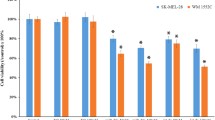
We studied the effects of berberine on the proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of skin melanoma A375 cells, as well as cell cycle-related miRNAs and their target genes, CDK1, CDK2, and cyclins D1 and A. The inhibitory effect of berberine on the growth of A375 cells was evaluated by MTT assay. Cell apoptosis was detected by trypan blue staining. Cell migration was assessed by the scratch test. Cell cycle phases were determined by flow cytometry. The levels of miRNA-582-5p and miRNA-188-5, and mRNA of their target genes encoding CDK1, CDK2, and cyclins D1 and A were measured by qRT-PCR. The expression of cell cycle-related proteins (CDK1, CDK2, and cyclins D1 and A) was determined by Western blotting. Berberine inhibited the proliferation of A375 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner and significantly and dose-dependently enhanced cell apoptosis. Scratch assay showed an inhibitory effect of berberine on migration of A375 cells. Berberine in low concentrations (20 and 40 μM) caused cell cycle arrest in the S and G2/M phases, while treatment with high concentrations of berberine (60 and 80 μM) arrested cell-cycle in the G2/M phase. The increase in berberine concentration led to an increase in miRNA-582-5p and miRNA-188-5p expression and a decrease in the expression of mRNA for the corresponding target genes encoding CDK1, CDK2, and cyclins D1 and A. Western blotting also revealed reduced expression of CDK1, CDK2, and cyclins D1 and A. Thus, berberine suppressed the growth and migration of human melanoma cells and promoted their apoptosis. Berberine can increase the expression of cell cycle-related miRNAs and cause degradation of the corresponding target genes, thereby blocking the cell cycle progression and inhibiting the melanoma A375 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bienvenu F, Jirawatnotai S, Elias JE, Meyer CA, Mizeracka K, Marson A, Frampton GM, Cole MF, Odom DT, Odajima J, Geng Y, Zagozdzon A, Jecrois M, Young RA, Liu XS, Cepko CL, Gygi SP, Sicinski P. Transcriptional role of cyclin D1 in development revealed by a genetic-proteomic screen. Nature. 2010;463:374-378.
Chen D, Farwell MA, Zhang B. MicroRNA as a new player in the cell cycle. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010;225(2):296-301.
Chen D, Li Y, Mei Y, Geng W, Yang J, Hong Q, Feng Z, Cai G, Zhu H, Shi S, Bai XY, Chen X. miR-34a regulates mesangial cell proliferation via the PDGFR-β/Ras-MAPK signaling pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014;71(20):4027-4042.
Lim S, Kaldis P. CDKs, cyclins and CKIs: roles beyond cell cycle regulation. Development. 2013;140(15):3079-3093.
Qi HW, Xin LY, Xu X, Ji XX, Fan LH. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers to predict response of Berberine in suppressing lung cancer invasion and metastasis. J. Transl. Med. 2014;12. ID 22. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-12-22
Tawbi H, Nimmagadda N. Targeted therapy in melanoma. Biologics. 2009;3:475-484.
Tsang CM, Cheung YC, Lui VW, Yip YL, Zhang G, Lin VW, Cheung KC, Feng Y, Tsao SW. Berberine suppresses tumorigenicity and growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by inhibiting STAT3 activation induced by tumor associated fibroblasts. BMC Cancer. 2013;13. ID 619. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-13-619
Uchino K, Takeshita F, Takahashi RU, Kosaka N, Fujiwara K, Naruoka H, Sonoke S, Yano J, Sasaki H, Nozawa S, Yoshiike M, Kitajima K, Chikaraishi T, Ochiya T. Therapeutic effects of microRNA-582-5p and -3p on the inhibition of bladder cancer progression. Mol. Ther. 2013;21(3):610-619.
Wu J, Lv Q, He J, Zhang H, Mei X, Cui K, Huang N, Xie W, Xu N, Zhang Y. MicroRNA-188 suppresses G1/S transition by targeting multiple cyclin/CDK complexes. Cell Commun. Signal. 2014;12. ID 66. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-014-0066-6
Yang LH, Li DX, Su YI, Su XI. Inhibitory effect of berberine on human melanoma A375 cells. Chinese J. Dermatovenereol. 2016;(11):1123-1126. doi: https://doi.org/10.13735/j.cjdv.1001-7089.201605119
Zhang H, Qi S, Zhang T, Wang A, Liu R, Guo J, Wang Y, Xu Y. miR-188-5p inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in prostate cancer by repressing LAPTM4B expression. Oncotarget. 2015;6(8):6092-6104.
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Yang J, Li S, Chen J. Upregulation of miR-582-5p inhibits cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and invasion by targeting Rab27a in human colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015;22(10):475-480.
Zhang Y, Huang W, Ran Y, Xiong Y, Zhong Z, Fan X, Wang Z, Ye Q. miR-582-5p inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CDK1 and AKT3. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(11):8309-8316.
Zhou JY, Shi R, Zheng WL, Ma W. microRNA, cell cycle regulation and its research method. Basic Clin. Med. 2013;(1):9-14. doi: https://doi.org/10.16352/j.issn.1001-6325.2013.01.025
Zou XY, Li LL. Cell cycle regulation and tumor. J. Int. Genet. 2006;(1):70-73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 169, No. 4, pp. 477-483, April, 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, M., Yang, L., Li, D. et al. Cell Cycle Regulation by Berberine in Human Melanoma A375 Cells. Bull Exp Biol Med 169, 491–496 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04916-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04916-4