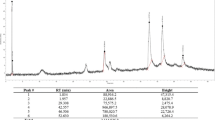
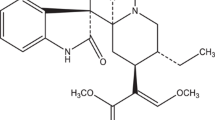
We studied antidepressant and antiparkinsonian properties of N-(5-hydroxynicotinoyl)-Lglutamic acid calcium salt (Ampasse) in rodents. It was found that Ampasse in a dose of 30 mg/kg exhibited antidepressant activity in the forced swimming test in mice and in a dose of 0.1 mg/kg maximally alleviates the symptoms of parkinsonian syndrome induced by systemic administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in C57Bl/6 mice, and haloperidol-induced catalepsy in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Makarenko A., Kovtun A, Petrov F, Vasilyeva I. Comparartive Analysis of Effects produced by medicines “Ampasse”, “M2” and “Cerebral” on the systemic glial cell responses of sensorimotor cerebral cortex it rats under modelled acute hemorrhagic stroke. Aktual. Prolem. Suchasn. Med. 2017;17(1):244-248. Russian.
Motin VG, Kiselev AV, Stovbun IS, Sergienko VI, Kalinina TS. N-(5-Hydroxynicotinoyl)-L-Glutamic Acid Calcium Salt Modifies Responses of Rat Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons during Orthodromic Stimulation. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018;165(1):27-30. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4091-0
Jakimuk PV, Stovbun SV, Litvin AA. Patent RU No. 2314293. N-(5-hydroxynicotinoyl)-l-glutamic acid mono- and bivalent salts possessing psychotropic (antidepressant and anxiolytic), neuroprotective, geroprotective and anti-insult effect. Bull. No. 1. Published January 10, 2008.
Manual on Experimental (Preclinical) Study of New Pharmacological Substances, Khabriev RU, ed. Moscow, 2005. Russian.
Stovbun SV, Kiselev AV, Sergienko VI. Experimental study of nootropic and neuroprotective properties of N-(5- hydroxynicotinoyl)-L-glutamic acid calcium salt. Vestn. Mos. Gos. Obl. Univer. Ser.: Estestv. Nauki. 2011;(2):83-93. Russian.
Booth HDE, Hirst WD, Wade-Martins R. The Role of Astrocyte Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2017;40(6):358-370.
Calabresi P, Mercuri NB, Di Filippo M. Synaptic plasticity, dopamine and Parkinson’s disease: one step ahead. Brain. 2009;132(Pt 2):285-287.
Dallé E, Mabandla MV. Early life stress, depression and Parkinson’s disease: a new approach. Mol. Brain. 2018;11(1). ID 18. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-018-0356-9
Goldman JG, Postuma R. Premotor and nonmotor features of Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2014;27(4):434-441.
Liu W, Ge T, Leng Y, Pan Z, Fan J, Yang W, Cui R. The role of neural plasticity in depression: from hippocampus to prefrontal cortex. Neural Plast. 2017;2017. ID 6871089. doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6871089
Marsh L. Depression and Parkinson’s disease: current knowledge. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013;13(12). ID 409. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-013-0409-5
Mena MA, García de Yébenes J. Glial cells as players in parkinsonism: the “good,” the “bad,” and the “mysterious” glia. Neuroscientist. 2008;14(6):544-560.
Rial D, Lemos C, Pinheiro H, Duarte JM, Gonçalves FQ, Real JI, Prediger RD, Gonçalves N, Gomes CA, Canas PM, Agostinho P, Cunha RA. Depression as a glial-based synaptic dysfunction. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016;9. ID 521. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00521
Schafer DP, Lehrman EK, Stevens B. The “quad-partite” synapse: microglia-synapse interactions in the developing and mature CNS. Glia. 2013;61(1):24-36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 168, No. 7, pp. 56-59, July, 2019
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiselev, A.V., Vedenkin, A.S., Stovbun, I.S. et al. Calcium Salt of N-(5-Hydroxynicotinoyl)-L-Glutamic Acid Weakens Depressive-Like Behavior and Parkinsonian Syndrome in Experiment on Rodents. Bull Exp Biol Med 168, 48–51 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04643-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04643-5