Abstract
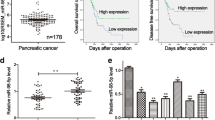
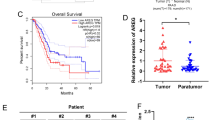
m6A demethylase FTO is confirmed to be involved in pancreatic cancer progression. FTO regulates miRNA processing. To investigate the regulatory effect of FTO on miR-383-5p and its role in pancreatic cancer. The expression of miR-383-5p, ITGA3, and FTO was predicted using bioinformatic analysis in tissues and was measured using qPCR in cells. Cell biological functions were investigated using MTT assay, Transwell assay, sphere formation assay, and qPCR. The targeting relationship between miR-383-5p and ITGA3 was evaluated using the dual-luciferase reporter assay. The effect of FTO on miR-383-5p processing was evaluated using RIP and MeRIP assay. FTO expression was upregulated in pancreatic cancer and silencing of FTO promoted the processing of miR-383-5p in an m6A-dependent manner. m6A-modified miRNA processing was recognized by IGF2BP1. Downregulation of miR-383-5p reversed FTO knockdown-induced inhibition of cellular processes. The FTO/miR-383-5p/ITGA3 axis facilitated cell viability, metastasis, and stemness in pancreatic cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The datasets used or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alarcón CR, Lee H, Goodarzi H, Halberg N, Tavazoie SF (2015) N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature 519(7544):482–485
Bi X, Lv X, Liu D, Guo H, Yao G, Wang L, Liang X, Yang Y (2021) METTL3-mediated maturation of miR-126-5p promotes ovarian cancer progression via PTEN-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cancer Gene Ther 28(3–4):335–349
Cai J, Chen H, Lu M, Zhang Y, Lu B, You L, Zhang T, Dai M, Zhao Y (2021) Advances in the epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: trends, risk factors, screening, and prognosis. Cancer Lett 520:1–11
Chen X, Liu F, Xue Q, Weng X, Xu F (2021) Metastatic pancreatic cancer: mechanisms and detection (review). Oncol Rep 46(5):1
Daoud AZ, Mulholland EJ, Cole G, McCarthy HO (2019) MicroRNAs in pancreatic cancer: biomarkers, prognostic, and therapeutic modulators. BMC Cancer 19(1):1130
Huang G, Guo X, Yang H (2021) Long noncoding RNA SNHG1 promotes human prostate cancer progression by sponging miR-383-5p. Anticancer Drugs 32(3):286–295
Idichi T, Seki N, Kurahara H, Fukuhisa H, Toda H, Shimonosono M, Yamada Y, Arai T, Kita Y, Kijima Y et al (2018) Involvement of anti-tumor miR-124-3p and its targets in the pathogenesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: direct regulation of ITGA3 and ITGB1 by miR-124-3p. Oncotarget 9(48):28849–28865
Jiang J, Xie C, Liu Y, Shi Q, Chen Y (2019) Up-regulation of miR-383-5p suppresses proliferation and enhances chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer cells by targeting TRIM27. Biomed Pharmacother 109:595–601
Jiao Y, Li Y, Liu S, Chen Q, Liu Y (2019) ITGA3 serves as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Oncotargets Ther 12:4141–4152
Kaushik G, Seshacharyulu P, Rauth S, Nallasamy P, Rachagani S, Nimmakayala RK, Vengoji R, Mallya K, Chirravuri-Venkata R, Singh AB et al (2021) Selective inhibition of stemness through EGFR/FOXA2/SOX9 axis reduces pancreatic cancer metastasis. Oncogene 40(4):848–862
Kawataki T, Yamane T, Naganuma H, Rousselle P, Anduren I, Tryggvason K, Patarroyo M (2007) Laminin isoforms and their integrin receptors in glioma cell migration and invasiveness: evidence for a role of alpha5-laminin(s) and alpha3beta1 integrin. Exp Cell Res 313(18):3819–3831
Kurozumi A, Goto Y, Matsushita R, Fukumoto I, Kato M, Nishikawa R, Sakamoto S, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Ichikawa T et al (2016) Tumor-suppressive microRNA-223 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting ITGA3/ITGB1 signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Sci 107(1):84–94
Liu ZX, Li LM, Sun HL, Liu SM (2018) Link between m6A modification and cancers. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 6:89
Michlewski G, Cáceres JF (2018) Post-transcriptional control of miRNA biogenesis. RNA 25(1):1–16
Mo WL, Deng LJ, Cheng Y, Yu WJ, Yang YH, Gu WD (2021) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0072309 promotes tumorigenesis and invasion by regulating the miR-607/FTO axis in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY) 13(8):11629–11645
Park W, Chawla A, O’Reilly EM (2021) Pancreatic cancer: a review. JAMA 326(9):851–862
Tang XR, Wen X, He QM, Li YQ, Ren XY, Yang XJ, Zhang J, Wang YQ, Ma J, Liu N (2017) MicroRNA-101 inhibits invasion and angiogenesis through targeting ITGA3 and its systemic delivery inhibits lung metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 8(1):e2566
Tang X, Liu S, Chen D, Zhao Z, Zhou J (2019) The role of the fat mass and obesity-associated protein in the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Lett 17(2):2473–2478
Tonini V, Zanni M (2021) Pancreatic cancer in 2021: what you need to know to win. World J Gastroenterol 27(35):5851–5889
Torphy RJ, Fujiwara Y, Schulick RD (2020) Pancreatic cancer treatment: better, but a long way to go. Surg Today 50(10):1117–1125
Vorvis C, Koutsioumpa M, Iliopoulos D (2016) Developments in miRNA gene signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer. Future Oncol 12(9):1135–1150
Wang JR, Liu B, Zhou L, Huang YX (2019) MicroRNA-124-3p suppresses cell migration and invasion by targeting ITGA3 signaling in bladder cancer. Cancer Biomark 24(2):159–172
Wang W, He Y, Zhai LL, Chen LJ, Yao LC, Wu L, Tang ZG, Ning JZ (2022) m(6)A RNA demethylase FTO promotes the growth, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through inhibiting TFPI-2. Epigenetics 17(12):1738–1752
Wei C, Gao J (2019) Downregulated miR-383-5p contributes to the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis. PeerJ (San Francisco, CA) 7:e7882
Wu K (2020) The role of miRNA biogenesis and DDX17 in tumorigenesis and cancer stemness. Biomed J 43(2):107–114
Xu K, Sun Y, Sheng B, Zheng Y, Wu X, Xu K (2019) Role of identified RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in liver. Anal Biochem 578:45–50
Zhang BY, Han L, Tang YF, Zhang GX, Fan XL, Zhang JJ, Xue Q, Xu ZY (2020) METTL14 regulates M6A methylation-modified primary miR-19a to promote cardiovascular endothelial cell proliferation and invasion. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(12):7015–7023
Zhao Z, Liu W (2020) Pancreatic cancer: a review of risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Technol Cancer Res Treat. https://doi.org/10.1177/1533033820962117
Zhou G, Yan K, Liu J, Gao L, Jiang X, Fan Y (2021) FTO promotes tumour proliferation in bladder cancer via the FTO/miR-576/CDK6 axis in an m6A-dependent manner. Cell Death Discov 7(1):329
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by Research Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (Youth) / 20204Y0169.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WZ, SH, YY, MX, AD and ML conceived the study; YY, MX and AD conducted the experiments; SH and ML analyzed the data; WZ wrote the manuscript; all the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors confirm that no conflicts of interest exist in this work.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Han, S., Yuan, Y. et al. FTO Knockdown-Mediated Maturation of miR-383-5p Inhibits Malignant Advancement of Pancreatic Cancer by Targeting ITGA3. Biochem Genet (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10560-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10560-0