Abstract
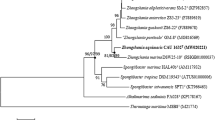
A polyphasic taxonomic study was performed on a strain, designated FHC16T, which was isolated from surface seawater collected from the South China Sea. Cells of strain FHC16T are Gram stain-negative, oxidase- and catalase-positive and non-motile rods. Growth was observed at 15–37 °C (optimum, 25–30 °C), at pH 6.0–9.0 (optimum, pH 7.0) and in the presence of 0–5 % (w/v) NaCl (optimum, 3 %). 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that strain FHC16T is most closely related to Tamlana sedimentorum JCM 19808T (98.2 % sequence similarity). The ANI value between strain FHC16T and T. sedimentorum JCM 19808T was found to be 81.82–81.81 %. The DNA–DNA hybridization estimated value between strain FHC16T and T. sedimentorum JCM 19808T was determined to be 25.8 ± 2.41 %. The principal fatty acids (>5 % of the total) were found to be iso-C15:0, iso G-C15:1, iso-C17:0 3-OH, iso-C15:0 3-OH and summed feature 3 (comprising C16:1 ω7c/C16:1 ω6c). The strain was found to have MK-6 as the major respiratory menaquinone, which is consistent with the other three recognized Tamlana species, T. sedimentorum, Tamlana crocina and Tamlana agarivorans. The polar lipids were found to comprise phosphatidylethanolamine, one unidentified aminophospholipid, two unidentified aminolipids and seven unidentified lipids. The G+C content of the chromosomal DNA was determined to be 34.2 mol%. On the basis of phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and molecular data, strain FHC16T is considered to represent a novel species of the genus Tamlana, for which the name Tamlana nanhaiensis sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is FHC16T (\( = \)LMG 27420T = CGMCC 1.12469T = MCCC 1A06648T).

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MCCC:
-
Marine Culture Collection of China
References
Bowman JP, McCammon SA, Lewis T, Skerratt JH, Brown JL, Nichols DS, McMeekin TA (1998) Psychroflexus torquis gen. nov., sp. nov. a psychrophilic species from Antarctic sea ice, and reclassification of Flavobacterium gondwanense (Dobson et al. 1993) as Psychroflexus gondwanense gen. nov., comb. nov. Microbiology 144:1601–1609
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Jeong SH, Park MS, Jin HM, Lee K, Park W, Jeon CO (2013) Aestuariibaculum suncheonense gen. nov., sp. nov., a marine bacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from a tidal flat and emended descriptions of the genera Gaetbulibacter and Tamlana. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:332–338
Kim O-S, Cho Y-J, Lee K, Yoon S-H, Kim M, Na H, Park S-C, Jeon YS, Lee J-H, Yi H (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kim M, Oh H-S, Park S-C, Chun J (2014) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:346–351
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Lai Q, Yuan J, Wu C, Shao Z (2009) Oceanibaculum indicum gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from deep seawater of the Indian Ocean. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1733–1737
Lee SD (2007) Tamlana crocina gen. nov., sp. nov., a marine bacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae, isolated from beach sediment in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:764–769
Liu C, Shao Z (2005) Alcanivorax dieselolei sp. nov., a novel alkane-degrading bacterium isolated from sea water and deep-sea sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1181–1186
Luo R, Liu B, Xie Y, Li Z, Huang W, Yuan J, He G, Chen Y, Pan Q, Liu Y (2012) SOAPdenovo2: an empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 1:18
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Goker M (2013a) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics 14:60
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Göker M, Spröer C, Klenk H-P (2013b) When should a DDH experiment be mandatory in microbial taxonomy? Arch Microbiol 195:413–418
Moore L, Moore E, Murray R, Stackebrandt E, Starr M (1987) Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:19126–19131
Romanenko LA, Tanaka N, Kurilenko VV, Svetashev VI (2014) Tamlana sedimentorum sp. nov., isolated from shallow sand sediments of the Sea of Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2891–2896
Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1992) A simple method for estimating and testing minimum-evolution trees. Mol Biol Evol 9:945–967
Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1993) Theoretical foundation of the minimum-evolution method of phylogenetic inference. Mol Biol Evol 10:1073–1095
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101, MIDI, Newark
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol today 33:152
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson CC, Chimetto L, Edwards RA, Swings J, Stackebrandt E, Thompson FL (2013) Microbial genomic taxonomy. BMC Genomics 14:913
Yoon J-H, Kang S-J, Lee M-H, Oh T-K (2008) Tamlana agarivorans sp. nov., isolated from seawater off Jeju Island in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1892–1895
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the fund of National Infrastructure of Microbial Resources (No. NIMR2014-9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiupian Liu and Qiliang Lai have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Lai, Q., Du, Y. et al. Tamlana nanhaiensis sp. nov., isolated from surface seawater collected from the South China Sea. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107, 1189–1196 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0410-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0410-x