Abstract
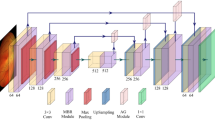
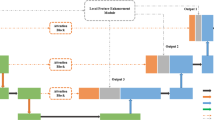
Retinal vessel segmentation plays an important role in the automatic assessment of eye health. Deep learning technology has been extensively employed in medical image segmentation. Specifically, U-net based methods achieve great success in medical image segmentation. However, due to its continuous pooling layer and convolution operation, the spatial information and texture information of the image are destroyed. To address this issue, we propose a SAT-Net that integrates side attention and dense atrous convolution block, which also consists of multi-scale input so that the network can retain more features of the image of the encoder stage. The dense atrous convolution block enables multiple receptive field fusion, which preserves the context information of the image, and the side attention mechanism further enhances the high-level information of the encoded features and reduces the noise in the feature map. We apply this method to different retinal image segmentation datasets and compare with the other methods. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hosny A, Parmar C, Quackenbush J, Schwartz LH, Aerts HJ (2018) Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat Rev Cancer 18(8):500–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-018-0016-5
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Pereira F, Burges CJC, Bottou L, Weinberger KQ (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems 25. http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks.pdf. Curran Associates, Inc, pp 1097–1105
Liu X, Zhu X, Li M, Wang L, Zhu E, Liu T, Kloft M, Shen D, Yin J, Gao W (2020) Multiple kernel k k-means with incomplete kernels. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42 (5):1191–1204. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2892416
Yu X, Ye X, Gao Q (2020) Infrared handprint image restoration algorithm based on apoptotic mechanism. IEEE Access 8:47334–47343. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2979018
Ciresan D, Giusti A, Gambardella LM, Schmidhuber J (2012) Deep neural networks segment neuronal membranes in electron microscopy images. In: Pereira F, Burges CJC, Bottou L, Weinberger KQ (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems 25. http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4741-deep-neural-networks-segment-neuronal-membranes-in-electron-microscopy-images.pdf. Curran Associates, Inc, pp 2843–2851
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells W M, Frangi A F (eds) Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention—MICCAI 2015. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 234–241
Fu H, Cheng J, Xu Y, Wong DWK, Liu J, Cao X (2018) Joint optic disc and cup segmentation based on multi-label deep network and polar transformation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 37(7):1597–1605
Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Yu F, Koltun V (2016) Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions. In: Yoshua Y., LeCun Y. (eds) 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2016, San Juan, Puerto Rico, May 2-4, 2016, Conference Track Proceedings. 1511.07122
Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc LL, Lee M, Heinrich M, Misawa K, Mori K, McDonagh S, Hammerla NY, Kainz B, Glocker B, Rueckert D (2018) Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. CoRR abs/1804.03999. 1804.03999
Yin H, Gong Y, Qiu G (2019) Side window filtering. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Ioffe S, Szegedy C (2015) Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Bach F R., Blei D M. (eds) Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2015, Lille, France, 6-11 July 2015. http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/ioffe15.html, vol 37. JMLR.org, pp 448–456
Clevert D-A, Unterthiner T, Hochreiter S (2016) Fast and Accurate Deep Network Learning by Exponential Linear Units (ELUs). In: Bengio Y, LeCun Y (eds) 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2016, San Juan, Puerto Rico, May 2-4, 2016, Conference Track Proceedings. 1511.07289
Shen Y, Fang Z, Gao Y, Xiong N, Zhong C, Tang X (2019) Coronary arteries segmentation based on 3D FCN with attention gate and level set function. IEEE Access 7(c):42826–42835. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2908039
Gu Z, Cheng J, Fu H, Zhou K, Hao H, Zhao Y, Zhang T, Gao S, Liu J (2019) Ce-net: context encoder network for 2d medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(10):2281–2292
Azad R, Asadi-Aghbolaghi M, Fathy M, Escalera S (2019) Bi-directional convlstm u-net with densley connected convolutions. In: The IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) workshops
Alom MZ, Hasan M, Yakopcic C, Taha TM, Asari VK (2018) Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on u-net (r2u-net) for medical image segmentation. CoRR arXiv:1802.06955
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Srivastava RK, Greff K, Schmidhuber J (2015) Highway networks
Huang G, Sun Y, Liu Z, Sedra D, Weinberger KQ (2016) Deep networks with stochastic depth. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds) Computer vision—ECCV 2016. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 646–661
Larsson G, Maire M, Shakhnarovich G (2016) FractalNet: Ultra-Deep Neural Networks without Residuals. CoRR abs/1605.07648. 1605.07648
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H (2017) Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. CoRR abs/1706.05587. 1706.05587
Chen L, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2018) Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848
Yang M, Yu K, Zhang C, Li Z, Yang K (2018) Denseaspp for semantic segmentation in street scenes. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, Li Y, Bao Y, Fang Z, Lu H (2019) Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Staal J, Abramoff MD, Niemeijer M, Viergever MA, van Ginneken B (2004) Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23(4):501–509
Hoover AD, Kouznetsova V, Goldbaum M (2000) Locating blood vessels in retinal images by piecewise threshold probing of a matched filter response. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 19(3):203–210
Roychowdhury S, Koozekanani DD, Parhi KK (2015) Blood vessel segmentation of fundus images by major vessel extraction and subimage classification. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 19(3):1118–1128. https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2014.2335617
Liskowski P, Krawiec K (2016) Segmenting retinal blood vessels with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(11):2369–2380. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2016.2546227
Li Q, Feng B, Xie L, Liang P, Zhang H, Wang T (2016) A cross-modality learning approach for vessel segmentation in retinal images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(1):109–118. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2015.2457891
Zhang Z, Liu Q, Wang Y (2018) Road extraction by deep residual u-net. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 15(5):749–753
Wang W, Yu K, Hugonot J, Fua P, Salzmann M (2019) Recurrent u-net for resource-constrained segmentation. In: The IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV)
Li L, Verma M, Nakashima Y, Nagahara H, Kawasaki R (2020) Iternet: retinal image segmentation utilizing structural redundancy in vessel networks. In: The IEEE Winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (No.18411952800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, H., Fang, Z., Wei, Z. et al. SAT-Net: a side attention network for retinal image segmentation. Appl Intell 51, 5146–5156 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01966-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01966-z