Abstract
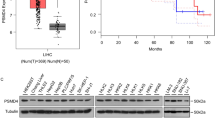
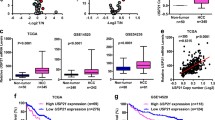
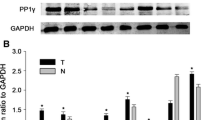
We have previously identified that PPPDE1 is a deubiquitinase (DUB) belonging to a cysteine isopeptidase family. Here we sought to explore the biological significance of PPPDE1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its underlying molecular mechanism. In the present study, we found that amplification and overexpression of PPPDE1 were associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We also demonstrated that knocking down of PPPDE1 could significantly block the clonal growth and tumorigenicity of human HCC cells, which revealed a critical role for PPPDE1 in HCC development. Furthermore, we proved that PPPDE1 is a key modulator of p53 protein level and its down stream apoptosis pathway. Taken together, these results suggested that PPPDE1 is a putative HCC driver gene and extensive studies should be conducted in the future to investigate the role of PPPDE1 in HCC and other tumors.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DUBs:
-
Deubiquitinating enzymes
- PPPDE:
-
After Permuted Papain fold Peptidases of DsRNA viruses and Eukaryotes
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA 65:87–108
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Farazi PA, DePinho RA (2006) Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer 6:674–687
Cheng W, Su Y, Xu F (2013) CHD1L: a novel oncogene. Mol Cancer 12:170
Liu L, Dai Y, Chen J et al (2014) Maelstrom promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition by way of Akt/GSK-3beta/Snail signaling. Hepatology 59:531–543
Wang K, Lim HY, Shi S et al (2013) Genomic landscape of copy number aberrations enables the identification of oncogenic drivers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 58:706–717
Xie X, Wang X, Jiang D et al (2017) PPPDE1 is a novel deubiquitinase belonging to a cysteine isopeptidase family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 488:291–296
Stegmeier F, Sowa ME, Nalepa G, Gygi SP, Harper JW, Elledge SJ (2007) The tumor suppressor CYLD regulates entry into mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8869–8874
Nakada S, Tai I, Panier S et al (2010) Non-canonical inhibition of DNA damage-dependent ubiquitination by OTUB1. Nature 466:941–946
Schwickart M, Huang X, Lill JR et al (2010) Deubiquitinase USP9X stabilizes MCL1 and promotes tumour cell survival. Nature 463:103–107
Singh N, Singh AB (2016) Deubiquitinases and cancer: a snapshot. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 103:22–26
Sippl W, Collura V, Colland F (2011) Ubiquitin-specific proteases as cancer drug targets. Future Oncol 7:619–632
Devine T, Dai MS (2013) Targeting the ubiquitin-mediated proteasome degradation of p53 for cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Des 19:3248–3262
Lim KH, Baek KH (2013) Deubiquitinating enzymes as therapeutic targets in cancer. Curr Pharm Des 19:4039–4052
Nanduri B, Suvarnapunya AE, Venkatesan M, Edelmann MJ (2013) Deubiquitinating enzymes as promising drug targets for infectious diseases. Curr Pharm Des 19:3234–3247
Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdottir H, Winckler W et al (2011) Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol 29:24–26
Campeau E, Ruhl VE, Rodier F et al (2009) A versatile viral system for expression and depletion of proteins in mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 4:e6529
Warner JR, McIntosh KB (2009) How common are extraribosomal functions of ribosomal proteins? Mol Cell 34:3–11
Zhang Y, Lu H (2009) Signaling to p53: ribosomal proteins find their way. Cancer Cell 16:369–377
Chen D, Zhang Z, Li M et al (2007) Ribosomal protein S7 as a novel modulator of p53-MDM2 interaction: binding to MDM2, stabilization of p53 protein, and activation of p53 function. Oncogene 26:5029–5037
Zhu Y, Poyurovsky MV, Li Y et al (2009) Ribosomal protein S7 is both a regulator and a substrate of MDM2. Mol Cell 35:316–326
Wu CT, Lin TY, Hsu HY, Sheu F, Ho CM, Chen EI (2011) Ling Zhi-8 mediates p53-dependent growth arrest of lung cancer cells proliferation via the ribosomal protein S7-MDM2-p53 pathway. Carcinogenesis 32:1890–1896
Zhang W, Tong D, Liu F et al (2016) RPS7 inhibits colorectal cancer growth via decreasing HIF-1alpha-mediated glycolysis. Oncotarget 7:5800–5814
Wang Z, Hou J, Lu L et al (2013) Small ribosomal protein subunit S7 suppresses ovarian tumorigenesis through regulation of the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. PLoS ONE 8:e79117
Levine AJ, Oren M (2009) The first 30 years of p53: growing ever more complex. Nat Rev Cancer 9:749–758
Fujimoto A, Furuta M, Totoki Y et al (2016) Whole-genome mutational landscape and characterization of noncoding and structural mutations in liver cancer. Nat Genet 48:500–509
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81201569, No. 81541151), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 7132186) and the National Key Sci-Tech Special Project of China (No. 2018ZX10302207, No. 2017ZX10203202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, X., Wang, X., Liao, W. et al. PPPDE1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development by negatively regulate p53 and apoptosis. Apoptosis 24, 135–144 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-018-1491-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-018-1491-6