Abstract
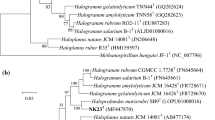
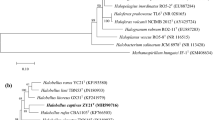
Two extremely halophilic archaea, designated YIM 90917 and YIM 93656T, were isolated from saline soils in Yunnan province and Lup nur region in Xinjiang province, western China, respectively. Colonies of the two strains were observed to be pink-pigmented. The cells were found to be Gram-stain negative, coccoid and non-motile. The organisms were found to be aerobic and could grow in an NaCl range of 6–35 % (optimum 18 %), temperatures ranging from 25 to 50 °C (optimum 37–42 °C), pH range from 6.0–8.5 (optimum pH 7.0–7.5) and Mg2+ range from 0 to 1.5 M (optimum 0.5–1.0 M); Mg2+ was not necessary for growth. Cells were not observed to lyse in distilled water. Strains YIM 90917 and YIM 93656T showed the highest 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities to Haladaptatus cibarius JCM 15962T (97.6 and 97.9 %, respectively). In addition, the DNA–DNA hybridizations of strains YIM 90917 and YIM 93656T with type strains H. cibarius JCM 15962T, Haladaptatus litoreus JCM 15771T and Haladaptatus paucihalophilus JCM 13897T were 37.2 and 38.2 %, 36.6 and 39.0 % and 27.9 and 27.7 %, respectively. The DNA G+C contents of strains YIM 90917 and YIM 93656T were determined to be 56.0 and 57.4 mol%. The major polar lipids of the two strains were identified as phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol phosphate methyl ester, phosphatidylglycerol sulfate, sulfated mannosyl glucosyl diether and other four unidentified glycolipids. On the basis of physiological, chemotaxonomic data and phylogenetic analysis, the strains YIM 90917 and YIM 93656T can be classified as a novel species of the genus Haladaptatus, for which the name Haladaptatus pallidirubidus sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is YIM 93656T (=JCM 17504T = CCTCC AB2010454T).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrow GI, Feltham RKA (1993) Cowan and Steel’s Manual for the Identification of Medical Bacteria, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Boucher Y, Douady CJ, Sharma AK, Kamekura M, Doolittle WF (2004) Intragenomic heterogeneity and intergenomic recombination among Haloarchaeal rRNA genes. J Bacteriol 186(12):3980–3990
Case RJ, Boucher Y, Dahllöf I, Holmström C, Doolittle WF, Kjelleberg S (2007) Use of 16S rRNA and rpoB genes as molecular markers for microbial ecology studies. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:278–288
Christensen H, Angen O, Mutters R, Olsen JE, Bisgaard M (2000) DNA-DNA hybridization determined in micro-wells using covalent attachment of DNA. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1095–1102
Cui HL, Lin ZY, Dong Y, Zhou PJ, Liu SJ (2007) Halorubrum litoreum sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2204–2206
Cui HL, Sun FF, Gao X, Dong Y, Xu XW, Zhou YG, Liu HC, Oren A, Zhou PJ (2010a) Haladaptatus litoreus sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a marinesolar saltern, and emended description of the genus Haladaptatus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1085–1089
Cui HL, Gao X, Yang X, Xu XW (2010b) Halorussus rarus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Extremophiles 14:493–499
Cui HL, Li XY, Gao X, Xu XW, Zhou YG, Liu HC, Oren A, Zhou PJ (2010c) Halopelagius inordinatus gen. nov., sp. Nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2089–2093
Dahllöf I, Baillie H, Kjelleberg S (2000) rpoB-based microbial community analysis avoids limitations inherent in 16S rRNA gene intraspecies heterogeneity. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(8):3376–3380
Dussault HP (1955) An improved technique for staining red halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol 70:484–485
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–789
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurae algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Gutiérrez MC, Castillo AM, Kamekura M, Ventosa A (2008) Haloterrigena salina sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2880–2884
Kates M (1986) Techniques of lipidology, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 106–107
Kim KS, Ko KS, Chang MW, Hahn TW, Hong SK, Kook YH (2003) Use of rpoB sequences for phylogenetic study of Mycoplasma species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 226:299–305
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA Gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1983) The neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Leifson E (1960) Atlas of Bacterial Flagellation. Academic Press, London
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin DE, Collins MD, Goodfellow M (1979) Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Cellulomonas, Oerskovia and related taxa. J Appl Bacteriol 47:87–95
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Mylvaganam S, Dennis PP (1992) Sequence heterogeneity between the two genes encoding 16S rRNA from the halophilic archaebacterium Haloarcula marismortui. Genetics 130:399–410
Ng WL, Yang CF, Halladay JT, Arora A, DasSarma S (1995) Protocol 25. Isolation of genomic and plasmid DNAs from Halobacterium halobium. In: DasSarma S, Fleischmann EM (eds) Archaea: a laboratory manual: halophiles. Cold Spring Harbor, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, NY, pp 179–180
Oren A, Ventosa A, Grant WD (1997) Proposed minimal standards for description of new taxa in the order Halobacteriales. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:233–238
Oren A (2000) The order Halobacteriales. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E The prokaryotes: an evolving electro-nic resource for the microbiological community, release 3.2 Springer, New York http://141.150.157.117:8080/prokPUB/index.htm
Roh SW, Nam YD, Chang HW, Sung Y, Kim KH, Oh HM, Bae JW (2007) Halalkalicoccus jeotgali sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon from shrimp jeotgal, a traditional Korean fermented seafood. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2296–2298
Roh SW, Lee ML, Bae JW (2010) Haladaptatus cibarius sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from seafood, and emended description of the genus Haladaptatus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1187–1190
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Savage KN, Krumholz LR, Oren A, Elshahed MS (2007) Haladaptatus paucihalophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a low-salt, sulfide-rich spring. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:19–24
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tang SK, Tian XP, Zhi XY, Cai M, Wu JY, Yang LL, Xu LH, Li WJ (2008) Haloactinospora alba gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic filamentous actinomycete of the family. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2075–2080
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Walsh DA, Bapteste E, Kamekura M, Doolittle WF (2004) Evolution of the RNA polymerase B′ subunit gene (rpoB′) in Halobacteriales: a complementary molecular marker to the SSU rRNA gene. Mol Biol Evol 21:2340–2351
Wang ZX, Li Yu, Zhou PG (2000) Taxonomy of a new species of haloalkalophilic archaeon. Acta Microbiologica Sinica 40:115–120
Williams ST, Goodfellow M, Alderson G (1989) Genus Streptomyces Waksman and Henrici 1943, 339AL. Bergey’s Manual Syst Bacteriol 4:2463–2468
Wright ADG (2006) Phylogenetic relationships within the order Halobacteriales inferred from 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1223–1227
Xue Y, Fan H, Ventosa A, Grant WD, Jones BE, Cowan DA, Ma Y (2005) Halalkalicoccus tibetensis gen. nov., sp. nov., representing a novel genus of haloalkaliphilic archaea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2501–2505
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Prof. Dr. George M. Garrity (Michigan State University, USA) for the Latin construction of the new taxon name, and Dr. Heng-Lin Cui (Jiangsu University, China) for his technical support and kind comments on this manuscript. This research was supported by National High-tech R & D Program of China (863 Program) (no. 2012AA021705). The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through the research group no. RGP-205. W-J Li was also supported by the ‘Hundred Talents Program’ of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Guangdong Province Higher Vocational Colleges & Schools Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bing–Bing Liu and Wan-Yu Zhao authors are contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, BB., Zhao, WY., Chu, X. et al. Haladaptatus pallidirubidus sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from saline soil samples in Yunnan and Xinjiang, China. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 106, 901–910 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0259-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0259-4