Abstract
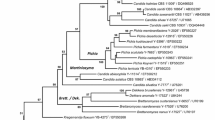
During a survey of yeasts associated with raw honey collected in Thailand, two strains of the Zygoascus clade were isolated from the Asian cavity-nesting honeybee Apis cerana and the stingless bee Homotrigona fimbriata. Phylogeny based on 26S rDNA D1/D2 sequences placed these yeasts as members of a clade including Candida bituminiphila, Candida patagonica and Candida polysorbophila. The strains of the two novel species, CBS 12271T and CBS 12270T, respectively, could be unquestionably distinguished from their relatives by rDNA sequences and other taxonomic characteristics. Therefore, the novel anamorphic species, Candida lundiana sp. nov. (type strain CBS 12271T = JCM 16823T) and Candida suthepensis sp. nov. (type strain CBS 12270T = JCM 16822T) are described.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Brysch-Herzberg M (2004) Ecology of yeasts in plant–bumblebee mutualism in Central Europe. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 50:87–100
Csoma H, Sipiczki M (2008) Taxonomic reclassification of Candida stellata strains reveals frequent occurrence of Candida zemplinina in wine fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res 8:328–336
Egli CM, Henick-Kling T (2001) Identification of Brettanomyces/Dekkera species based on polymorphism in the rRNA internal transcribed spacer region. Am J Enol Vitic 52:241–247
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Gilliam M (1979) Microbiology of pollen and bee bread: the yeasts. Apidologie 10:43–53
Gilliam M (1997) Identification and roles of non-pathogenic microflora associated with honey bees. FEMS Microbiol Lett 155:1–10
Gilliam M, Wickerham LJ, Morton HL, Martin RD (1974) Yeasts isolated from honey bees, Apis mellifera, fed 2, 4-D and antibiotics. J Invert Pathol 24:349–356
Inglis GD, Sigler L, Goettel MS (1993) Aerobic microorganisms associated with alfalfa leafcutter bees (Megachile rotundata). Microb Ecol 26:125–143
James SA, Bond CJ, Roberts IN (2001) Candida sorbosivorans sp. nov., a new member of the genus Candida Berkhout. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1215–1219
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kurtzman CP (2007) New anamorphic yeast species: Candida infanticola sp. nov., Candida polysorbophila sp. nov., Candida transvaalensis sp. nov. and Trigonopsis californica sp. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 92:221–231
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (1997) Identification of clinically important ascomycetous yeasts based on nucleotide divergence in the 5′ end of the large-subunit (26S) ribosomal DNA gene. J Clin Microbiol 35:1216–1223
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (1998) Identification and phylogeny of ascomycetous yeasts from analysis of nuclear large subunit (26S) ribosomal DNA partial sequences. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 73:331–371
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (2007) Multigene phylogenetic analysis of the Trichomonascus, Wickerhamiella and Zygoascus yeast clades, and the proposal of Sugiyamaella gen.nov. and 14 new species combinations. FEMS Yeast Res 7:141–151
Lachance MA, Bowles JM, Díaz MMC, Janzen DH (2001a) Candida cleridarum, Candida tilneyi and Candida powellii, three new yeast species isolated from insects associated with flowers. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1201–1207
Lachance MA, Starmer WT, Rosa CA, Bowles JM, Barker JSF, Janzen DH (2001b) Biogeography of the yeasts of ephemeral flowers and their insects. FEMS Yeast Res 1:1–8
Lachance MA, Dobson J, Wijayanayaka DN, Smith AME (2010) The use of parsimony network analysis for the formal delineation of phylogenetic species of yeasts: Candida apicola, Candida azyma, and Candida parazyma sp. nov., cosmopolitan yeasts associated with floricolous insects. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 97:155–170
Michener CD (2007) The bees of the world, 2nd edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Péter G, Tornai-Lehoczki J, Dlauchy D (2009) Trichomonascus apis sp. nov., a heterothallic yeast species from honeycomb. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1550–1554
Pimentel MRC, Antonini Y, Martins RP, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2005) Candida riodocensis and Candida cellae, two new yeast species from the Starmerella clade associated with solitary bees in the Atlantic rain forest of Brazil. FEMS Yeast Res 5:875–879
Robert V, Bonjean B, Karutz M, Paschold H, Peeters W, Wubbolts MG (2001) Candida bituminiphila, a novel anamorphic species of yeast. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2171–2176
Rosa CA, Viana EM, Martins RP, Antonini Y, Lachance MA (1999) Candida batistae, a new yeast species associated with solitary digger nesting bees in Brazil. Mycologia 91:428–433
Rosa CA, Lachance MA, Silva JOC, Teixeira ACP, Marini MM, Antonini Y, Martins RP (2003) Yeast communities associated with stingless bees. FEMS Yeast Res 4:271–275
Rosa CA, Pagnocca FC, Lachance MA, Ruivo CCC, Medeiros AO, Pimentel MRC, Fontenelle JCR, Martins RP (2007) Candida flosculorum sp. nov. and Candida floris sp. nov., two yeast species associated with tropical flowers. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2970–2974
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Saksinchai S, Suzuki M, Chantawannakul P, Ohkuma M, Lumyong S (2011) A novel ascosporogenous yeast species, Zygosaccharomyces siamensis, and the sugar tolerant yeasts associated with raw honey collected in Thailand. Fungal Divers (In press). doi:10.1007/s13225-011-0115-z
Sangorrín MP, Lopes CA, Belloch C, Querol A, Caballero AC (2007) Candida patagonica sp. nov., a new species of yeast from cellar surfaces. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 92:77–81
Sipiczki M (2003) Candida zemplinina sp. nov., an osmotolerant and psychrotolerant yeast that ferments sweet botrytized wines. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:2079–2083
Smith MTH, Robert V, Poot GA, Epping W, de Cock AWAM (2005) Taxonomy and phylogeny of the ascomycetous yeast genus Zygoascus, with proposal of Zygoascus meyerae sp. nov. and related anamorphic varieties. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1353–1363
Snowdon JA, Cliver DO (1996) Microorganisms in honey. Int J Food Microbiol 31:1–26
Solieri L, Landi S, de Vero L, Giudici P (2006) Molecular assessment of indigenous yeast population from traditional balsamic vinegar. J Appl Microbiol 101:63–71
Stratford M, Bond CJ, James SA, Roberts IN, Steels H (2002) Candida davenportii sp. nov., a potential soft-drinks spoilage yeast isolated from a wasp. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1369–1375
Teixeira ACP, Marini MM, Nicoli JR, Antonini Y, Martins RP, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2003) Starmerella meliponinorum sp. nov., a novel ascomycetous yeast species associated with stingless bees. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:339–343
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Troller JA (1979) Food spoilage by microorganisms tolerating low-aw environments. Food Technol 33:72–75
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, Taylor TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide for methods and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 315–322
Yarrow D (1998) Methods for the isolation, maintenance and identification of yeasts. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW (eds) The yeasts, a taxonomic study, 4th edn edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 77–100
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Thai Government Science and Technology Scholarship for Ph.D. Study, awarded to Sujinan Saksinchai, the Thailand Research Fund, the National Research University, and Office of the Higher Education Commission. We acknowledge fellowships granted by the Graduate School, Chiang Mai University. We appreciate Prapan Triyasut and Yaowanoot Promnuan at Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Chiang Mai University for collection assistance in Chiang Mai province. Permission from various local authorities to collect in many sites is gratefully acknowledged. Appreciation goes to Dr. Michael Burgett and Keegan Kennedy for help with the article’s English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saksinchai, S., Suzuki, M., Lumyong, S. et al. Two new species of the genus Candida in the Zygoascus clade, Candida lundiana sp. nov. and Candida suthepensis sp. nov., isolated from raw honey in Thailand. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 101, 633–640 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9677-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9677-8