Abstract
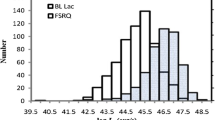
We use a large sample of Fermi flat-spectrum radio quasars (FSRQs), BL Lacertae objects (BL Lacs) and flat-spectrum radio-loud narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies (F-RLNLS1s) to study the relationship between them. Our main results are as follows: (i) Compared with FSRQs, the F-RLNLS1s have lower redshift, black hole mass and jet kinetic power. However, the F-RLNLS1s have higher redshift, broad-line region luminosity, accretion rate and jet kinetic power than BL Lacs on the average. When we use the median black hole mass to normalize the jet kinetic and radiation power, we find a small difference between FSRQs and F-RLNLS1s in normalized jet kinetic power. (ii) According to the BZ theory, we find that both of FSRQs and most of F-RLNLS1s may have a strong accretion disk which dominated by the radiation-pressure. (iii) Most of these F-RLNLS1s and FSRQs have accretion disk luminosity (\(L_{\text{Disk}}\)) larger than jet radiation power (\(P_{\text{rad}}\)), \(\log L_{\text{Disk}} > \log P_{\text{rad}}\), which suggests that FSRQs and F-RLNLS1s may have a strong accretion disk. We use a linear regression to analyze the relationship between jet power and accretion disk luminosity. It is interesting to note that the slopes of FSRQs are similar to that of F-RLNLS1s in jet power vs. accretion disk luminosity panel. These results above may suggest that the formation mechanism of jets in F-RLNLS1s is similar to that of FSRQs. (iv) By using the multiple linear regression analysis, we find that the accretion and black hole mass may have a different contribution to jet kinetic power for F-RLNLS1s. What’s more, the contribution of black hole mass is larger than that of accretion rate. These results imply that the jet kinetic power of F-RLNLS1s less than FSRQs may due to the low black hole mass of F-RLNLS1s.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdo, A.A., et al.: Astrophys. J. 700, 597 (2009a)
Abdo, A.A., Ackermann, M., Ajello, M., et al.: Astrophys. J. 699, 976 (2009b)
Ackermann, M., et al.: Astrophys. J. 810, 14 (2015)
Baldwin, J.A., Netzer, H.: Astrophys. J. 226, 1 (1978)
Berton, M., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 614, A87 (2018)
Blandford, R.D., Payne, D.G.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 199, 883 (1982)
Blandford, R.D., Rees, M.J.: In: Wolfe, A.M. (ed.) Pittsburgh Conference on BL Lac Objects, p. 328 (1978)
Blandford, R.D., Znajek, R.L.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 179, 433 (1977)
Boroson, T.A.: Astrophys. J. 565, 78 (2002)
Calderone, G., Ghisellini, G., Colpi, M., Dotti, M.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 431, 210 (2013)
Cao, X.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 570, L13 (2002)
Cao, X.: Astrophys. J. 599, 147 (2003)
Cao, X., Jiang, D.R.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 307, 802 (1999). (C99)
Cavaliere, A., D’Elia, V.: Astrophys. J. 571, 226 (2002)
Celotti, A., Padovani, P., Ghisellini, G.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 286, 415 (1997). (C97)
Chai, B., Cao, X., Gu, M.: Astrophys. J. 759, 114 (2012). (C12)
Chen, Y.Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, H.J., Yu, X.L.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 451, 4193 (2015a)
Chen, Y.Y., Zhang, X., Xiong, D.R., Yu, X.L.: Astron. J. 150, 8 (2015b)
Doi, A., Nagira, H., Kawakatu, N., Kino, M., Nagaiand, H., Asada, K.: Astrophys. J. 760, 41 (2012)
Falcke, H., Biermann, P.L.: Astron. Astrophys. 293, 665 (1995)
Foschini, L.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. Conf. Ser. 28, 1460188 (2014)
Foschini, L.: Front. Astron. Space Sci. 4, 6 (2017)
Foschini, L., Berton, M., Caccianiga, A., Ciroi, S., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 575, A13 (2015)
Francis, P.J., Hewett, P.C., Foltz, C.B., Chaffee, F.H., Weymann, R.J., Morris, S.L.: Astrophys. J. 373, 465 (1991)
Gebhardt, K., et al.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 543, L5 (2000)
Ghisellini, G., Tavecchio, F., Ghirlanda, G.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 399, 2041 (2009)
Ghisellini, G., Tavecchio, F., Foschini, L., Ghirlanda, G., Maraschi, L., Celotti, A.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 402, 497 (2010)
Ghisellini, G., Tavecchio, F., Foschini, L., Ghirlanda, G.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 414, 2674 (2011). (G11)
Ghisellini, G., Tavecchio, F., Maraschi, L., Celotti, A., Sbarrato, T.: Nature 515, 376 (2014)
Ghosh, P., Abramowicz, M.A.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 292, 887 (1997)
Goodrich, R.W.: Astrophys. J. 342, 224 (1989)
Heinz, S., Sunyaev, R.A.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 343, L59 (2003)
Kellermann, K.I., Sramek, R., Schmidt, M., Shaffer, D.B., Green, R.: Astron. J. 98, 1195 (1989)
Laor, A.: Astrophys. J. 543, L111 (2000)
Lister, M.L.: Proc. Sci. (2018). arXiv:1805.05258v1
Liu, Y., Jiang, D.R., Gu, M.F.: Astrophys. J. 637, 669 (2006). (L06)
McHardy, I.M., Koerding, E., Knigge, C., Uttley, P., Fender, R.P.: Nature 444, 730 (2006)
Moderski, R., Sikora, M.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 283, 854 (1996)
Netzer, H.: Active Galactic Nuclei p. 57. Springer, Berlin (1990)
Osterbrock, D.E., Pogge, R.W.: Astrophys. J. 297, 166 (1985)
Paliya, V.S., Stalin, C.S., Shukla, A., Sahayanathan, S.: Astrophys. J. 768, 52 (2013)
Rawlings, S., Saunders, R.: Nature 349, 138 (1991)
Sbarrato, T., Ghisellini, G., Maraschi, L., Colpi, M.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 421, 1764 (2012). (Sb12)
Shaw, M.S., et al.: Astrophys. J. 748, 49 (2012). (Sh12)
Shen, Y., et al.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 194, 45 (2011). (S11)
Smith, M.G., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 195, 437 (1981)
Sun, X.N., Zhang, J., Lu, Y., Liang, E.W., Zhang, S.N.: J. Astrophys. Astron. (2014). arXiv:1302.5500
Sun, X.N., Zhang, J., Lin, D.B., Xue, Z.W., Liang, E.W., Zhang, S.N.: Astrophys. J. 798, 43 (2015)
Tremaine, S., et al.: Astrophys. J. 574, 740 (2002)
Urry, C.M., Padovani, P.: Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 107, 803 (1995)
Venters, T.M., Pavlidou, V., Reyes, L.C.: Astrophys. J. 703, 1939 (2009)
Wang, J.M., Luo, B., Ho, L.C.: Astrophys. J. 615, L9 (2004). (W04)
Woo, J.H., Urry, C.M.: Astrophys. J. 579, 530 (2002). (W02)
Yuan, W., Zhou, H.Y., Komossa, S., et al.: Astrophys. J. 685, 801 (2008)
Zhang, S.N.: Astrophys. J. 798, 43 (2015)
Zhang, J., Sun, X.N., Zhang, S.N., Liang, E.W.: In: Zhang, C.M., Belloni, T., Mendiz, M., Zhang, S.N. (eds.) Feeding Compact Objects: Accretion on all Scales. IAU Symp., vol. 290, p. 359. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2013)
Zhou, M., Cao, X.: Res. Astron. Astrophys. 9, 293 (2009). (Z09)
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the referee for the very helpful report. This work was support from the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFA0404502), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC grants 11733002 and 11773013), the Excellent Youth Foundation of the Jiangsu Scientific Committee (BK20150014), and National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFA0402704). This research has made use of the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED), that is operated by Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Gu, Q. The black hole mass, jet power and accretion in blazars and flat-spectrum radio-loud narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies. Astrophys Space Sci 364, 123 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-019-3617-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-019-3617-x