Abstract
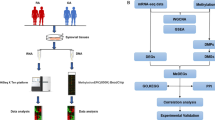
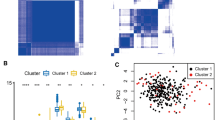
m6A modification is the most abundant mRNA modifications and plays an integral role in various biological processes in eukaryotes. However, the role of m6A regulators in rheumatoid arthritis remains unknown. To determine the expression of m6A RNA methylation regulators in rheumatoid arthritis and their possible functional and prognostic value. In this study, we performed differential analysis in the comprehensive gene expression database GSE93272 dataset between non-rheumatoid arthritis patients and rheumatoid arthritis patients to obtain 15 important m6A regulators. A random forest model and lasso regression were used to screen the five most important m6A regulators to predict the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. After further validation using in vitro qPCR experiments, a nomogram model was developed based on the four most important m6A regulators (ELAVL1, WTAP, YTHDF1, and ALKBH5). Immuno-infiltration analysis and consensus clustering analysis were then performed. An analysis of the decision curve showed that the nomogram model could be beneficial to patients. According to selected important m6A regulators, patients with rheumatoid arthritis were classified into two m6A models (ClusterA and ClusterB) via consensus approach. Activated B cells, CD56dim natural killer cells, immature B cells, monocytes, natural killer T cells, and T lymphocytes were associated with ClusterA in immune infiltration analysis. Importantly, immune infiltration in patients with high ELAVL1 expression was strikingly similar to ClusterA. m6A regulators play a non-negligible role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. A study of m6A patterns may provide future therapeutic options for rheumatoid arthritis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The primary datasets obtained during this analysis are available for download in the Gene Expression Omnibus database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/).
References
Burmester GR, Pope JE (2017) Novel treatment strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 389(10086):2338–2348
Csepany T et al (1990) Sequence specificity of mRNA N6-adenosine methyltransferase. J Biol Chem 265(33):20117–20122
Fan XC, Steitz JA (1998) Overexpression of HuR, a nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling protein, increases the in vivo stability of ARE-containing mRNAs. Embo j 17(12):3448–3460
Gertel S, Amital H (2014) Putative approaches to bypass the citrulline-specific autoimmune response in rheumatoid arthritis. Isr Med Assoc J 16(9):587–590
Guo X et al (2020) RNA demethylase ALKBH5 prevents pancreatic cancer progression by posttranscriptional activation of PER1 in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Mol Cancer 19(1):91
Han D et al (2019) Anti-tumour immunity controlled through mRNA m(6)A methylation and YTHDF1 in dendritic cells. Nature 566(7743):270–274
Hori H (2014) Methylated nucleosides in tRNA and tRNA methyltransferases. Front Genet 5:144
Horiuchi K et al (2006) Wilms’ tumor 1-associating protein regulates G2/M transition through stabilization of cyclin A2 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(46):17278–17283
Ji L, Chen X (2012) Regulation of small RNA stability: methylation and beyond. Cell Res 22(4):624–636
Jia G, Fu Y, He C (2013) Reversible RNA adenosine methylation in biological regulation. Trends Genet 29(2):108–115
Ke S et al (2015) A majority of m6A residues are in the last exons, allowing the potential for 3’ UTR regulation. Genes Dev 29(19):2037–2053
Kumar LD et al (2016) Advancement in contemporary diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Pharmacother 79:52–61
Lebedeva S et al (2011) Transcriptome-wide analysis of regulatory interactions of the RNA-binding protein HuR. Mol Cell 43(3):340–352
Martin GV et al (2019) Mosaicism of XX and XXY cells accounts for high copy number of Toll like Receptor 7 and 8 genes in peripheral blood of men with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep 9(1):12880
Petrelli F et al (2022) Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: one year in review 2022. Clin Exp Rheumatol 40(3):475–482
Ping XL et al (2014) Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res 24(2):177–189
Roignant JY, Soller M (2017) m(6)A in mRNA: an ancient mechanism for fine-tuning gene expression. Trends Genet 33(6):380–390
Roundtree IA et al (2017) Dynamic RNA Modifications in Gene Expression Regulation. Cell 169(7):1187–1200
Simone LE, Keene JD (2013) Mechanisms coordinating ELAV/Hu mRNA regulons. Curr Opin Genet Dev 23(1):35–43
Wang X et al (2015) N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell 161(6):1388–1399
Yue Y, Liu J, He C (2015) RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. Genes Dev 29(13):1343–1355
Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, He C (2017) Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(1):31–42
Zhou KI et al (2016) N(6)-Methyladenosine Modification in a Long Noncoding RNA Hairpin Predisposes Its Conformation to Protein Binding. J Mol Biol 428(5):822–833
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HYW and XGZ conceptualized the article. HYW, JPL, and XGZ contributed to the methodology. SXZ and SS conducted the experimental validation. SXZ and XGZ visualized the results. Finally, SXZ and YJZ drafted the original manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Institutional Review Board
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Yuxi People's Hospital (with protocol code: 2022kmykdx6f157 and date of approval: November 4, 2022).
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Sun, S., Zhang, Y. et al. Comprehensive Analysis of N6-Methyladenosine RNA Methylation Regulators in the Diagnosis and Subtype Classification of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biochem Genet (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10610-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10610-7