Abstract
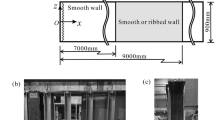
Direct numerical simulation (DNS) of turbulent channel flow over a two-dimensional irregular rough wall with uniform blowing (UB) was performed. The main objective is to investigate the drag reduction effectiveness of UB on a rough-wall turbulent boundary layer toward its practical application. The DNS was performed under a constant flow rate at the bulk Reynolds number values of 5600 and 14000, which correspond to the friction Reynolds numbers of about 180 and 400 in the smooth-wall case, respectively. Based upon the decomposition of drag into the friction and pressure contributions, the present flow is considered to belong to the transitionally-rough regime. Unlike recent experimental results, it turns out that the drag reduction effect of UB on the present two-dimensional rough wall is similar to that for a smooth wall. The friction drag is reduced similarly to the smooth-wall case by the displacement of the mean velocity profile. Besides, the pressure drag, which does not exist in the smooth-wall case, is also reduced; namely, UB makes the rough wall aerodynamically smoother. Examination of turbulence statistics suggests that the effects of roughness and UB are relatively independent to each other in the outer layer, which suggests that Stevenson’s formula can be modified so as to account for the roughness effect by simply adding the roughness function term.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wood, R.M.: Impact of advanced aerodynamic technology on transportation energy consumption. SAE Paper 2004-01-1306 (2004)
Kornilov, V.I.: Current state and prospects of researches on the control of turbulent boundary layer by air blowing. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 76, 1–23 (2015)
Moin, P., Bewley, T.: Feedback control of turbulence Appl. Mech. Rev. 47, S3–S13 (2001)
Gad-el-Hak, M.: Flow control: The future. J. Aircraft 38, 402–421 (2001)
Walsh, M.J.: Riblets as a viscous drag reduction technique. AIAA J. 21, 485–486 (1983)
Dean, B., Bhushan, B.: Shark-skin surfaces for fluid-drag reduction in turbulent flow: a review. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 368, 4775–4806 (2010)
Rothstein, J.P.: Slip on superhydrophobic surfaces. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 42, 89–109 (2010)
Kim, J.: Control of turbulent boundary layers. Phys. Fluids 15, 1093–1105 (2003)
Kasagi, N., Suzuki, Y., Fukagata, K.: Microelectromechanical system-based feedback control of turbulence for skin friction reduction. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 41, 231–251 (2009)
Choi, H., Moin, P., Kim, J.: Active turbulence control for drag reduction in wall-bounded flows. J. Fluid Mech. 262, 75–110 (1994)
Jung, W.J., Mangiavacchi, N., Akhavan, R.: Suppression of turbulence in wall-bounded flows by high-frequency spanwise oscillations. Phys. Fluids A 4, 1605–1607 (1992)
Baron, A., Quadrio, M.: Turbulent drag reduction by spanwise wall oscillations. Appl. Sci. Res. 55, 311–326 (1996)
Quadrio, M., Ricco, P.: Critical assessment of turbulent drag reduction through spanwise wall oscillations. J. Fluid Mech. 521, 251–271 (2004)
Quadrio, M., Ricco, P., Viotti, C.: Streamwise-travelling waves of spanwise wall velocity for turbulent drag reduction. J. Fluid Mech. 627, 161–178 (2009)
Quadrio, M.: Drag reduction in turbulent boundary layers by in-plane wall motion. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 369, 1428–1442 (2011)
Min, T., Kang, S.M., Speyer, J.L., Kim, J.: Sustained sub-laminar drag in a fully developed channel flow. J. Fluid Mech. 558, 309–318 (2006)
Nakanishi, R., Mamori, H., Fukagata, K.: Relaminarization of turbulent channel flow using traveling wave-like wall deformation. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 35, 152–159 (2012)
Mamori, H., Iwamoto, K., Murata, A.: Effect of the parameters of traveling waves created by blowing and suction on the relaminarization phenomena in fully developed turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 26, 015101 (2014)
Bewley, T.R.: A fundamental limit on the balance of power in a transpiration-controlled channel flow. J. Fluid Mech 632, 443–446 (2009)
Fukagata, K., Sugiyama, K., Kasagi, N.: On the lower bound of net driving power in controlled duct flows. Phys. D 238, 1082–1086 (2009)
Prandtl, L.: Über Flüssigkeitsbewegung Bei Sehr Kleiner Reibung. In: Verhandlungen Des III Internationalen Mathematiker-Kongresses, Heidelberg, pp 484–491 (1904)
Mickley, H.S., Ross, R.C., Squyers, A.L., Stewart, W.E.: Heat, mass, and momentum transfer for flow over a flat plate with blowing or suction. NACA Technical Note 3208 (1957)
Mickley, H.S., Davis, R.S.: Momentum transfer for flow over a flat plate with blowing. NACA Technical Note 4017 (1957)
Jeromin, L.O.F.: The status of research in turbulent boundary layers with fluid injection. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 10, 65–189 (1970)
Moin, P.: Numerical Simulation of Wall-Bounded Turbulent Shear Flows. In: Krause, E. (ed.) Eighth International Conference on Numerical Methods in Fluid Dynamics. Lecture Notes in Physics, vol. 170, pp 55–76. Springer, Berlin (1982)
Sumitani, Y., Kasagi, N.: Direct numerical simulation of turbulent transport with uniform wall injection and suction. AIAA J. 32, 1220–1228 (1995)
Fukagata, K., Iwamoto, K., Kasagi, N.: Contribution of Reynolds stress distribution to the skin friction in wall-bounded flows. Phys. Fluids 14, L73–L76 (2002)
Kametani, Y., Fukagata, K.: Direct numerical simulation of spatially developing turbulent boundary layers with uniform blowing or suction. J. Fluid Mech. 681, 154–172 (2011)
Kametani, Y., Fukagata, K., Örlü, R., Schlatter, P.: Effect of uniform blowing/suction in a turbulent boundary layer at moderate Reynolds number. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 55, 132–142 (2015)
Kametani, Y., Fukagata, K., Örlü, R., Schlatter, P.: Drag reduction in spatially developing turbulent boundary layers by spatially intermittent blowing at constant mass-flux. J. Turbul. 17, 913–929 (2016)
Liu, P.Q., Duan, H.S., He, Y.W.: Numerical study of suction-blowing flow control technology for an airfoil. J. Aircraft 47, 229–239 (2010)
Noguchi, D., Fukagata, K., Tokugawa, N.: Friction drag reduction of a spatially developing boundary layer using a combined uniform suction and blowing. J. Fluid Sci. Technol. 11, JFST0004 (2016)
Schetz, J.A., Nerney, B.: Turbulent boundary layer with injection and surface roughness. AIAA J. 15, 1288–1294 (1977)
Voisinet, R.L.P.: Influence of roughness and blowing on compressible turbulent boundary layer flow. Final Report, Naval Surface Weapons Center, Silver Spring, MD, NSWC TR 79–153 (1979)
Miller, M.A., Martin, A., Bailey, S.C.C.: Investigation of the scaling of roughness and blowing effects on turbulent channel flow. Exp. Fluids 55, 1675 (2014)
Schultz, M.P., Flack, K.A.: Turbulent boundary layers on a systematically varied rough wall. Phys. Fluids 21, 015104 (2009)
Clauser, F.H.: Turbulent boundary layer. Adv. Appl. Mech. 4, 1–51 (1956)
Perry, A.E., Li, J.D.: Experimental support for the attached-eddy hypothesis in zero-pressure gradient turbulent boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 218, 405–438 (1990)
Stevenson, T.N.: A law of the wall for turbulent boundary layers with suction and injection. CoA Report Aero No. 166 The College of Aeronautics Cranfield (1963)
Raupach, M.R., Antonia, R.A., Rajagopalan, S.: Rough-wall turbulent boundary layers. Appl. Mech. Rev. 44, 1–25 (1991)
Jiménez, J.: Turbulent flows over rough walls. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 36, 173–196 (2004)
Cardillo, J., Chen, Y., Araya, G., Newman, J., Jansen, K., Castillo, L.: DNS Of a turbulent boundary with surface roughness. J. Fluid Mech. 729, 603–637 (2013)
Napoli, E., Armenio, V., De Marchis, M: The effect of the slope of irregularly distributed roughness elements on turbulent wall-bounded flows. J. Fluid Mech. 613, 385–394 (2008)
Milici, B., De Marchis, M., Sardina, G., Napoli, E.: Effects of roughness on particle dynamics in turbulent channel flows: a DNS analysis. J. Fluid Mech. 739, 465–478 (2014)
Kang, S., Choi, H.: Active wall motions for skin-friction drag reduction. Phys. Fluids 12, 3301–3304 (2000)
Kajishima, T: Finite-difference method for convective terms using non-uniform grid. Trans. JSME/B 65, 1607–1612 (1999). (in Japanese)
Spalart, P.R., Moser, R.D., Rogers, M.M.: Spectral methods for the Navier-Stokes equations with one infinite and two periodic directions. J. Comput. Phys. 96, 297–324 (1991)
Amsden, A.A., Harlow, F.H.: A simplified MAC technique for incompressible fluid flow calculations. J. Comput. Phys. 6, 322–325 (1970)
Quadrio, M., Frohnapfel, B., Hasegawa, Y.: Does the choice of the forcing term affect flow statistics in DNS of turbulent channel flow. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 55, 286–293 (2016)
De Marchis, M., Napoli, E., Armenio, V.: Turbulence structures over irregular rough surfaces. J. Turbul. 11, N3 (2010)
Moser, R.D., Kim, J., Mansour, N.N.: Direct numerical simulation of turbulent channel flow up to Re, τ = 590. Phys. Fluids 11, 943–945 (1999)
Flack, K., Schultz, M.P.: Review of hydraulic roughness scales in the fully rough regime. J. Fluids Eng. 132, 041203 (2010)
Raupach, M.R., Shaw, R.H.: Averaging procedures for flow within vegetation canopies. Bound.-Layer Meteor. 22, 79–90 (1982)
Bhaganagar, K., Leighton, R.: Three-level decomposition for the analysis of turbulent flow over rough-wall. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 6, 257–265 (2013)
Durbin, P.A., Medic, G., Seo, J.-M., Eaton, J.K., Song, S.: Rough wall modification of two-layer k − 𝜖. J. Fluids Eng. 123, 16–21 (2001)
Flack, K., Schultz, M.P., Rose, W.B.: The onset of roughness effects in the transitionally rough regime. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 35, 160–167 (2012)
Krogstad, P.-Å., Anderson, H.I., Bakken, O.M., Ashrafian, A.: An experimental and numerical study of channel flow with rough walls. J. Fluid Mech. 530, 327–352 (2005)
White, F.M.: Fluid Mechanics, 8th Edition in SI Units, p 327. McGraw-Hill, New York (2016)
Avsarkisov, V., Oberlack, M., Hoyas, S.: New scaling laws for turbulent Poiseuille flow with wall transpiration. J. Fluid Mech. 746, 99–122 (2014)
Townsend, A.A.: The Structure of Turbulent Shear Flows, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1976)
Bhaganagar, K., Kim, J., Coleman, G.: Effect of roughness on wall-bounded turbulence. flow Turbul Combust. 72, 463–492 (2004)
Flack, K.A., Schultz, M.P.: Roughness effects on wall-bounded turbulent flows. Phys. Fluids 26, 101305 (2016)
Vigdorovich, I.: A law of the wall for turbulent boundary layers with suction: Stevenson’s formula revisited. Phys. Fluids 28, 085102 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Drs. Shinnosuke Obi and Keita Ando (Keio University) for fruitful discussion and Messrs. Yuta Ikeya and Ken Kawai (Keio University) for assistance in language improvement. This work was done in the framework of Student Exchange Agreement between Politecnico di Milano and Keio University. The was partly supported through JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP25420129.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, E., Quadrio, M. & Fukagata, K. Turbulent Drag Reduction by Uniform Blowing Over a Two-dimensional Roughness. Flow Turbulence Combust 99, 765–785 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-017-9858-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-017-9858-2