Abstract
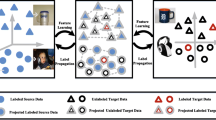
Heterogeneous domain adaptation (HDA) aims to adapt a trained model on a source domain with different input feature space to an unlabeled target domain. In fact, HDA is a challenging issue, since there exists feature and distribution discrepancies across domains. In this paper, we propose a novel approach named as heterogeneous domain adaptation with statistical distribution alignment and progressive pseudo label selection (SDA-PPLS). SDA-PPLS learns two projection matrices for source and target domains to map them into a latent subspace to have a shared feature space. Moreover, to mitigate the distribution gap, SDA-PPLS aligns both first-order and second-order statistical information, simultaneously, to improve the target classification model performance. In addition, to discriminate instances into distinct classes, SDA-PPLS aligns the class conditional distributions by pseudo label refinement of target domain data. Finally, to prevent the propagation of inaccurate pseudo labels to the next iteration, a progressive technique is proposed to select instances with higher probability. Experimental results on several real-word datasets on image to image, text to text and text to image tasks with different feature representations, demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms other state-of-the-art HDA methods.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Li W, Ogunbona P (2017) Joint geometrical and statistical alignment for visual domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 1859–1867
Saray S N, Tahmoresnezhad J (2021) Joint distinct subspace learning and unsupervised transfer classification for visual domain adaptation. Signal Image Vid Process 15(2):279–87
Tang B, He H, Baggenstoss P M, Kay S (2016) A Bayesian classification approach using class-specific features for text categorization. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 28(6):1602–1606
Dhar A, Mukherjee H, Dash N S, Roy K (2021) Text categorization: past and present. Artif Intell Rev 54(4):3007–3054
Sharma R, Menghani B, Thanvi A, Kumar M, Jangir S K (2021) An approach toward information retrieval through machine learning and its algorithms: a review. Rising Threats Expert Appl Sol 1187:643–649
Wang J, Feng W, Chen Y, Yu H, Huang M, Yu PS (2018) Visual domain adaptation with manifold embedded distribution alignment. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM international conference on Multimedia. pp 402–410
Csurka G (2017) A comprehensive survey on domain adaptation for visual applications. In: Domain adaptation in computer vision applications. Springer, pp 1–35
Pereira LA, da Silva Torres R (2018) Semi-supervised transfer subspace for domain adaptation. Pattern Recogn 75:235–249
Ahmadvand M, Tahmoresnezhad J (2021) Metric transfer learning via geometric knowledge embedding. Appl Intell 51(2):921–934
Day O, Khoshgoftaar T M (2017) A survey on heterogeneous transfer learning. J Big Data 4 (1):29
Luo Y, Wen Y, Tao D (2017) Heterogeneous multitask metric learning across multiple domains. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(9):4051–4064
Ren C-X, Feng J, Dai D-Q, Yan S (2019) Heterogeneous domain adaptation via covariance structured feature translators. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics
Li H, Pan SJ, Wan R, Kot AC (2019) Heterogeneous transfer learning via deep matrix completion with adversarial kernel embedding. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. pp 8602–8609
Huang J, Zhou Z, Shang J, Niu C (2020) Heterogeneous domain adaptation with label and structural consistency. Multimed Tools Appl 79(25/26):17923–17943
Kadhim A I (2019) Survey on supervised machine learning techniques for automatic text classification. Artif Intell Rev 52(1):273–292
Becker K, Moreira V P, dos Santos A G (2017) Multilingual emotion classification using supervised learning: Comparative experiments. Inf Process Manag 53(3):684–704
Hoffman J, Tzeng E, Darrell T, Saenko K (2017) Simultaneous deep transfer across domains and tasks. In: Domain adaptation in computer vision applications. Springer, pp 173–187
Zhao J, Li L, Deng F, He H, Chen J (2020) Discriminant geometrical and statistical alignment with density peaks for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Cybern
Li S, Song S, Huang G (2016) Prediction reweighting for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(7):1682–1695
Huang J, Gretton A, Borgwardt K, Schölkopf B, Smola A (2006) Correcting sample selection bias by unlabeled data. Adv Neural Inform Process Syst 19:601–608
Liu H, Shao M, Ding Z, Fu Y (2018) Structure-preserved unsupervised domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 31(4):799–812
Li L, Wan Z, He H (2020) Dual alignment for partial domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Cybern
Gholenji E, Tahmoresnezhad J (2020) Joint discriminative subspace and distribution adaptation for unsupervised domain adaptation. Appl Intell 50(7):2050–2066
Zhang W, Ouyang W, Li W, Xu D (2018) Collaborative and adversarial network for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 3801–3809
Yang B, Ma A J, Yuen P C (2018) Learning domain-shared group-sparse representation for unsupervised domain adaptation. Pattern Recogn 81:615–632
Cao Y, Long M, Wang J (2018) Unsupervised domain adaptation with distribution matching machines. In: AAAI. pp 2795–2802
Ding Z, Nasrabadi N M, Fu Y (2018) Semi-supervised deep domain adaptation via coupled neural networks. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(11):5214–5224
Rezaei S, Tahmoresnezhad J, Solouk V (2021) A transductive transfer learning approach for image classification. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 12(3):747–762
Gholenji E, Tahmoresnezhad J (2020) Joint local and statistical discriminant learning via feature alignment. Signal Image Vid Process 14(3):609–616
Li S, Liu C H, Su L, Xie B, Ding Z, Chen CP, Wu D (2020) Discriminative transfer feature and label consistency for cross-domain image classification. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst
Tahmoresnezhad J, Hashemi S (2017) Visual domain adaptation via transfer feature learning. Knowl Inf Syst 50(2):585–605
Rahman M M, Fookes C, Baktashmotlagh M, Sridharan S (2020) Correlation-aware adversarial domain adaptation and generalization. Pattern Recogn 100:107124
Ghifary M, Balduzzi D, Kleijn W B, Zhang M (2016) Scatter component analysis: A unified framework for domain adaptation and domain generalization. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(7):1414–1430
Lu H, Shen C, Cao Z, Xiao Y, van den Hengel A (2018) An embarrassingly simple approach to visual domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(7):3403–3417
Li J, Lu K, Zhu L, Li Z (2017) Locality-constrained transfer coding for heterogeneous domain adaptation. In: Australasian database conference. Springer, pp 193–204
Niu C, Shang J, Huang J, Wang Y, Zhou Z (2018) Structure consistency and class discriminative feature learning for heterogeneous domain adaptation. In: 2018 IEEE 3rd international conference on communication and information systems (ICCIS). IEEE, pp 217–221
Chen C, Fu Z, Chen Z, Jin S, Cheng Z, Jin X, Hua X-S (2020) HoMM: Higher-order moment matching for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 04, pp 3422–3429
Xu J, Ye P, Li Q, Du H, Liu Y, Doermann D (2016) Blind image quality assessment based on high order statistics aggregation. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(9):4444–4457
Sun B, Feng J, Saenko K (2017) Correlation alignment for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Domain adaptation in computer vision applications. Springer, pp 153–171
Zhang W, Zhang X, Lan L, Luo Z (2020) Maximum mean and covariance discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. Neural Process Lett 51(1):347–366
Xie X, Sun S, Chen H, Qian J (2018) Domain adaptation with twin support vector machines. Neural Process Lett 48(2):1213– 1226
Zhu L, Zhang X, Zhang W, Huang X, Guan N, Luo Z (2017) Unsupervised domain adaptation with joint supervised sparse coding and discriminative regularization term. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE, pp 3066–3070
Hoffman J, Rodner E, Donahue J, Darrell T, Saenko K (2013) Efficient learning of domain-invariant image representations. arXiv:13013224
Li W, Duan L, Xu D, Tsang I W (2013) Learning with augmented features for supervised and semi-supervised heterogeneous domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(6):1134–1148
Hoffman J, Rodner E, Donahue J, Kulis B, Saenko K (2014) Asymmetric and category invariant feature transformations for domain adaptation. Int J Comput Vis 109(1-2):28–41
Shi X, Liu Q, Fan W, Philip SY, Zhu R (2010) Transfer learning on heterogenous feature spaces via spectral transformation. In: 2010 IEEE international conference on data mining. IEEE, pp 1049–1054 ure
Wang C (2011) Mahadevan S Heterogeneous domain adaptation using manifold alignment. In: IJCAI proceedings-international joint conference on artificial intelligence, vol 1, p 1541
Yao Y, Zhang Y, Li X, Ye Y (2020) Discriminative distribution alignment: A unified framework for heterogeneous domain adaptation. Pattern Recogn 101:107165
Fang W-C, Chiang Y-T (2018) A discriminative feature mapping approach to heterogeneous domain adaptation. Pattern Recogn Lett 106:13–19
Fukunaga K (2013) Introduction to statistical pattern recognition. Elsevier
Yan S, Xu D, Zhang B, Zhang H -J, Yang Q, Lin S (2006) Graph embedding and extensions: A general framework for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(1):40–51
Tsai HY-H, Yeh Y-R, Wang FY-C (2016) Learning cross-domain landmarks for heterogeneous domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 5081–5090
Huang K, Wen H, Zhou C, Yang C, Gui W (2020) Transfer dictionary learning method for cross-domain multimode process monitoring and fault isolation. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 69(11):8713–8724
Huang K, Wu Y, Wang C, Xie Y, Yang C, Gui W (2020) A projective and discriminative dictionary learning for high-dimensional process monitoring with industrial applications. IEEE Trans Industr Inf 17(1):558–568
Li J, Lu K, Huang Z, Zhu L, Shen H T (2018) Transfer independently together: A generalized framework for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Cybern 49(6):2144–2155
Shen C, Guo Y (2018) Unsupervised heterogeneous domain adaptation with sparse feature transformation. In: Asian conference on machine learning. pp 375–390
Li J, Lu K, Huang Z, Zhu L, Shen H T (2018) Heterogeneous domain adaptation through progressive alignment. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(5):1381–1391
Zou Y, Yu Z, Kumar B, Wang J (2018) Unsupervised domain adaptation for semantic segmentation via class-balanced self-training. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV). pp 289–305
Wang Q, Breckon T (2020) Unsupervised domain adaptation via structured prediction based selective pseudo-labeling. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 04, pp 6243–6250
Liang J, He R, Sun Z, Tan T (2019) Exploring uncertainty in pseudo-label guided unsupervised domain adaptation. Pattern Recogn 96:106996
Wang Q, Bu P, Breckon TP (2019) Unifying unsupervised domain adaptation and zero-shot visual recognition. In: 2019 International joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN). IEEE, pp 1–8
Chen C, Xie W, Huang W, Rong Y, Ding X, Huang Y, Xu T, Huang J (2019) Progressive feature alignment for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 627–636
Yao Y, Zhang Y, Li X, Ye Y (2019) Heterogeneous domain adaptation via soft transfer network. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM international conference on multimedia. pp 1578– 1586
Gretton A, Borgwardt K M, Rasch M J, Schölkopf B, Smola A (2012) A kernel two-sample test. J Mach Learn Res 13(1):723–773
Belkin M, Niyogi P, Sindhwani V (2006) Manifold regularization: A geometric framework for learning from labeled and unlabeled examples. Jo Mach Learning Res 7(Nov):2399–2434
Lee H, Battle A, Raina R, Ng A (2006) Efficient sparse coding algorithms. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 19:801–808
Li J, Zhao J, Lu K (2016) Joint feature selection and structure preservation for domain adaptation. In: IjCAI. pp 1697–1703
Berlind C, Urner R (2015) Active nearest neighbors in changing environments. In: International conference on machine learning. pp 1870–1879
Gentleman R, Carey VJ (2008) Unsupervised machine learning. In: Bioconductor case studies. Springer, pp 137–157
Saenko K, Kulis B, Fritz M, Darrell T (2010) Adapting visual category models to new domains. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 213–226
Griffin G, Holub A, Perona P (2007) Caltech-256 object category dataset
Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L (2008) Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput Vis Image Underst 110(3):346–359
Donahue J, Jia Y, Vinyals O, Hoffman J, Zhang N, Tzeng E, Darrell T (2014) Decaf: A deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition. In: International conference on machine learning. pp 647–655
Amini MR, Usunier N, Goutte C (2009) Learning from multiple partially observed views-an application to multilingual text categorization. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 28–36
Tommasi T, Tuytelaars T (2014) A testbed for cross-dataset analysis. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 18–31
Chua T-S, Tang J, Hong R, Li H, Luo Z, Zheng Y (2009) NUS-WIDE: a real-world web image database from national university of singapore. In: Proceedings of the ACM international conference on image and video retrieval. pp 1–9
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L-J, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Ieee, pp 248–255
Chen W-Y, Hsu T-MH, Tsai Y-HH, Wang Y-CF, Chen M-S (2016) Transfer neural trees for heterogeneous domain adaptation. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 399–414
Li W, Duan L, Xu D, Tsang I W (2013) Learning with augmented features for supervised and semi-supervised heterogeneous domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(6):1134–1148
Li J, Jing M, Lu K, Zhu L, Shen H T (2019) Locality preserving joint transfer for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(12):6103–6115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alipour, N., Tahmoresnezhad, J. Heterogeneous domain adaptation with statistical distribution alignment and progressive pseudo label selection. Appl Intell 52, 8038–8055 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02756-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02756-x