Abstract
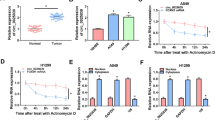
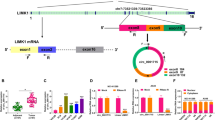
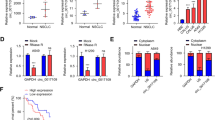
Circular RNAs are vital players in tumorigenesis. We held the purpose to investigate the role and mechanism of circ_0103809 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The expressions of circ_0103809, miR-153-3p and HDAC1 mRNA were determined using quantitative real-time PCR assay, and HDAC1 protein was quantified using western blot analysis. MTT, EdU, flow cytometry, tube-formation, wound healing and tube-formation assays were conducted for functional analysis. The predicted relationship among circ_0103809, miR-153-3p and HDAC1 was ascertained using dual-luciferase analysis, RIP assay and pull-down analysis. Animal models were further constructed to realize circ_0103809’s role in vivo. Circ_0103809 was upregulated NSCLC specimens, cells and serum-derived exosomes. Serum exosomal circ_0103809 had the potency to be a diagnostic biomarker for NSCLC. Circ_0103809 silencing inhibited NSCLC cell growth, metastasis and angiogenesis and triggered cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Circ_0103809 deficiency also suppressed the growth of transplanted tumors. Circ_0103809 acted as the miR-153-3p sponge, and the biological effects of circ_0103809 knockdown were relieved by miR-153-3p inhibition. HDAC1 was directly targeted by miR-153-3p, and miR-153-3p enrichment inhibited NSCLC cell malignant phenotypes by sequestering HDAC1. Circ_0103809 knockdown repressed NSCLC malignant progression partly by regulating miR-153-3p/HDAC1 signaling.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Ardekani AM, Naeini MM (2010) The role of microRNAs in human diseases. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 2:161
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Burotto M, Thomas A, Subramaniam D, Giaccone G, Rajan A (2014) Biomarkers in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: current concepts and future directions. J Thorac Oncol 9:1609–1617. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000302
Cai H, Hu B, Ji L, Ruan X, Zheng Z (2018) Hsa_circ_0103809 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting miR-490-5p/SOX2 signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res 10:1690–1702
Cao LL, Song X, Pei L, Liu L, Wang H, Jia M (2017) Histone deacetylase HDAC1 expression correlates with the progression and prognosis of lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Med (Baltim) 96:e7663. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000007663
Cocucci E, Meldolesi J (2015) Ectosomes and exosomes: shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol 25:364–372
Dai J, Su Y, Zhong S, Cong L, Liu B, Yang J, Tao Y, He Z, Chen C, Jiang Y (2020) Exosomes: key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5:145. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00261-0
Ge R, Tan E, Sharghi-Namini S, Asada HH (2012) Exosomes in Cancer Microenvironment and Beyond: have we overlooked these extracellular. Messengers? Cancer Microenviron 5:323–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-012-0110-2
Ge P, Chen X, Liu J, Jing R, Zhang X, Li H (2023) Hsa_circ_0088036 promotes nonsmall cell lung cancer progression by regulating miR-1343-3p/Bcl-3 axis through TGFbeta/Smad3/EMT signaling. Mol Carcinog 62:1073–1085. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.23547
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495:384–388. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11993
Hirsch FR, Suda K, Wiens J, Bunn PA Jr (2016) New and emerging targeted treatments in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. The Lancet 388:1012–1024
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS (2020) The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977
Kerr KM, Bibeau F, Thunnissen E, Botling J, Ryska A, Wolf J, Ohrling K, Burdon P, Malapelle U, Buttner R (2021) The evolving landscape of biomarker testing for non-small cell lung cancer in Europe. Lung Cancer 154:161–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.02.026
Lee YS, Dutta A (2009) MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 4:199–227. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092222
Li X, Yang L, Chen LL (2018) The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell 71:428–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.034
Li Y, Feng W, Kong M, Liu R, Wu A, Shen L, Tang Z, Wang F (2021) Exosomal circRNAs: a new star in cancer. Life Sci 269:119039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119039
Lin CL, Tsai ML, Lin CY, Hsu KW, Hsieh WS, Chi WM, Huang LC, Lee CH (2019) HDAC1 and HDAC2 double knockout triggers cell apoptosis in advanced thyroid cancer. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020454
Martin M, Kettmann R, Dequiedt F (2009) Class IIa histone deacetylases: conducting development and differentiation. Int J Dev Biol 53:291–301. https://doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.082698mm
Parra M, Verdin E (2010) Regulatory signal transduction pathways for class IIa histone deacetylases. Curr Opin Pharmacol 10:454–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.004
Qu S, Liu Z, Yang X, Zhou J, Yu H, Zhang R, Li H (2018) The emerging functions and roles of circular RNAs in cancer. Cancer Lett 414:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.11.022
Shang Q, Yang Z, Jia R, Ge S (2019) The novel roles of circRNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer 18:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0934-6
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62:10–29
Su Q, Lv X (2020) Revealing new landscape of cardiovascular disease through circular RNA-miRNA-mRNA axis. Genomics 112:1680–1685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2019.10.006
Vishnoi A, Rani S (2017) MiRNA biogenesis and regulation of diseases: an overview. Methods Mol Biol 1509:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6524-3_1
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, Conrad R (2012) Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:940–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.03.017
Wang T, Wang X, Du Q, Wu N, Liu X, Chen Y, Wang X (2019) The circRNA circP4HB promotes NSCLC aggressiveness and metastasis by sponging miR-133a-5p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 513:904–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.04.108
Xu Y, Feng Y, Sun Z, Li Q (2021) RNF168 promotes RHOC degradation by ubiquitination to restrain gastric cancer progression via decreasing HDAC1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 557:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.03.123
Yan Y, Fu G, Ye Y, Ming L (2017) Exosomes participate in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of gastric cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol 52:499–504. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365521.2016.1278458
Yang H, Zhao M, Zhao L, Li P, Duan Y, Li G (2020) CircRNA BIRC6 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell progression by sponging microRNA-145. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 43:477–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00503-x
Yang G, Li X, Liu J, Huang S, Weng Y, Zhu J, Lin D, Jiang O (2021) Hsa_circ_0008537 facilitates liver carcinogenesis by upregulating MCL1 and Snail1 expression via miR–153–3p. Oncol Rep 45:1072–1082. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2021.7941
Yin Y, Long J, He Q, Li Y, Liao Y, He P, Zhu W (2019) Emerging roles of circRNA in formation and progression of cancer. J Cancer 10:5015–5021. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.30828
Zhang L, Bu L, Hu J, Xu Z, Ruan L, Fang Y, Wang P (2018a) HDAC1 knockdown inhibits invasion and induces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biol Chem 399:603–610. http://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2017-0306
Zhang Z, Yang T, Xiao J (2018b) Circular RNAs: promising biomarkers for Human Diseases. EBioMedicine 34:267–274. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018b.07.036
Zhang N, Nan A, Chen L, Li X, Jia Y, Qiu M, Dai X, Zhou H, Zhu J, Zhang H, Jiang Y (2020) Circular RNA circSATB2 promotes progression of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer 19:101. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01221-6
Zhao G, Zhang Y, Zhao Z, Cai H, Zhao X, Yang T, Chen W, Yao C, Wang Z, Wang Z, Han C, Wang H (2020a) MiR-153 reduces stem cell-like phenotype and tumor growth of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting Jagged1. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:170. http://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01679-7
Zhao L, Bi M, Zhang H, Shi M (2020b) Downregulation of NEAT1 suppresses cell proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in NSCLC Via sponging miR-153-3p. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 35:362–370. http://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2019.3119
Zheng JP, Dai YM, Chen Z, Chen Q, Zheng Y, Lin X, Cui TJ (2020) Circular RNA circ-ABCB10 promotes non-small cell lung cancer proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis through repressing KISS1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:2518–2524. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202003_20519
Zhou X, Liu HY, Wang WY, Zhao H, Wang T (2018) Hsa_circ_0102533 serves as a blood-based biomarker for non-small-cell lung cancer diagnosis and regulates apoptosis in vitro. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 11:4395–4404
Zuo J, Zhao M, Fan Z, Liu B, Wang Y, Li Y, Lv P, Xing L, Zhang X, Shen H (2020) MicroRNA-153-3p regulates cell proliferation and cisplatin resistance via Nrf-2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Thorac Cancer 11:738–747. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13326
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XY designed and performed the research; XC, YS, QS, XC analyzed the data; XY wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants and this study was permitted by the Ethics Committee of Shanxi Province Cancer Hospital/ Shanxi Hospital Affiliated to Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences/Cancer Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10528_2023_10470_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 1.Knockdown of circ_0103809 strengthened NSCLC cell apoptosis and reduced cell migration. A549 and H1299 cells were transfected with si-NC, si-circ_0103809#1 or si-circ_0103809#2. (A) Western blot assay was used to detect CDK2, Bcl-2, Bad, and c-PARP protein levels. (B) The protein levels of E-cadherin and Vimentin were measured by western blot assay. (C) Transwel assay was performed to examine cell migration. ***P<0.001 (TIF 2254.7 kb)
10528_2023_10470_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 2.Circ_0103809 knockdown suppressed NSCLC cell migration, invasion and angiogenesis by sponging miR-153-3p. (A-C) The images of migration, invasion and tube formation were presented in A549 and H1299 cells transfected with si-NC, si-circ_0103809#1, si-circ_0103809#1 + anti-miR-NC, or si-circ_0103809#1 + anti-miR-153-3p (TIF 7295.7 kb)
10528_2023_10470_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 3.MiR-153-3p overexpression inhibited NSCLC cell migration, invasion and angiogenesis by targeting HDAC1. (A-C) The images of migration, invasion and tube formation were dispalyed in A549 and H1299 cells transfected with miR-NC, miR-153-3p, miR-153-3p + pcDNA3.1, or miR-153-3p + HDAC1 (TIF 6461.6 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Chai, X., Song, Y. et al. Deficiency of circ_0103809 Attenuates Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Malignant Progression by Controlling miR-153-3p/HDAC1 Network. Biochem Genet 62, 1160–1181 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10470-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10470-1