Abstract
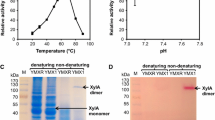
The conventional method of transketolase (TKT) activity assay uses ribose 5-phosphate and xylulose 5-phosphate as substrates. However, a new method of TKT assay is currently required since xylulose 5-phosphate is no longer commercially available and is difficult to synthesize chemically. Although there are effective assays for TKT using non-natural substrates, these are inadequate for evaluating changes in enzyme activity and affinity toward real substrates. As a solution to such problems, we describe a novel assay system using xylulokinase (XK) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. As for this purpose, the XK was overexpressed in E. coli, separated and purified in a single step, added to induce a reaction that generated xylulose 5-phosphate, which was integrated into the conventional TKT assay. The new coupling assay gave reproducible results with E. coli TKT and had a detection limit up to 5 × 10−4 unit/mg protein. A reliable result was also achieved for the incorporation of XK and TKT into a single reaction.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Scopes RK (2002) Isolation and properties of a constitutive d-xylulokinase from a novel thermophilic Saccharococcus caldoxylosilyticus DSM 12041 (ATCC 700356). Enzyme Microb Technol 30:627–632
Boros LG, Lee WN, Go VW (2002) A metabolic hypothesis of cell growth and death in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 24:26–33
French C, Ward JM (1995) Improved production and stability of E. coli recombinants expressing transketoalse for large scale biotransformation. Biotechnol Lett 17:247–252
Hobbs GR, Mitra RK, Chauhan RP et al (1996) Enzyme-catalyzed carbon-carbon bond formation: large scale production of Escherichia coli transketolase. J Biotechnol 45:173–179
Josephson BL, Fraenkel DG (1974) Sugar metabolism in transketolase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 118:1082–1089
Kamada N, Yasuhara A, Takano Y, Nakano T, Ikeda M (2001) Effect of transketolase modifications on carbon flow to the purine-nucleotide pathway in Corynebacterium ammoniagenes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:710–717
Lee TH, Kim MD, Park YC et al (2003) Effects of xylulokinase activity on ethanol production from d-xylulose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Appl Microbiol 95:847–852
Richard P, Toivari MH, Penttila M (2000) The role of xylulokinase in Saccaromyces cerevisiae xylulose catabolism. FEMS Microbiol Lett 190:39–43
Rodriguez-Pena JM, Cid VJ, Arroyo J, Nombela C (1998) The YGR194c (XKS1) gene encodes the xylulokinase from the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Let 162:155–160
Sevestre A, Helaine V, Guyot G, Martin C, Hecquet L (2003) A fluorogenic assay for transketolase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Tetrahedron Lett 44:827–830
Smith ME, Kaulmann U, Ward JM, Hailes HC (2006) A colorimetirc assay for screening transketolase activity. Bioorg Med Chem 14:7062–7065
Soh Y, Song BJ, Jeng J, Kallarakal AT (1998) Critical role of Arg433 in rat transketolase activity as probed by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem J 333:367–372
Wikner C, Meshalkina L, Nilsson U et al (1994) Analysis of an invariant cofactor-protein interaction in thiamin diphosphate-dependent enzymes by site-directed mutagenesis. Glutamic acid 418 in transketolase is essential for catalysis. J Biol Chem 269:32144–32150
Zimmermann FT, Schneider A, Schörken U et al (1999) Efficient multi-enzymatic synthesis of d-xylulose 5-phosphate. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 10:1643–1646
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JY., Cheong, DE. & Kim, GJ. A novel assay system for the measurement of transketolase activity using xylulokinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Biotechnol Lett 30, 899–904 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9616-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9616-y