Abstract
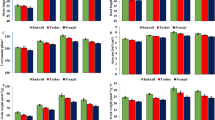
Peppermint (Mentha piperita) is a perennial medicinal plant containing active ingredients that can be used for treating liver and prostate cancers, acute respiratory infections, allergies, digestive problems, neuralgia, and migraines. The objective of this research is to investigate the expression of essential genes in the menthol pathway of Mentha piperita, including Pulegone reductase (Pr), Menthofuran synthase (Mfs), and limonene synthase (Ls) using qPCR, physiological analysis and essential oil composition in response to methyl jasmonate (MeJA) (0.5 mM) elicitation. Physiological analysis showed that 0.5 mM MeJA triggers defensive responsiveness in Mentha piperita by increasing superoxide dismutase (SOD) and Peroxidase (POD) enzymes activity. The highest transcript levels of Pr and Mfs genes were observed during 8 and 12 h after treatment respectively, but following 24 h, they were down-regulated. Essential oil analysis indicated that the percentage of constituents in the essential oil was changed using MeJA at 48 h and 96 h after post-treatment. Effective antimicrobial compounds, α-pinene, β-pinene, linalool and methyl acetate, were induced after 48 h. A non-significant positive relationship was detected between menthol content, and expression of the Pr and Mfs genes. Due to the significant change in the expression of Pr and Mfs genes in the menthol pathway, role of Pr gene in directing the pathway to the valuable compound menthol and deviation of the menthol pathway to the menthofuran as an undesirable component of essential oil by Mfs gene, it can be deduced that they are the most critical genes in response to MeJA treatment, which are appropriate candidates for metabolite engineering. In addition, MeJA improved defensive responsiveness and percentage of some constituents with antimicrobial properties in Mentha piperita.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This declaration is “not applicable”.
References
Afarin S, Huang JJ, Luo ZY (2015) JA-mediated transcriptional regulation of secondary metabolism in medicinal plants. Sci Bull 60(12):1062–1072. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1282607
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts, polyphennoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE (1995) Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York
Biondi S, Scaramagli S, Capitani F, Altamura MM, Torrigiani P (2001) Methyl jasmonate up regulates biosynthetic gene expression, oxidation and conjugation of polyamines, and inhibits shoot formation in tobacco thin layers. J Exp Bot 52:231–242. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.355.231
Bose SK, Yadav RK, Mishra S, Sangwan RS, Singh AK, Mishra B, Srivastava AK, Sangwan NS (2013) Effect of gibberellic acid and calliterpenone on plant growth attributes, trichomes, essential oil biosynthesis and pathway gene expression in differential manner in Mentha arvensis L. Plant Physiol Biochem 66:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.02.011
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgeram quantitis of protein utilizing the principle of ‘“protein- dye binding.”’ Annu Rev Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Chanjirakul K, Wang SY, Wang CY, Siriphanich J (2006) Effect of natural volatile compounds on antioxidant capacity and antioxidant enzymes in raspberries. Postharvest Biol Technol 40:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2006.01.004
Cotado A, Muller M, Morales M, Munne-Bosch S (2018) Linking jasmonates with pigment accumulation and photoprotection in a high-mountain endemic plants, Saxifraga longifolia. Environ Expe Bot 154:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.12.018
Croteau RB, Davis EM, Ringer KL, Wildung MR (2005) (−)-Menthol biosynthesis and molecular genetics. Naturwissenschaften 92:562–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-005-0055-0
da Silva Rivas AC, Lopes PM, de Azevedo Barros MM, Costa Machado DC, Alviano CS, Alviano DS (2012) Biological activities of α-pinene and β-pinene enantimores. Molecules 17(6):6305–6316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17066305
Dolzhenko Y, Bertea CM, Occhipinti A, Bossi S, Maffei ME (2010) UV-B modulates the interplay between terpenoids and flavonoids in peppermint (Mentha piperita L.). J Photochem Photobiolo B 100(2):67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2010.05.003
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60111a017
Erasto P, Viljoen AM (2008) Limonene—a review: biosynthetic, ecological and pharmacological relevance. NPC 3(7):1193–1202. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X0800300728
Farooq MA, Gill RA, Islam F, Ali B, Liu H, Xu J, He S, Zhou W (2016) Methyl jasmonate regulates antioxidant defense and suppresses arsenic uptake in Brassica napus. Front Plant Sci 7:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00468
Farsi M, Abdollahi F, Salehi A, Ghasemi S (2019) Growth responses of Origanum majorana to methyl jasmonic under limited irrigation conditions. J Essent Oil-Bear Plants 22(2):455–468. https://doi.org/10.1080/0972060X.2019.1602481
Gershenzon J, McConkey M, Croteau R (2000) Regulation of monoterpene accumulation in leaves of peppermint (Mentha piperita L.). Plant Physiol 122:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.122.1.205
Gholamipourfard K, Salehi M, Banchio E (2021) Mentha piperita phytochemicals in agriculture, food industry and medicine: features and applications. S Afr J Bot 141:183–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2021.05.014
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases: II. Purification and quantitative relationship with watersoluble protein in seedlings. Plant Physiol 59:315–318. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.59.2.315
Grulova D, Martino LD, Mancini E, Salamonc I, De Feo V (2015) Seasonal variability of the main components in essential oil of Mentha piperita. J Sci Food Agric 95(3):621–627. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6802
Hahlbrock K, Bednarek P, Ciolkowski I, Hamberger B, Heise A, Liedgens H, Logeman E, Nurnberger T, Schmelzer E, Somssich IE, Tan J (2003) Non-self-recognition, transcriptional reprogramming, and secondary metabolite accumulation during plant/pathogen interactions. PNAS 100:14569–14576. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0831246100
Hefner J, Ketchum REB, Croteau R (1998) Cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase from Taxus canadensis and assessment of the role of this prenyltransferase in cells induced for taxol production. Arch Bioch Biophys 360:62–74. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1998.0926
Helder M (2011) Stress response in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Chemistry, Umea University, Sweden
Helrich K (1990) Official methods of analysis, 15th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemistry, Washington, pp 17–33
Hyun-Jin K, Chen F, Wang X, Rajapakes NC (2006) Effect of methyl jasmonate on secondary metabolites of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). J Agric Food Chem 54:2327–2332. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf051979g
Kar M, Mishra D (1976) Catalase, peroxidase and polyphenol-oxidase activities during rice leaf senescence. Plant Physiol 57:315–319. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.57.2.315
Krizek DT, Kramer GF, Upadhyaya A, Mirecki RM (1993) UV-B response of cucumber seedling grown under metal halide and high pressure sodium/deluxe lamps. Plant Physiol 88:350–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1993.tb05509.x
Leite AM, Lima EDO, Souza ELD, Dinia FFM, Trajano VN, Medeiros AD (2007) Inhibitory effect of α-pinene, β-pinene and eugenol on the growth of potential infectious endocarditis causing gram-positive bacteria. Braz J Pharm Sci 43(1):121–126. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-93322007000100015
Liu R, Wang Z, Zheng J, Xu Z, Tang X, Huang Z, Zhang N, Dong Y, Li T (2022) The effect of methyl jasmonate on growth, gene expression and metabolite accumulation in Isatis indigotica. Ind Crop pro 177:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114482
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NT, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52451-6
Mahmoud SS, Croteau RB (2003) Menthofuran regulates essential oil biosynthesis in peppermint by controlling a downstream monoterpene reductase. PNAS 100(24):14481–14486. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2436325100
Mangas S, Bonfill M, Osuna L, Moyano E, Tortoriello J, Cusido RM, Pinol MT, Palazon J (2006) The effect of methyl jasmonate on triterpene and sterol metabolisms of Centella asiatica, Ruscus aculeatus and Galphimia glauca cultured plants. Phytochemistry 67:2041–2049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.06.025
McConkey ME, Gershenzon J, Croteau RB (2000) Developmental regulation of monoterpene biosynthesis in the glandular trichomes of peppermint. Plant Physiol 122:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.122.1.215
Miao YJ, Qu RJ, Sha JT, Cao YW, Guan JL, Tang XQ, Wang FQ, Yang J (2019) Growth, secondary metabolism, and related gene expression in response to interactions of nitrogen and sulfur in Isatis indigotica. Biol Plant 63:411–417. https://doi.org/10.32615/bp.2019.053
Park EJ, Kim SH, Kim BJ, Kim SY, So I, Jeon JH (2009) N Menthol enhances an antiproliferative activity of 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in LNCaP cells. J Clin Biochem Nutr 44:125–130. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.08-201
Park S-N, Lim YK, Freire MO, Cho E, Jin D, Kook J-K (2012) Antimicrobial effect of linalool and α-terpineol against periodontopathic and cariogenic bacteria. Anaerobe 18(3):369–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2012.04.001
Pauwels L, Morreel K, Witte ED, Lammertyn F, Montagu MV, Boerjan W, Inze D, Goossens A (2008) Mapping methyl jasmonate-mediated transcriptional reprogramming of mapping methyl jasmonate-mediated transcriptional reprogramming of metabolism and cell cycle progression in cultured Arabidopsis cells. PNAS 105(4):1380–1385. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0711203105
Poonam S, Kaur H, Geetika S (2013) Effect of jasmonic acid on photosynthetic pigments and stress markers in Cajanus cajan seedlings under copper stress. Am J Plant Sci 4:817–823. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2013.44100
Rahimi Y, Taleei A, Ranjbar M (2017) Changes in the expression of key genes involved in the biosynthesis of menthol and menthofuran in Mentha piperita under drought stress. Acta Physiol Plant 39(1–9):1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2502-x
Rios-Estepa R, Lange I, Lee M, Lange M (2015) Mathematical modeling-guided evaluation of biochemical, developmental, environmental, and genotypic determinants of essential oil composition and yield in peppermint leaves. Plant Physiol 152(4):2105–2119. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.152256
Santino A, Taurino M, De Domenico S, Bonsegna S, Pastor V, Flors V (2013) Jasmonate signalling in plant development and defence response to multiple abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 32:1085–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1441-2
Shi J, Zuo J, Zhou F, Gao L, Wang Q, Jiang A (2018) Low-temperature conditioning enhances chilling tolerance and reduces damage in cold-stored eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) fruit. Postharvest Biol Technol 141:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.03.007
Shoji T, Yamada Y, Hashimoto T (2000) Jasmonate induction of putrescine N-methyltransferase genes in the root of Nicotiana sylvestris. Plant Cell Physiol 41:831–839. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcd001
Sirhindi G, Mushtaq R, Gill SS, Sharma P, Abd-Allah EF, Ahmad P (2020) Photosynthetic activity and expression of photosystem II subunit genes in Brassica oleracea. Sci Rep 10(1):1–15
Soleymani F, Taheri H, Shafeinia A (2015) Effect of gibberellic acid on gene expression of menthol biosynthesis pathway in peppermint (Mentha piperita L.). IJACEBS 2:131–134
Soleymani F, Taheri H, Shafeinia AR (2017) Relative expression of genes of menthol biosynthesis pathway in peppermint (Mentha piperita) after chitosan, gibberllic acid and methyl jasmonate treatments. Russ J Plant Physiol 64(1):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443717010150
Su Y, Huang X, Dong R, Wang M, Tang J, Jabang C, Chen J, Zhang X, Nie G (2021) Exogenous methyl jasmonate improves heat tolerance of perennial ryegrass through alteration of osmotic adjustment antioxidant defense and expression of jasmonic acid-responsive genes. Front Plant Sci 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.664519
Uyanik GK, Guler N (2013) A study on multiple linear regression analysis. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 106:234–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.12.027
Wasternack C, Hause B (2013) Jasmonates: biosynthesis, perception, signal transduction and action in plant stress response, growth and development. Ann Bot 111(6):1021–1058. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mct067
Wasternack C, Strnad M (2016) Jasmonate signaling in plant stress responses and development–active and inactive compounds. New Biotechnol 33(5):604–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2015.11.001
Yuan ZQ, Zhang JY, Liu T (2017) Enhancement of polysaccharides accumulation in Dendrobium offficinale by exogenously applied methyl jasmonate. Biol Platarum 61(3):438–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0702-7
Zhao J, Davis LC, Verpoorte R (2005) Elicitor signal transduction leading to production of plant secondary metabolites. Biotechnol Adv 23:283–333
Funding
This declaration is “not applicable”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis and first draft of the manuscript was performed by Soheila afkar. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This declaration is “not applicable”.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Afkar, S., Karimzadeh, G. Changes in Physiological Traits, Gene Expression and Phytochemical Profile of Mentha piperita in Response to Elicitor. Biochem Genet (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10805-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10805-6