Abstract
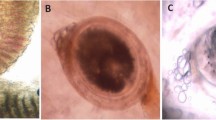
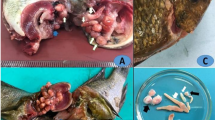
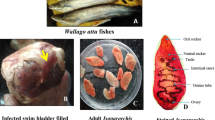
The aim of this study is to assess the toxicity of some heavy metals and parasitic infection in fishes as well as the immunological status of these fishes infected with different parasites. Between January 2018 and January 2019, 360 Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) near four farms and in the Nile River in Giza were examined for external and internal parasites. In addition, samples were expressed for two genes using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Samples were also taken from muscles and water for toxicological analysis of different heavy metals. In the skin, the mean TNF-α levels in the monogenea and mixed protozoan parasites (Trichodina and Myxobolus spp.) were 18.00 ± 0.67 and 13.65 ± 0.54, respectively. In the gills, the mean TNF-α of monogenea, Centrocestus formosanus, and encysted metacercaria (EMC) with monogenea group means was 20.45 ± 0.74, 23.00 ± 0.74, and 25.78 ± 0.74, respectively. In muscles with EMC, the mean TNF-α level was 14.67 ± 0.70. In livers with EMC, the mean TNF-α level was 26.78 ± 0.70. In the skin, the mean IL-1β level in monogenea and protozoan parasites (Trichodina and Myxobolus spp.) was significantly different (25.00 ± 0.69 and 15.00 ± 0.43, respectively). In the gills, the mean IL-1β level of the monogenean group was 21.00 ± 0.79, whereas C. formosanus showed the significantly highest value (27.00 ± 0.74). The mean IL-1β level of EMC with the monogenea group was 24.00 ± 1.54. Results showed that the level of Zn, Pb, Cu, and Cd was the highest in tissues of fish than permissible limits (PLs). Histopathological examination of different examined tissues exhibited serious pathological alterations. Monogenetic trematodes were detected in the examined fish, and their presence was accompanied by hyperplasia and fusion of the secondary gill lamellae. EMC of digenetic trematodes was frequently observed in the gills and in the cartilage rod. In conclusion, the parasite infection can upregulate the immunological cytokines with different levels with different infections.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-elala NM, Younis NA, Abubakr HO et al (2018) Efficacy of dietary yeast cell wall supplementation on the nutrition and immune response of Nile tilapia. Egypt J Aquatic Res 44(4):333–341
Adeyemo AO, Agbede SA (2008) Histopathology of tilapia tissues harbouring Clinostomum tilapiae parasites. Afr J Biomed Res 11:115–118
Agoz HM, Abbas HH, Mahmoud HM (2005) Rice-fish-azolla integrated culture systems. J Egypt Acad Soc Environ Dev 6(2):65–85
Akbari M, Taghizadeh V, Heidarieh M, Hajimoradloo A (2017) The key role of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in vaccinated rainbow trout via irradiated Ichthyophthirius multifiliis trophont. Vet Arhiv 87(2):229–237
Ali MHH, Abdel-satar AM (2005) Studies of some heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and fish diets in some fish farms in El-Fayoum province, Egypt. Egypt J Aquatic Res, 1687–4285 31(2):261–273
Aly (2016) Comparison of heavy metals levels in muscles, liver, and gills of three fish species collected from agricultural drainage water AT El- Abbassa fish farm, Sharkia, Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Biol & Fish 20(3):103–112
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1985) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 16th Edition. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C., New York
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1995) Standard methods for the analysis of water and wastewater
APHA (American Public Health Association) (2005): Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed. American public health association, Washington, D.C
APHA, AWWA, WEF, Rice EW, Eaton AD, Clesceri LS (2005) American Public Health Association, American Water Work Association, Water Environment Federation. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn 800, I St. NW., Washington DC 20001–3710
Arguedas, C. Cesare Ortega S, Simón Imon Martínez C. &ÁngelAstroza C. (2017) Parasites of Nile tilapia larvae Oreochromis niloticus (Pisces: Cichlidae) in concrete ponds in Guanacaste, northern Costa Rica Donald. Cuadernos de Investigación UNED (ISSN: 1659–4266) Vol. 9(2): 313–319
Attia MM, El-Gameel SM, Ismael E (2020) Evaluation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α); gamma interferon (IFN-γ) genes and oxidative stress in sheep: immunological responses induced by Oestrus ovis (Diptera: Oestridae) infestation. J Parasit Dis 44:332–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-020-01220-w
Bancroft JD, Gamble M (2008) Theory and practice of histological techniques. Elsevier health sciences
Baruš V, Jrkovský J, Prokeš M (2007) Philometra ovata (Nematoda: Philometroidea): a potential sentinel species of heavy metal accumulation. Parasitol Res 100:929–933
Blazer VS, Gratzek JB (1985) Cartilage proliferation in response to metacercarial infections of fish gills. J Comp Pathol 95(2):273–280
Buchmann K, Sigh J, Nielsen CV, Dalgaard M (2001) Host responses against the fish parasitizing ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Vet Parasitol 100:105–116
Burger J, Gaines KF, Boring S, Stephens L, Snodgrass J, Dixon C, McMahon M, Shukla S, Shukla T, Gochfeld M (2002) Metal levels in fish from the Savannah River: potential hazards to fish and other receptors. Environ Res 89:85–97
Canli M, Ay Ö, Kalay M (1998) Levels of heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Cu, Cr and Ni) in tissue of Cyprinus Carpio, Barbus Capito and Chondrostoma Regium from the Seyhan River, Turkey. Tr J of Zoology 22:149–157
Cole DW, Cole R, Gaydos SJ, Gray J, Hyland G, Cole ML, Powell-Dunford N, Sawhney C, Au WW (2009) Aquaculture: environmental, toxicological, and health issues. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212:369–377
E O S Q C (Egyptian Organization for Standardization and Quality Control) (2005) The permissible limits for fish., 1–889
El-Sayed AE-S, El-Ayyat MS, Nasr E-S, Khater ZZK (2011) Assessment of heavy metals in water, sediment and fish tissues, from Sharkia province, Egypt Khater, Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. & Fish. 15(2):125–144 ISSN 1110–1131)
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2001) Parameters of water quality; Interpretation and Standards, EPA, Ireland. ISBN 1-84096-015-3
FAO/WHO, Expert Committee on Food Additives. (1999) Summary and conclusion, 53rd meeting, Rome, 1–10 June
Fujiki K, Shin DH, Nakao M, Yano T (2000) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of carp (Cyprinus carpio) interleukin-1 beta, high affinity immunoglobulin E Fc receptor gamma subunit and serum amyloid A. Fish Shellfish Immunol 10:229–242
Fujimoto RY, Neves M d S, Santos RFB, Cruz C, Diniz DG, Eiras JC (2014) Histopathological evaluation of seven Amazon species of freshwater ornamental armored catfish. Acta Sci 36:349
Golterman HL (1971): Methods for chemical analysis of freshwaters IBP handbook 3:1-166
Gonzalez SF, Buchmann K, Nielsen ME (2007) Real-time gene expression analysis in carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) skin: inflammatory responses caused by the ectoparasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 22:641–650
Haiyan W, Stuanes AO (2003) Heavy metal pollution in air-water-soil-plant system of Zhuzhou City, Hunan Province, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 147:79–107
Heinecke RD, Buchmann K (2013) Inflammatory response of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792) larvae against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 34:521–528
Hodgson E (2011) A textbook of modern toxicology. http://scihub.tw/https://books.google.com.eg/books?isbn=1118211294
Hossain MK, Hossain MD, Rahman MH (2007) Histopathology of some diseased fishes. J Life Earth Sci 2:47–50
Jiang S, Zhang D, Li J, Liu Z (2008) Molecular characterization, recombinant expression and bioactivity analysis of the interleukin-1 beta from the yellowfin sea bream, Acanthopagrus latus (Houttuyn). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 24:323–336
Kantham KPL, Richards RH (1995) Effect of buffers on the gill structure of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L., and rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. J Fish Dis 18:411–423
Linnik PM, Zubenko IB (2000) Role of bottom sediments in the secondary pollution of aquatic environments by heavy-metal compounds. Lakes and Reservoirs: Res and Man 5:11–21
Mahmoud MA, Mansour HA, Abdelsalam M, AbuBakr HO, Aljuaydi SH, Afify M (2019a) Evaluation of electrofishing adopted by Egyptian fish farmers. Aquaculture 498:380–387
Mahmoud MA, Abd El-Rahim AH, Mahrous KF, Abdelsalam M, Abu-Aita NA, Afify M (2019b) The impact of several hydraulic fracking chemicals on Nile tilapia and evaluation of the protective effects of Spirulina platensis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(19):19453–19467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05246-3
Mood SM, Ebrahimzadeh Mousavi HA, Mokhayer B, Ahmadi M, Soltani M, Sharifpour I (2010) Centrocestus formosanus metacercarial infection of four ornamental fish species imported into Iran. Bull Eur Ass Fish Pathol 30(30):146–149
Nachev M, Schertzinger G, Sures B (2013) Comparison of the metal accumulation capacity between the acanthocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis and larval nematodes of the genus Eustrongylides sp. infecting barbel (Barbus barbus)., Parasites & Vectors 2013, 6:21, http://www.parasitesandvectors.com/content/6/1/21
Palíková M, Baruš V (2003) Mercury content in Aguillicola crassus (Nematoda) and its host Anguilla anguilla. Acta Vet Brno 72:289–294
Paperna I (1996) Parasites, infections and diseases of fishes in Africa. An update. CIFA Tech. Pap. No. 31. 220 p. FAO, Rome
Paruruckumani PS, Maharajan A, Ganapiriya V, Narayanaswamy Y, Raja Jeyasekar R (2015) Surface ultrastructural changes in the gill and liver tissue of Asian sea bass Lates calcarifer (Bloch) exposed to copper. Biol Trace Elem Res 168:500–507
Picard-Sanchez A, Estensoro I, del Pozo R, Piazzon MC, Palenzuela O, Sitja-Bobadilla A (2019) Acquired protective immune response in a fish-myxozoan model encompasses specific antibodies and inflammation resolution. Fish Shellfish Immunol 90:349–362
Praveen K, Evans DL, Jaso-Friedmann L (2006) Constitutive expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in cytotoxic cells of teleosts and its role in regulation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Mol Immunol 43(3):279–291
Ramelow GJ, Webre CL, Mueller CL, Beck JN, Young JC, Langley MP (1989) Variations of heavy metals and arsenic in fish and other organisms from the Calcasien River and Lake, Louisiana. Archive of Environ Contam and Toxicol 18:804–818
Roberts RJ, Rodger HD (2012) The pathophysiology and systematic pathology of teleosts. Fish Pathol:62–143
Saha M, Bandyopadhyay PK (2017) Parasitological and histological analysis of a new species of the genus Thalohanellus and description of a myxozoan parasite (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) from cultured ornamental goldfish, Carassius auratus L. Aquacult Rep 8:8–15
Santos MA, Jerônimo GT, Cardoso L, Tancredo KR, Medeiros PB, Ferrarezi JV, Gonçalves ELT, da Costa Assis G, Martins ML (2017) Parasitic fauna and histopathology of farmed freshwater ornamental fish in Brazil. Aquaculture 470:103–109
Shareef PA, Abidi SMA (2012) Incidence and histopathology of encysted progenetic metacercaria of Clinostomum complanatum (Digenea: Clinostomidae) in Channa punctatus and its development in experimental host. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2(6):421–426
Shinn AP, Hansen H, Bachmann OK, Bakke L, T.A (2004) The use of morphometric characters to discriminate specimens of laboratory-reared and wild populations of Gyrodactylus salaris and G. thymalli (Monogenea). Folia Parasitol 51:239–252
Simon Jones RM (2001) The occurrence and mechanisms of innate immunity against parasites in fish. Dev Comp Immunol 25:841–852
SMWW (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 20th edition
Sures B (2008a ) Environmental parasitology. Interactions between parasites and pollutants in the aquatic environment. Parasite 15, 434–438) numerical or physiological responses to pollutants can be positive, negative, or absent depending on the species, [ref:
Sures B (2008b) Host parasite interactions in polluted environments. J Fish Biol 73:1–10
Sures B, Taraschewski H, Jackwerth E (1994) Lead content of Paratenuisentis ambiguus (Acanthocephala), Anguillicola crassus (Nematodes) and their host Anguilla anguilla. Dis Aquat Organ 19:105–107
Suziki KT, Sunaga H, Aoki Y, Hatakeyama S, Sumi Y, Suziki T (1988) Binding of cadmium and copper in the mayfly Baetis thermicus larvae that inhabit in a river polluted with heavy metals. Comp Biochem Physiol 91(C):487–492
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. EXS. 101:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Tenora F, Baruš V, Kráčmar S, Dvořáček J, Srnková J (1999) Parallel analysis of some heavy metals concentrations in the Anguillicola crassus (Nematoda) and the European eel Anguilla anguilla (Osteichthyes). Helminthologia 36:79–81
Tenora F, Baruš V, Kráčmar S, Dvořáček J (2000) Concentration of some heavy metals in Ligula intestinalis plerocercoids (Cestoda) and Philometra ovate (Nematoda) compared to some their hosts (Osteichthyes). Helminthologia 37:15–18
Vinobaba P (1994) Some aspects of the biology of Dactylogyrus vastator Nybelin, 1924, (Monogenea) a gill parasite of Cyprinus carpio L. PhD Thesis. Institute of Aquaculture, University of Stirling, Stirling, U.K. pp. 1–46
Wang Q, Yu Y, Xiaoting, Zhen X (2019) Immune responses of fish to Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Ich): a model for understanding immunity against protozoan parasites. Dev Comp Immunol 93:93–102
WHO (1993) Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminates (Forty-first report of joint FAO/WHO export committee on food Additives). WHO Technical Report Series NO. 837, WHO, Geneva
Zhou H, Cheung R, Chan K, Wong M (1998) Metal concentrations in sediments and tilapia collected from inland waters of Hong Kong. Water Res 32:3331–3340
Zhu L, Nie L, Zhu G, Xiang LX, Shao J-Z (2013) Advances in research of fish immune-relevant genes: a comparative overview of innate and adaptive immunity in teleosts. Dev Comp Immunol 39(2013):39–62
Zou J, Secombes CJ (2016) The function of fish cytokines. Biology 5:23. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5020023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors share in the aim of works. Nehal A. Younis: collect the samples and identify the clinical sign on the fish, Samah E. Laban: analyze the water quality and toxic substance in fish tissues, Asmaa K. Al-Mokaddem: examine the histopathological changes of the fish tissues, Marwa M. attia: examine the parasites inside the fishes and analyze the gene expression. All authors share in writing this manuscript and revise it.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Younis, N.A., Laban, S.E., Al-Mokaddem, A.K. et al. Immunological status and histopathological appraisal of farmed Oreochromis niloticus exposed to parasitic infections and heavy metal toxicity. Aquacult Int 28, 2247–2262 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00589-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00589-y