kuroda S, Tanizawa K, Fukuda H (2004) Over-expression system for secretory phospholipase D by Streptomyces lividans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:823–828
Ohnishi Y, Ishikawa J, Hara H, Suzuki H, Ikenoya M, Ikeda H, Yamashita A, Hattori M, Horinouchi S (2008) Genome sequence of the streptomycin-producing microorganism Streptomyces griseus IFO 13350. J Bacteriol 190:4050–4060
Satoh E, Uchimura T, Kudo T, Komagata K (1997) Purification, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of an intracellular maltotriose-producing α-amylase from Streptococcus bovis 148. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4941–4944
Syed DG, Agasar D, Pandey A (2009) Production and partial purification of α-amylase from a novel isolate Streptomyces gulbargensis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:189–194
Vigal T, Gil JA, Daza A, García-González MD, Martín JF (1991) Cloning, characterization and expression of an α-amylase gene from Streptomyces griseus IMRU3570. Mol Gen Genet 225:278–288
Wako K, Hashimoto S, Kubomura S, Yokota K, Aikawa K, Kanaeda J (1979) Purification and some properties of a maltotriose-producing amylase. J Jpn Soc Starch Sci 26:175–181
Yang CH, Liu WH (2007) Cloning and characterization of a maltotriose-producing α-amylase gene from Thermobifida fusca. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:325–330
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology, Creation of Innovation Centers for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research Areas (Innovative Bioproduction, Kobe), Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kashiwagi, N., Miyake, M., Hirose, S. et al. Cloning and starch degradation profile of maltotriose-producing amylases from Streptomyces species. Biotechnol Lett 36, 2311–2317 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1611-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1611-5