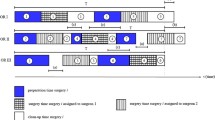
Abstract
In this paper, we consider a two-stage stochastic weekly operating room planning problem with an exponential number of scenarios. The objective function is to minimize the sum of the fixed opening cost of operating rooms and the expected overtime costs that are computed in the second stage. We propose a state-variable model to formulate the two-stage stochastic operating room planning problem and prove its validity. The main advantage of the proposed state-variable model is that it has a pseudo-polynomial number of variables and constraints that are significantly fewer than the number of variables and constraints in an equivalent scenario-based stochastic programming model. We improve the quality of the proposed model by developing an enhanced model that includes remarkably fewer variables and constraints. We also strengthen the model by developing several valid inequalities, including worst-case scenario and symmetry-breaking cuts. We carried out extensive computational experiments to evaluate the performance of the proposed model. The computational results show that the proposed model is capable of finding optimal solutions of instances with 50 surgeries and 1.55E+40 scenarios that is a significant improvement over the state-of-the-art models. The results revealed that the model finds feasible solutions with an average optimality gap of 0.78% for instances with 80 surgeries and 1.48E+64 scenarios.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addis, B., Carello, G., Grosso, A., & Tànfani, E. (2016). Operating room scheduling and rescheduling: A rolling horizon approach. Flexible Services and Manufacturing Journal, 28(1–2), 206–232.
Aghighi, A., Alireza, G., Behnam, M., Erfan Babaee, T. (2021). The stochastic location-routing-inventory problem of perishable products with reneging and balking. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 1–20.
Alinezhad, M., Iraj, M., Milad, H., Erfan Babaee, T. (2021). A fuzzy multi-objective optimization model for sustainable closed-loop supply chain network design in food industries. Environment, Development and Sustainability 1–28.
Atighehchian, A., Sepehri, M. M., Shadpour, P., & Kianfar, K. (2020). A two-step stochastic approach for operating rooms scheduling in multi-resource environment. Annals of Operations Research, 292(1), 191–214.
Bandi, C., & Gupta, D. (2020). Operating room staffing and scheduling. Manufacturing and Service Operations Management, 22(5), 958–974.
Breuer, D. J., Lahrichi, N., Clark, D. E., & Benneyan, J. C. (2020). Robust combined operating room planning and personnel scheduling under uncertainty. Operations Research for Health Care, 27, 100276.
Cardoen, B., Demeulemeester, E., & Beliën, J. (2010). Operating room planning and scheduling: A literature review. European Journal of Operational Research, 201(3), 921–932.
Choi, S., & Wilhelm, W. E. (2014). On capacity allocation for operating rooms. Computers and Operations Research, 44, 174–184.
Denton, B. T., Miller, A. J., Balasubramanian, H. J., & Huschka, T. R. (2010). Optimal allocation of surgery blocks to operating rooms under uncertainty. Operations Research, 58(4–part–1), 802–816.
Doulabi, H., Hossein, L.-M.R., & Pesant, G. (2016). A constraint-programming-based branch-and-price-and-cut approach for operating room planning and scheduling. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 28(3), 432–448.
Erekat, A., Servis, G., Madathil, S. C., & Khasawneh, M. T. (2020). Efficient operating room planning using an ensemble learning approach to predict surgery cancellations. IISE Transactions on Healthcare Systems Engineering, 10(1), 18–32.
Fei, H., Chengbin, C., Meskens, N., & Artiba, A. (2008). Solving surgical cases assignment problem by a branch-and-price approach. International Journal of Production Economics, 112(1), 96–108.
Fei, H., Chu, C., & Meskens, N. (2009). Solving a tactical operating room planning problem by a column-generation-based heuristic procedure with four criteria. Annals of Operations Research, 166(1), 91.
Freeman, N. K., Melouk, S. H., & Mittenthal, J. (2015). A scenario-based approach for operating theater scheduling under uncertainty. Manufacturing and Service Operations Management, 18(2), 245–261.
Guerriero, F., & Guido, R. (2011). Operational research in the management of the operating theatre: A survey. Health Care Management Science, 14(1), 89–114.
Guo, C., Merve, B., Aleman, D. M., Urbach, D. R. (2021). Logic-based benders decomposition and binary decision diagram based approaches for stochastic distributed operating room scheduling. INFORMS Journal on Computing .
Hans, E., Wullink, G., Van Houdenhoven, M., & Kazemier, G. (2008). Robust surgery loading. European Journal of Operational Research, 185(3), 1038–1050.
Hashemi Doulabi, H., Shabbir, A., George, N. (2020). State-variable modeling for a class of two-stage stochastic optimization problems. Accepted in INFORMS Journal on Computing, available on https://bit.ly/3hMEwTO .
Jafarzadeh Ghoushchi, S., Ramin, R., Saeed Aghasoleimani, N., Elnaz, O., Erfan Babaee, T. (2021). An extended approach to the diagnosis of tumour location in breast cancer using deep learning. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 1–11.
Jebali, A., & Diabat, A. (2015). A stochastic model for operating room planning under capacity constraints. International Journal of Production Research, 53(24), 7252–7270.
Kropat, E., Weber, G.-W., & Tirkolaee, E. B. (2020). Foundations of semialgebraic gene-environment networks. Journal of Dynamics and Games, 7(4), 253.
Lamiri, M., Xie, X., Dolgui, A., & Grimaud, F. (2008). A stochastic model for operating room planning with elective and emergency demand for surgery. European Journal of Operational Research, 185(3), 1026–1037.
Lotfi, R., Kargar, B., Gharehbaghi, A., and Weber, G-W. (2021a). Viable medical waste chain network design by considering risk and robustness. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–16.
Lotfi, R., Zahra, Y., Seyed Hossein, H., Amir Hossein, K., Erfan Babaee, T., Gerhard-Wilhelm, W. (2020). A robust time-cost-quality-energy-environment trade-off with resource-constrained in project management: A case study for a bridge construction project. Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization.
Lotfi, R., Mardani, N., & Weber, G.-W. (2021b). Robust bi-level programming for renewable energy location. International Journal of Energy Research, 45(5), 7521–7534.
Lotfi, R., Mehrjerdi, Y. Z., Pishvaee, M. S., Sadeghieh, A., & Weber, G.-W. (2021c). A robust optimization model for sustainable and resilient closed-loop supply chain network design considering conditional value at risk. Numerical Algebra, Control and Optimization, 11(2), 221.
Marques, I., & Eugénia Captivo, M. (2017). Different stakeholders’ perspectives for a surgical case assignment problem: Deterministic and robust approaches. European Journal of Operational Research, 261(1), 260–278.
Marques, I., Eugénia Captivo, M., & Pato, M. V. (2012). An integer programming approach to elective surgery scheduling. OR Spectrum, 34(2), 407–427.
Mateus, C., Inês Marques, M. C. (2017). Local search heuristics for a surgical case assignment problem. Operations Research for Health Care .
Min, D., & Yih, Y. (2010). Scheduling elective surgery under uncertainty and downstream capacity constraints. European Journal of Operational Research, 206(3), 642–652.
Molina-Pariente, J. M., Fernandez-Viagas, V., & Framinan, J. M. (2015). Integrated operating room planning and scheduling problem with assistant surgeon dependent surgery durations. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 82, 8–20.
Naderi, B., Vahid, R., Begen, M. A., Aleman, D. A., Urbach, D. R. (2021). Increased surgical capacity without additional resources: Generalized operating room planning and scheduling. Production and Operations Management.
Neyshabouri, S., & Berg, B. P. (2017). Two-stage robust optimization approach to elective surgery and downstream capacity planning. European Journal of Operational Research, 260(1), 21–40.
Ogulata, S. N., & Erol, R. (2003). A hierarchical multiple criteria mathematical programming approach for scheduling general surgery operations in large hospitals. Journal of Medical Systems, 27(3), 259–270.
Ozkarahan, I. (2000). Allocation of surgeries to operating rooms by goal programing. Journal of Medical Systems, 24(6), 339–378.
Park, J., Kim, B.-I., Eom, M., & Choi, B. K. (2021). Operating room scheduling considering surgeons’ preferences and cooperative operations. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 157, 107306.
Roshanaei, V., Booth, K. E. C., Aleman, D. M., Urbach, D. R., & Christopher Beck, J. (2020). Branch-and-check methods for multi-level operating room planning and scheduling. International Journal of Production Economics, 220, 107433.
Roshanaei, V., Luong, Curtiss, Aleman, D. M., & Urbach, D. (2017). Propagating logic-based benders’ decomposition approaches for distributed operating room scheduling. European Journal of Operational Research, 257(2), 439–455.
Roshanaei, V., & Naderi, B. (2021). Solving integrated operating room planning and scheduling: Logic-based benders decomposition versus branch-price-and-cut. European Journal of Operational Research, 293(1), 65–78.
Shehadeh, K. S., & Padman, R. (2021). A distributionally robust optimization approach for stochastic elective surgery scheduling with limited intensive care unit capacity. European Journal of Operational Research, 290(3), 901–913.
Tirkolaee, E. B., Abbasian, P., & Weber, G.-W. (2021). Sustainable fuzzy multi-trip location-routing problem for medical waste management during the covid-19 outbreak. Science of the Total Environment, 756, 143607143607.
Vijayakumar, B., Parikh, P. J., Scott, R., Barnes, A., & Gallimore, J. (2013). A dual bin-packing approach to scheduling surgical cases at a publicly-funded hospital. European Journal of Operational Research, 224(3), 583–591.
Vinden, C., Malthaner, R., Jacob McGee, J., McClure, A., Winick-Ng, J., Liu, Kuan, et al. (2016). Teaching surgery takes time: The impact of surgical education on time in the operating room. Canadian Journal of Surgery, 59(2), 87.
Wang, S., Jinlin, L., Chun, P. (2017). Distributionally robust chance-constrained program surgery planning with downstream resource. Service Systems and Service Management (ICSSSM), 2017 International Conference on. IEEE, 1–6.
Wang, Y., Tang, J., & Fung, R. Y. K. (2014). A column-generation-based heuristic algorithm for solving operating theater planning problem under stochastic demand and surgery cancellation risk. International Journal of Production Economics, 158, 28–36.
Zhang, J., Dridi, M., & El Moudni, A. (2020). Column-generation-based heuristic approaches to stochastic surgery scheduling with downstream capacity constraints. International Journal of Production Economics, 229, 107764.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemi Doulabi, H., Khalilpourazari, S. Stochastic weekly operating room planning with an exponential number of scenarios. Ann Oper Res 328, 643–664 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04686-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04686-4