Abstract
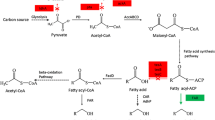
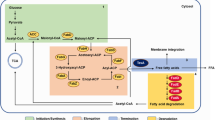
To investigate the effect of cellular fatty acids composition on ethanol tolerance in Escherichia coli, we overexpressed either des, encoding fatty acid desaturase from Bacillus subtilis, or fabA, encoding β-hydroxydecanoyl thio-ester dehydrase from E. coli, or both genes together, into E. coli. Recombinant E. coli harboring fabA had elevated tolerance against ethanol compared to wild type strain. In contrast, des decreased resistance to ethanol. Co-expression of both genes together complemented ethanol tolerance of E. coli. This result indicates how to engineer bacterial strains to be resistant to higher concentrations of ethanol.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar PS, Cronan JE, de Mendoza D (1998) A Bacillus subtilis gene induced by cold shock encodes a membrane phospholipid desaturase. J Bacteriol 180:2194–2200
Bonamor A, Macone A, Colotti G, Matarese RM, Boffi A (2006) The desaturase from Bacillus subtilis, a promising tool for the selective olefination of phospholipids. J Biotechnol 121:49–53
Carey VC, Ingram LO (1983) Lipid composition of Zymomonas mobilis: effects of ethanol and glucose. J Bacteriol 154:1291–1300
Clark DP, DeMendoza D, Polacco ML, Cronan JE (1983) β-hydroxydecanoyl thio ester dehydrase does not catalyze a rate-limiting step in Escherichia coli unsaturated fatty acid synthesis. Biochemistry 22:5897–5902
Heath RJ, Rock CO (1996) Roles of the FabA and FabZ β-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratases in Escherichia coli fatty acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 271:27795–27801
Ingram LO (1976) Adaptation of membrane lipids to alcohols. J Bacteriol 125:670–678
Ingram LO, Vreeland NS, Eaton LC (1980) Alcohol tolerance in Escherichia coli. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13(Suppl 1):191–195
Kajiwara S, Shirai A, Fujii T, Toguri T, Nakamura K, Ohtaguchi K (1996) Polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: expression of ethanol tolerance and the FAD2 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4309–4313
Uchida K (1974) Lipids of alcoholophilic Lactobacilli II. Occurrence of polar lipids with unusually long acyl chains in Lactobacillus heterohiochii. Biochim Biophys Acta 369:146–155
You KM, Rosenfield CL, Knipple DC (2003) Ethanol tolerance in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is dependent on cellular oleic acid content. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1499–1503
Zhang YM, Rock CO (2008) Membrane lipid homeostasis in bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:222–233
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from KRIBB Research Initiative Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lian Hua Luo and Pil-Soo Seo are co-first authors and contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, L.H., Seo, PS., Seo, JW. et al. Improved ethanol tolerance in Escherichia coli by changing the cellular fatty acids composition through genetic manipulation. Biotechnol Lett 31, 1867–1871 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0092-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0092-4