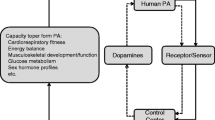
Abstract
Emerging evidence suggests that physical activity and sedentary behavior [reflected in physical inactivity (PI)], might be two different phenotypes that may have distinct underlying physiological mechanisms. The purpose of this review is to summarize the existing literature on the genetic determinants of PA and PI phenotypes in humans, considering them as distinct behaviors. Completed in January 2011, this review includes family studies, twin studies, association studies, genome-wide linkage studies and genome-wide association scan (GWAs) reporting different physical activity/inactivity-related phenotypes. In regards to PA, familial aggregation studies resulted in heritability estimates ranging from 0 to 60 %, and twin studies yielded heritability estimates (a2) and shared environment (c2) scores for PA phenotypes ranging from 0.00 to 0.85 and 0.00 to 0.84, respectively. Unique environmental (e2) results are well dispersed from 0.12 to 0.72. Suggestive linkages were found with markers nearby different activity-related genes: EDNRB, MC4R, UCP1, FABP2, CASR, SLC9A9. Significant associations with PA phenotypes were found for Ace, Gln223ARrg, MC4R and DRD2 genes. We found one GWAs that reported novel SNPs in the PAPSS2 gene on chromosome 10q23.2 and in two intergenic regions on chromosomes 2q33.1 and 18p11.32. Heritability estimates for PI ranged from 25 to 60 % and linkage studies recorded higher LOD scores for PI versus PA. The ACE genotype was strongly associated with PI. There are potentially different genetic influences on PA versus PI phenotypes. Future studies should focus on the different genetic influences on PA and PI to improve our understanding of underlying determinants of these behaviors.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaltonen S, Ortega-Alonso A, Kujala UM, Kaprio J (2010) A longitudinal study on genetic and environmental influences on leisure time physical activity in the Finnish twin cohort. Twin Res Hum Genet 13(5):475–481
Aarnio M, Winter T, Kujala UM, Kaprio J (1997) Familial aggregation of leisure-time physical activity—a three generation study. Int J Sports Med 18(7):549–556
Baecke JA, Burema J, Frijters JE (1982) A short questionnaire for the measurement of habitual physical activity in epidemiological studies. Am J Clin Nutr 36(5):936–942
Berentzen T, Kring SI, Holst C, Zimmermann E, Jess T, Hansen T, Pedersen O, Toubro S, Astrup A, Sorensen TI (2008) Lack of association of fatness-related FTO gene variants with energy expenditure or physical activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(7):2904–2908
Beunen G, Thomis M (1999) Genetic determinants of sports participation and daily physical activity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 23(Suppl 3):S55–S63
Bey L, Hamilton MT (2003) Suppression of skeletal muscle lipoprotein lipase activity during physical inactivity: a molecular reason to maintain daily low-intensity activity. J Physiol 551(Pt 2):673–682
Boomsma DI, van den Bree MB, Orlebeke JF, Molenaar PC (1989) Resemblances of parents and twins in sports participation and heart rate. Behav Genet 19(1):123–141
Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Leblanc C, Lortie G, Savard R, Theriault G (1983) A method to assess energy expenditure in children and adults. Am J Clin Nutr 37(3):461–467
Bouchard C, Rankinen T, Chagnon YC, Rice T, Perusse L, Gagnon J, Borecki I, An P, Leon AS, Skinner JS, Wilmore JH, Province M, Rao DC (2000) Genomic scan for maximal oxygen uptake and its response to training in the HERITAGE Family Study. J Appl Physiol 88(2):551–559
Bray MS, Hagberg JM, Perusse L, Rankinen T, Roth SM, Wolfarth B, Bouchard C (2009) The human gene map for performance and health-related fitness phenotypes: the 2006–2007 update. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(1):35–73
Butte NF, Cai G, Cole SA, Comuzzie AG (2006) Viva la Familia Study: genetic and environmental contributions to childhood obesity and its comorbidities in the Hispanic population. Am J Clin Nutr 84(3):646–654; quiz 673–644
Cai G, Cole SA, Butte N, Bacino C, Diego V, Tan K, Goring HH, O’Rahilly S, Farooqi IS, Comuzzie AG (2006) A quantitative trait locus on chromosome 18q for physical activity and dietary intake in Hispanic children. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14(9):1596–1604
Carlsson S, Andersson T, Lichtenstein P, Michaelsson K, Ahlbom A (2006) Genetic effects on physical activity: results from the Swedish Twin Registry. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38(8):1396–1401
Caspersen CJ, Powell KE, Christenson GM (1985) Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: definitions and distinctions for health-related research. Public Health Rep 100(2):126–131
Chevalley T, Bonjour JP, Ferrari S, Hans D, Rizzoli R (2005) Skeletal site selectivity in the effects of calcium supplementation on areal bone mineral density gain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in prepubertal boys. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(6):3342–3349
Choh AC, Demerath EW, Lee M, Williams KD, Towne B, Siervogel RM, Cole SA, Czerwinski SA (2009) Genetic analysis of self-reported physical activity and adiposity: the Southwest Ohio Family Study. Public Health Nutr 12(8):1052–1060
Christin L, O’Connell M, Bogardus C, Danforth E Jr, Ravussin E (1993) Norepinephrine turnover and energy expenditure in Pima Indian and white men. Metabolism 42(6):723–729
Cole SA, Butte NF, Voruganti VS, Cai G, Haack K, Kent JW Jr, Blangero J, Comuzzie AG, McPherson JD, Gibbs RA (2010) Evidence that multiple genetic variants of MC4R play a functional role in the regulation of energy expenditure and appetite in Hispanic children. Am J Clin Nutr 91(1):191–199
Cordain L, Gotshall RW, Eaton SB, Eaton SB 3rd (1998) Physical activity, energy expenditure and fitness: an evolutionary perspective. Int J Sports Med 19(5):328–335
De Moor MH, Posthuma D, Hottenga JJ, Willemsen G, Boomsma DI, De Geus EJ (2007a) Genome-wide linkage scan for exercise participation in Dutch sibling pairs. Eur J Hum Genet 15(12):1252–1259
De Moor MH, Spector TD, Cherkas LF, Falchi M, Hottenga JJ, Boomsma DI, De Geus EJ (2007b) Genome-wide linkage scan for athlete status in 700 British female DZ twin pairs. Twin Res Hum Genet 10(6):812–820
De Moor MH, Stubbe JH, Boomsma DI, De Geus EJ (2007c) Exercise participation and self-rated health: do common genes explain the association? Eur J Epidemiol 22(1):27–32
De Moor MH, Liu YJ, Boomsma DI, Li J, Hamilton JJ, Hottenga JJ, Levy S, Liu XG, Pei YF, Posthuma D, Recker RR, Sullivan PF, Wang L, Willemsen G, Yan H, de Geus EJ, Deng HW (2009) Genome-wide association study of exercise behavior in Dutch and American adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(10):1887–1895
Dishman RK, Sallis JF, Orenstein DR (1985) The determinants of physical activity and exercise. Public Health Rep 100(2):158–171
Duncan GE, Goldberg J, Noonan C, Moudon AV, Hurvitz P, Buchwald D (2008) Unique environmental effects on physical activity participation: a twin study. PLoS ONE 3(4):e2019
Eriksson M, Rasmussen F, Tynelius P (2006) Genetic factors in physical activity and the equal environment assumption—the Swedish young male twins study. Behav Genet 36(2):238–247
Esparza J, Fox C, Harper IT, Bennett PH, Schulz LO, Valencia ME, Ravussin E (2000) Daily energy expenditure in Mexican and USA Pima Indians: low physical activity as a possible cause of obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24(1):55–59
Fisher A, van Jaarsveld CH, Llewellyn CH, Wardle J (2010) Environmental influences on children’s physical activity: quantitative estimates using a twin design. PLoS ONE 5(4):e10110
Franks PW, Ravussin E, Hanson RL, Harper IT, Allison DB, Knowler WC, Tataranni PA, Salbe AD (2005) Habitual physical activity in children: the role of genes and the environment. Am J Clin Nutr 82(4):901–908
Frederiksen H, Christensen K (2003) The influence of genetic factors on physical functioning and exercise in second half of life. Scand J Med Sci Sports 13(1):9–18
Fuentes RM, Perola M, Nissinen A, Tuomilehto J (2002) ACE gene and physical activity, blood pressure, and hypertension: a population study in Finland. J Appl Physiol 92(6):2508–2512
Gingrich JA, Caron MG (1993) Recent advances in the molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 16:299–321
Good DJ, Coyle CA, Fox DL (2008) Nhlh2: a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor controlling physical activity. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 36(4):187–192
Hakanen M, Raitakari OT, Lehtimaki T, Peltonen N, Pahkala K, Sillanmaki L, Lagstrom H, Viikari J, Simell O, Ronnemaa T (2009) FTO genotype is associated with body mass index after the age of seven years but not with energy intake or leisure-time physical activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(4):1281–1287
Hamilton MT, Hamilton DG, Zderic TW (2007) Role of low energy expenditure and sitting in obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes 56(11):2655–2667
Joosen A, Gielen M, Vlietinck R, Westerterp KR (2005) Genetic analysis of physical activity in twins. Am J Clin Nutr 82(6):1253–1259
Kaprio J, Koskenvuo M, Sarna S (1981) Cigarette smoking, use of alcohol, and leisure-time physical activity among same-sexed adult male twins. Prog Clin Biol Res 69(Pt C):37–46
Katzmarzyk PT (2010) Physical activity, sedentary behavior, and health: paradigm paralysis or paradigm shift? Diabetes 59(11):2717–2725
Koopmans JR, Lorenz JPVD, Boomsma DI (1994) Smoking and sports participation. In: Goldbourt U, Faire U, Berg K (eds) Factors in coronary heart disease. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 217–235
Larsen LH, Echwald SM, Sorensen TI, Andersen T, Wulff BS, Pedersen O (2005) Prevalence of mutations and functional analyses of melanocortin 4 receptor variants identified among 750 men with juvenile-onset obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(1):219–224
Lauderdale DS, Fabsitz R, Meyer JM, Sholinsky P, Ramakrishnan V, Goldberg J (1997) Familial determinants of moderate and intense physical activity: a twin study. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29(8):1062–1068
Lee RB (2003) The Dobe Ju/’hoansi. Wadsworth Publishing, Belmont
Liu GF, Zhu HD, Lagou V, Gutin B, Stallmann-Jorgensen IS, Treiber FA, Dong YB, Snieder H (2010) FTO variant rs9939609 is associated with body mass index and waist circumference, but not with energy intake or physical activity in European- and African-American youth. BMC Med Genet 11:57
Loos RJ, Rankinen T, Tremblay A, Perusse L, Chagnon Y, Bouchard C (2005) Melanocortin-4 receptor gene and physical activity in the Quebec Family Study. Int J Obes (Lond) 29(4):420–428
Lorentzon M, Lorentzon R, Lerner UH, Nordstrom P (2001) Calcium sensing receptor gene polymorphism, circulating calcium concentrations and bone mineral density in healthy adolescent girls. Eur J Endocrinol 144(3):257–261
Maia JA, Thomis M, Beunen G (2002) Genetic factors in physical activity levels: a twin study. Am J Prev Med 23(2 Suppl):87–91
McCaffery JM, Papandonatos GD, Bond DS, Lyons MJ, Wing RR (2009) Gene × environment interaction of vigorous exercise and body mass index among male Vietnam-era twins. Am J Clin Nutr 89(4):1011–1018
Mitchell BD, Rainwater DL, Hsueh WC, Kennedy AJ, Stern MP, Maccluer JW (2003) Familial aggregation of nutrient intake and physical activity: results from the San Antonio Family Heart Study. Ann Epidemiol 13(2):128–135
Montoye HJ, Kemper HCH, Washburn RA, Saris WH (1996) Measuring physical activity and energy expenditure. Human Kinetics Publishers, Champaign
Nagasaka J, Tsuji M, Takeda H, Matsumiya T (1999) Role of endothelin receptor subtypes in the behavioral effects of the intracerebroventricular administration of endothelin-1 in conscious rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 64(1):171–176
Palatini P, Graniero GR, Mormino P, Nicolosi L, Mos L, Visentin P, Pessina AC (1994) Relation between physical training and ambulatory blood pressure in stage I hypertensive subjects. Results of the HARVEST trial. Hypertension and ambulatory recording Venetia study. Circulation 90(6):2870–2876
Pereira MA, FitzerGerald SJ, Gregg EW, Joswiak ML, Ryan WJ, Suminski RR, Utter AC, Zmuda JM (1997) A collection of Physical Activity Questionnaires for health-related research. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29(6 Suppl):S1–S205
Perusse L, Leblanc C, Bouchard C (1988) Familial resemblance in lifestyle components: results from the Canada Fitness Survey. Can J Public Health 79(3):201–205
Perusse L, Tremblay A, Leblanc C, Bouchard C (1989) Genetic and environmental influences on level of habitual physical activity and exercise participation. Am J Epidemiol 129(5):1012–1022
Raitakari OT, Taimela S, Porkka KV, Leino M, Telama R, Dahl M, Viikari JS (1996) Patterns of intense physical activity among 15- to 30-year-old Finns. The cardiovascular risk in young Finns study. Scand J Med Sci Sports 6(1):36–39
Rankinen T, Perusse L, Rauramaa R, Rivera MA, Wolfarth B, Bouchard C (2001) The human gene map for performance and health-related fitness phenotypes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33(6):855–867
Rankinen T, Roth SM, Bray MS, Loos R, Perusse L, Wolfarth B, Hagberg JM, Bouchard C (2010) Advances in exercise, fitness, and performance genomics. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42(5):835–846
Richardson MT, Ainsworth BE, Wu HC, Jacobs DR Jr, Leon AS (1995) Ability of the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC)/Baecke questionnaire to assess leisure-time physical activity. Int J Epidemiol 24(4):685–693
Richert L, Chevalley T, Manen D, Bonjour JP, Rizzoli R, Ferrari S (2007) Bone mass in prepubertal boys is associated with a Gln223Arg amino acid substitution in the leptin receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(11):4380–4386
Scillitani A, Guarnieri V, De Geronimo S, Muscarella LA, Battista C, D’Agruma L, Bertoldo F, Florio C, Minisola S, Hendy GN, Cole DE (2004) Blood ionized calcium is associated with clustered polymorphisms in the carboxyl-terminal tail of the calcium-sensing receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(11):5634–5638
Scuteri A, Sanna S, Chen WM, Uda M, Albai G, Strait J, Najjar S, Nagaraja R, Orru M, Usala G, Dei M, Lai S, Maschio A, Busonero F, Mulas A, Ehret GB, Fink AA, Weder AB, Cooper RS, Galan P, Chakravarti A, Schlessinger D, Cao A, Lakatta E, Abecasis GR (2007) Genome-wide association scan shows genetic variants in the FTO gene are associated with obesity-related traits. PLoS Genet 3(7):e115
Seabra AF, Mendonca DM, Goring HH, Thomis MA, Maia JA (2008) Genetic and environmental factors in familial clustering in physical activity. Eur J Epidemiol 23(3):205–211
Sherwood NE, Jeffery RW (2000) The behavioral determinants of exercise: implications for physical activity interventions. Annu Rev Nutr 20:21–44
Simonen RL, Perusse L, Rankinen T, Rice T, Rao DC, Bouchard C (2002) Familial aggregation of physical activity levels in the Quebec Family Study. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34(7):1137–1142
Simonen RL, Rankinen T, Perusse L, Leon AS, Skinner JS, Wilmore JH, Rao DC, Bouchard C (2003a) A dopamine D2 receptor gene polymorphism and physical activity in two family studies. Physiol Behav 78(4–5):751–757
Simonen RL, Rankinen T, Perusse L, Rice T, Rao DC, Chagnon Y, Bouchard C (2003b) Genome-wide linkage scan for physical activity levels in the Quebec Family study. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(8):1355–1359
Simonen R, Levalahti E, Kaprio J, Videman T, Battie MC (2004) Multivariate genetic analysis of lifetime exercise and environmental factors. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36(9):1559–1566
Snitker S, Tataranni PA, Ravussin E (2001) Spontaneous physical activity in a respiratory chamber is correlated to habitual physical activity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25(10):1481–1486
Spinath FM, Wolf H, Angleitner A, Borkenau P, Riemann R (2002) Genetic and environmental influences on objectively assessed activity in adults. Personality Individ Differ 33(4):633–645
Stefan N, Vozarova B, Del Parigi A, Ossowski V, Thompson DB, Hanson RL, Ravussin E, Tataranni PA (2002) The Gln223Arg polymorphism of the leptin receptor in Pima Indians: influence on energy expenditure, physical activity and lipid metabolism. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 26(12):1629–1632
Stubbe JH, Boomsma DI, De Geus EJ (2005) Sports participation during adolescence: a shift from environmental to genetic factors. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37(4):563–570
Stubbe JH, Boomsma DI, Vink JM, Cornes BK, Martin NG, Skytthe A, Kyvik KO, Rose RJ, Kujala UM, Kaprio J, Harris JR, Pedersen NL, Hunkin J, Spector TD, de Geus EJ (2006) Genetic influences on exercise participation in 37,051 twin pairs from seven countries. PLoS ONE 1:e22
Tang-Christensen M, Havel PJ, Jacobs RR, Larsen PJ, Cameron JL (1999) Central administration of leptin inhibits food intake and activates the sympathetic nervous system in rhesus macaques. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(2):711–717
Tsao TS, Li J, Chang KS, Stenbit AE, Galuska D, Anderson JE, Zierath JR, McCarter RJ, Charron MJ (2001) Metabolic adaptations in skeletal muscle overexpressing GLUT4: effects on muscle and physical activity. FASEB J 15(6):958–969
Tudge C (1999) Neanderthals, bandits and farmers: how agriculture really began. Yale University Press, New Haven
Wang JG, Staessen JA (2000) Genetic polymorphisms in the renin-angiotensin system: relevance for susceptibility to cardiovascular disease. Eur J Pharmacol 410(2–3):289–302
Winnicki M, Accurso V, Hoffmann M, Pawlowski R, Dorigatti F, Santonastaso M, Longo D, Krupa-Wojciechowska B, Jeunemaitre X, Pessina AC, Somers VK, Palatini P (2004) Physical activity and angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism in mild hypertensives. Am J Med Genet 125A(1):38–44
Wolfarth B, Bray MS, Hagberg JM, Perusse L, Rauramaa R, Rivera MA, Roth SM, Rankinen T, Bouchard C (2005) The human gene map for performance and health-related fitness phenotypes: the 2004 update. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37(6):881–903
Wood AC, Rijsdijk F, Saudino KJ, Asherson P, Kuntsi J (2008) High heritability for a composite index of children’s activity level measures. Behav Genet 38(3):266–276
Zderic TW, Hamilton MT (2006) Physical inactivity amplifies the sensitivity of skeletal muscle to the lipid-induced downregulation of lipoprotein lipase activity. J Appl Physiol 100(1):249–257
Acknowledgments
Thanks are expressed to the three anonymous reviewers, as well as to the FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia for granting this research (PTDC/DES/67569/2006 FCOMP-01-0124-FEDEB-09608 and SFRH/BD/65290/2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by Yoon-Mi Hur.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Vilhena e Santos, D.M., Katzmarzyk, P.T., Seabra, A.F.T. et al. Genetics of Physical Activity and Physical Inactivity in Humans. Behav Genet 42, 559–578 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-012-9534-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-012-9534-1