Abstract
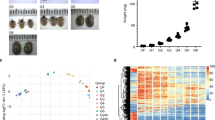
The cattle tick, Rhipicephalus microplus, is a serious pest of cattle, with significant economic consequences to the livestock industries of tropical and semitropical countries. Rhipicephalus microplus belongs to the Metastriata group of the Ixodidae family known as hard ticks. When adult hard ticks feed, mating has not yet occurred and an initial host attachment phase of 1–2 days is followed by a slow feeding phase that can last several days. Once mating occurs, feeding concludes with a rapid engorgement phase that is completed in 12–36 h. Our group’s interest in mining the genome and transcriptome of R. microplus for novel targets for development of tick control technologies led us to investigate the early transcriptional events occurring upon tick attachment and subsequent feeding. We placed newly molted unfed adult R. microplus females upon a bovine host and harvested the attached ticks after 3, 6, 12, and 24 h. We also placed a group of these ticks in a gas-permeable tube taped onto the side of the bovine host. These ticks were able to sense the host but unable to penetrate the tube to begin attachment and were ultimately harvested after 3 h. This study produced a comprehensive transcriptome from newly molted adult ticks and will provide a useful resource for studies of tick feeding and host perception and also assist genome annotation refinements.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljamali MN, Ramakrishnan VG, Weng H, Tucker JS, Sauer JR, Essenberg RC (2009) Microarray analysis of gene expression changes in feeding female and male lone star ticks, Amblyomma americanum (L). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 71:236–253
Andersen CL, Ledet-Jensen J, Ørntoft T (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data: a model based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization - applied to bladder- and colon-cancer data-sets. Cancer Res 64:5245–5250
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B 57:289–300
Bock R, Jackson L, de Vos A, Jorgensen W (2004) Babesiosis of cattle. Parasitology 129(Suppl):247–269
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Bushmanova E, Antipov D, Lapidus A, Suvorov V, Prjibelski AD (2016) rnaQUAST: a quality assessment tool for de novo transcriptome assemblies. Bioinformatics 32:2210–2212
Canales M, Enriquez A, Ramos E, Cabrera D, Dandie H, Soto A, Falcon V, Rodriguez M, de la Fuente J (1997) Large-scale production in Pichia pastoris of the recombinant vaccine Gavac against cattle tick. Vaccine 15:414–422
Canales M, Almazan C, Naranjo V, Jongejan F, de la Fuente J (2009) Vaccination with recombinant Boophilus annulatus Bm86 ortholog protein, Ba86, protects cattle against B. annulatus and B. microplus infestations. BMC Biotechnol 9:29
Conesa A, Götz S (2008) Blast2GO: a comprehensive suite for functional analysis in Plant Genomics. Int J Plant Genomics 2008:619832
Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Talón M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21:3674–3676
Davey RB, Garza J Jr, Thompson GD (1980) Ovipositional biology of the cattle tick, Boophilus annulatus (Acari: Ixodidae), in the laboratory. J Med Entomol 17:287–289
Goff SA, Vaughn M, McKay S, Lyons E, Stapleton AE, Gessler D, Matasci N, Wang L, Hanlon M, Lenards A, Muir A, Merhcant N, Lowry S, Mock S, Helmke M, Kubach A, Narro M, Hopkins N, Micklos D, Hilgert U, Gonzales M, Jordan C, Skidmore E, Dooley R, Cazes J, McLay R, Lu Z, Pasternak S, Koesterke L, Piel WH, Grene R, Noutsos C, Gendler K, Feng X, Tang C, Lent M, Kim SJ, Kvilekval K, Manjunath BS, Tannen V, Stamatakis A, Sanderson M, Welch SM, Cranston KA, Soltis P, Soltis D, O’Meara B, Ane C, Brunell T, Kleibenstain DJ, White JW, Leebens-Mack J, Donoghue MJ, Splading EP, Vision TJ, Myers CR, Lowenthal D, Enquist BJ, Boyle B, Akoglu A, Andrews G, Ram S, Ware D, Stein L, Stanzione D (2011) The iPlant collaborative: cyberinfrastructure for plant biology. Front Plant Sci 2:34
Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Williams TD, Nagaraji SH, Nueda MJ, Robles M, Talón M, Dopazo J, Conesa A (2008) High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res 36:3420–3435
Götz S, Arnold R, Sebastián-León P, Martín-Rodríguez S, Tischler P, Jehl MA, Dopazo J, Rattei T, Conesa A (2011) B2G-FAR, a species-centered GO annotation repository. Bioinformatics 27:919–924
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, Gnirke A, Rhind N, di Palma F, Birren BW, Nusbaum C, Lindblad-Toh K, Friedman N, Regev A (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652
Guerrero FD, Lovis L, Martins JR (2012) Acaricide resistance mechanisms in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet Jaboticabal 21:1–6
Guerrero FD, Andreotti R, Bendele KG, Cunha RC, Miller RJ, Yeater K, Pérez de Léon AA (2014) Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus aquaporin as an effective vaccine antigen to protect against cattle tick infestations. Parasite Vectors 7:475
Haas BJ, Papanicolaou A, Yassour M, Grabherr M, Blood PD, Bowden J, Couger MB, Eccles D, Li B, Lieber M, Macmanes MD, Ott M, Orvis J, Pochet N, Strozzi F, Weeks N, Westerman R, William T, Dewey CN, Henschel R, Leduc RD, Friedman N, Regev A (2013) De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat Protoc 8:1494–1512
Heekin AM, Guerrero FD, Bendele KG, Saldivar L, Scoles GA, Dowd SE, Gondro C, Nene V, Djikeng A, Brayton KA (2013) Gut transcriptome of replete adult female cattle ticks, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, feeding upon a Babesia bovis-infected bovine host. Parasitol Res 112:3075–3090
Kopylova E, Noé L, Touzet H (2012) SortMeRNA: fast and accurate filtering of ribosomal RNAs in metatranscriptomic data. Bioinformatics 18:3211–3217
Merchant N, Lyons E, Goff S, Vaughn M, Ware D, Micklos D, Antin P (2016) The iPlant collaborative: cyberinfrastructure for enabling data to discovery for the life sciences. PLoS Biol 14:e1002342
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by rna-seq. Nat Methods 5:621–628
Mulenga A, Blandon M, Khumthong R (2007) The molecular basis of the Amblyomma americanum tick attachment phase. Exp Appl Acarol 41:267–287
Nolan T, Hands RE, Bustin SA (2006) Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat Protoc 1:1559–1582
Perner J, Provazník J, Schrenková J, Urbanová V, Ribeiro JMC, Kopáček P (2016) RNA-seq analyses of the midgut from blood- and serum-fed Ixodes ricinus ticks. Sci Rep 6:36695
Popara M, Villar M, Mateos-Hernández L, Fernández de Mera IG, Marina A, del Valle M, Almazán C, Domingos A, de la Fuente J (2013) Lesser protein degradation machinery correlates with higher BM86 tick vaccine efficacy in Rhipicephalus annulatus when compared to Rhipicephalus microplus. Vaccine 31:4728–4735
Robinson MD, Smyth GK (2008) Small-sample estimation of negative binomial dispersion, with applications to sage data. Biostatistics 9:321–332
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2010) edger: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26:139–140
Rudenko N, Golovchenko M, Edwards MJ, Grubhoffer L (2005) Differential expression of Ixodes ricinus tick genes induced by blood feeding or Borrelia burgdorferi infection. J Med Entomol 42:36–41
Schurch NJ, Schofield P, Gierlinski M, Cole C, Sherstnev A, Singh V, Wrobel N, Gharbi K, Simpson GG, Owen-Hughes T, Blaxter M, Barton GJ (2016) How many biological replicates are needed in an RNA-seq experiment and which differential expression tool should you use? RNA 22:839–851
Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM (2015) BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 31:3210–3212
Sonenshine DE, Anderson JM (2014) Mouthparts and digestive systems: anatomy and molecular biology of feeding and digestion. In: Sonenshine DE, Roe RM (eds) Biology of ticks, vol. 1, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 122–162
Stutzer C, van Zyl WA, Olivier NA, Richards S, Maritz-Olivier C (2013) Gene expression profiling of adult female tissues in feeding Rhipicephalus microplus cattle ticks. Int J Parasitol 43:541–554
Wang Y, Coleman-Derr D, Chen G, Gu YQ (2015) OrthoVenn: a web server for genome wide comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res 43:W78–W84
Willadsen P, Bird P, Cobon GS, Hungerford J (1995) Commercialisation of a recombinant vaccine against Boophilus microplus. Parasitology 110:S43–S50
Xie Y, Wu G, Tang J, Luo R, Patterson J, Liu S, Huang W, He G, Gu S, Li S, Zhou X, Lam T, Li Y, Xu X, Wong GK, Wang J (2014) SOAPdenovo-Trans: de novo transcriptome assembly with short RNA-Seq reads. Bioinformatics 30:1660–1666
Xu X-L, Cheng T-Y, Yang H, Liao Z-H (2016) De novo assembly and analysis of midgut transcriptome of Haemaphysalis flava and identification of genes involved in blood digestion, feeding and defending from pathogens. Inf Genet Evol 38:62–72
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the late Ernie Retzel, National Center for Genome Resources for his inspiration and guidance at the inception of this research. This research has been supported through funding (FDG) from the U. S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service (USDAARS) Project Nos. 6205-32000-031-00D and 3094-32000-036-00D. USDA is an equal opportunity employer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FDG conceived the study, participated in the cattle exposure experiments, conducted the RNA isolations, and drafted the manuscript. KGB participated in the cattle exposure experiments and led the bioinformatics for the gene expression analysis. CC led the transcriptome sequencing and the assembly of the Illumina reads. DMB conducted the RT-PCR experiments. RJM led the cattle exposure experiments. All coauthors participated in revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with ethical standards of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee for the Knipling-Bushland U. S. Livestock Insects Research Laboratory and Cattle Fever Tick Research Laboratory.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10493_2019_420_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 1 (DOCX 15459 kb) Supplementary File S1: Unigene fasta DNA sequences assembled from the R. microplus Unfed sequence reads
10493_2019_420_MOESM2_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 2 (DOCX 12504 kb) Supplementary File S2: Unigene fasta DNA sequences assembled from the R. microplus 3 Hr Fed sequence read
10493_2019_420_MOESM3_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 3 (DOCX 15454 kb) Supplementary File S3: Unigene fasta DNA sequences assembled from the R. microplus 3 Hr Frustrated sequence reads
10493_2019_420_MOESM4_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 4 (DOCX 25895 kb) Supplementary File S4: Unigene fasta DNA sequences assembled from the R. microplus Adult Female Pooled sequence reads
10493_2019_420_MOESM5_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 5 (XLSX 45 kb) Supplementary Table S1: Transcriptome assembly optimization results. CLC, Trinity, and Soapdenovo assemblers were utilized with varying kmer and bubble sizes to obtain optimal assemblies of the Unfed, 3 Hr Fed, 3 Hr Frustrated, and Adult Female Pooled transcriptomes. BUSCO analysis was also included in the ultimate determination of optimal assembly for submission to NCBI
10493_2019_420_MOESM6_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 6 (XLSX 8729 kb) Supplementary Table S2: Annotation associated with transcripts from the UnFed transcriptome. Blast2GO PRO version 5.1.13 was used to perform BlastX against the UniProt/SwissProt database with an e-value of 1.0E-10 and default blast parameters. BlastX, InterProScan, GO mapping, enzyme code assignment and KEGG analysis results are tabulated
10493_2019_420_MOESM7_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 7 (XLSX 8342 kb) Supplementary Table S3: Annotation associated with transcripts from the 3 Hr Fed transcriptome. Blast2GO PRO version 5.1.13 was used to perform BlastX against the UniProt/SwissProt database with an e-value of 1.0E-10 and default blast parameters. BlastX, InterProScan, GO mapping, enzyme code assignment and KEGG analysis results are tabulated
10493_2019_420_MOESM8_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 8 (XLSX 9300 kb) Supplementary Table S4: Annotation associated with transcripts from the 3 Hr Frustrated transcriptome. Blast2GO PRO version 5.1.13 was used to perform BlastX against the UniProt/SwissProt database with an e-value of 1.0E-10 and default blast parameters. BlastX, InterProScan, GO mapping, enzyme code assignment and KEGG analysis results are tabulated
10493_2019_420_MOESM9_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 9 (XLSX 11202 kb) Supplementary Table S5: Annotation associated with transcripts from the Adult Female Pooled transcriptome. Blast2GO PRO version 5.1.13 was used to perform BlastX against the UniProt/SwissProt database with an e-value of 1.0E-10 and default blast parameters. BlastX, InterProScan, GO mapping, enzyme code assignment and KEGG analysis results are tabulated
10493_2019_420_MOESM10_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 10 (XLSX 53 kb) Supplementary Table S6: Listing and rankings of the top 100 BP, CC, and MF GO terms for the Unfed, 3 Hr Fed, 3 Hr Frustrated, and Adult Female Pooled transcriptomes. Terms are also shown in relation to their ranking in the Adult Female Pooled transcriptome
10493_2019_420_MOESM11_ESM.xlsx
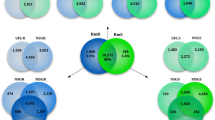
Supplementary material 11 (XLSX 480 kb) Supplementary Table S7: : OrthoVenn analysis cluster lists of translated transcripts for Unfed, 3 Hr Fed and 3 Hr Frustrated. The table includes a separate tab for each set of cluster lists found during OrthoVenn analysis of Unfed, 3 Hr Fed and 3 Hr Frustrated translated contigs from assembled transcriptomes. Each row is a protein cluster determined by the OrthoVenn program
10493_2019_420_MOESM12_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 12 (XLSX 7746 kb) Supplementary Table S8: Differential gene expression analysis data for Unfed vs. 3 Hr Fed. Using the EdgeR package 3.4.0-based algorithm of the CLC Genomics Workbench 8.0.1, we mapped reads to the Adult Female Pooled transcriptome and show expression data for each transcript. The table includes read counts from each transcriptome replicate and data generated from the EDGE test of Unfed vs. 3 Hr Fed, including fold-change, and p-values
10493_2019_420_MOESM13_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 13 (XLSX 9535 kb) Supplementary Table S9: Differential gene expression analysis data for Unfed vs. 3 Hr Frustrated. Using the EdgeR package 3.4.0-based algorithm of the CLC Genomics Workbench 8.0.1, we mapped reads to the Adult Female Pooled transcriptome and show expression data for each transcript. The table includes read counts from each transcriptome replicate and data generated from the EDGE test of Unfed vs. 3 Hr Frustrated, including fold-change, and p-values
10493_2019_420_MOESM14_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 14 (XLSX 7724 kb) Supplementary Table S10: Differential gene expression analysis data for 3 Hr Fed vs. 3 Hr Frustrated. Using the EdgeR package 3.4.0-based algorithm of the CLC Genomics Workbench 8.0.1, we mapped reads to the Adult Female Pooled transcriptome and show expression data for each transcript. The table includes read counts from each transcriptome replicate and data generated from the EDGE test of 3 Hr Fed vs. 3 Hr Frustrated, including fold-change, and p-values
10493_2019_420_MOESM15_ESM.pptx
Supplementary material 15 (PPTX 447 kb) Supplementary Figure S1: Pie charts showing unigenes with BlastX hits. Each pie chart slice displays number and % of total of the Unfed, 3 Hr Fed, 3 Hr Frustrated and Adult Female Pooled transcriptome unigenes that have a BlastX hit with associated GO terms, have a BlastX hit without associated GO terms, have no BlastX hit but have an InterProScan entry, and have no BlastX hit and no annotation terms
10493_2019_420_MOESM16_ESM.pptx
Supplementary material 16 (PPTX 4224 kb) Supplementary Figure S2: Bar graphs showing E-values for each transcriptome’s BlastX hits. For each of the Unfed, 3 Hr Fed, 3 Hr Frustrated, and Adult Female Pooled transcriptome, E-Value (represented by 1e-X with X indicated on the Y axis) is plotted vs. the number of unigenes with a BlastX hit at that specific E-value
10493_2019_420_MOESM17_ESM.pptx
Supplementary material 17 (PPTX 1509 kb) Supplementary Figure S3: Bar graphs showing the top 35 most common species showing as the top BlastX hit for the Unfed, 3 Hr Fed, 3 Hr Frustrated, and Adult Female Pooled transcriptomes
10493_2019_420_MOESM18_ESM.pptx
Supplementary material 18 (PPTX 2108 kb)Supplementary Figure S4: Bar graphs showing the 35 most common hits to InterProScan Domains for the Unfed, 3 Hr Fed, 3 Hr Frustrated, and Adult Female Pooled transcriptomes
10493_2019_420_MOESM19_ESM.pptx
Supplementary material 19 (PPTX 1513 kb) Supplementary Figure S5: Bar graphs showing the 35 most common hits to InterProScan Sites for the Unfed, 3 Hr Fed, 3 Hr Frustrated, and Adult Female Pooled transcriptomes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bendele, K.G., Guerrero, F.D., Cameron, C. et al. Gene expression during the early stages of host perception and attachment in adult female Rhipicephalus microplus ticks. Exp Appl Acarol 79, 107–124 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-019-00420-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-019-00420-1