Abstract
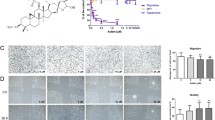
Tumor growth depends on angiogenesis and inducing angiogenesis is one of the most important hallmarks in the cancer development. Treatment with small molecules that inhibit angiogenesis has been an effective strategy for anti-cancer therapy. Some anti-angiogenic factors are derived from traditional Chinese herbs. Usnic acid (UA), an active compound mainly found in lichens, has shown some biological and physiological activities. However, the role and mechanism of UA in tumor angiogenesis are still unknown. The aim of this study was to assess the effects of UA on tumor angiogenesis. In this study, we demonstrated that UA strongly inhibited in vivo angiogenesis in a chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane assay and vascular endothelial growth factor-induced mouse corneal angiogenesis model. In a mouse xenograft tumor model, UA suppressed Bcap-37 breast tumor growth and angiogenesis without affecting mice body weight. In an in vitro assay, UA not only significantly inhibited endothelial cell proliferation, migration and tube formation, but also induced morphological changes and apoptosis in endothelial cells. In addition, UA inhibited Bcap-37 tumor cell proliferation. Moreover, western blot analysis of cell signaling molecules indicated that UA blocked vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) 2 mediated Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2(ERK1/2) and AKT/P70S6K signaling pathways in endothelial cells. These results provided the first evidence of the biological function and molecular mechanism of UA in tumor angiogenesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Thairu N, Kiriakidis S, Dawson P, Paleolog E (2011) Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in arthritis in 2011: learning the lessons of the colorectal cancer experience. Angiogenesis. doi:10.1007/s10456-011-9208-2
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100(1):57–70. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81683-9
Cao R, Eriksson A, Kubo H, Alitalo K, Cao Y, Thyberg J (2004) Comparative evaluation of FGF-2-, VEGF-A-, and VEGF-C-induced angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, vascular fenestrations, and permeability. Circ Res 94(5):664–670. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000118600.91698.BB
Ferrara N (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25(4):581–611. doi:10.1210/er.2003-0027
Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M, Kraus AE, Gale D, White GC II, Vansluys J (2008) Defective angiogenesis, endothelial migration, proliferation, and MAPK signaling in Rap1b-deficient mice. Blood 111(5):2647–2656. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-08-109710
Jiang BH, Liu LZ (2008) AKT signaling in regulating angiogenesis. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8(1):19–26
Abu-Ghazaleh R, Kabir J, Jia H, Lobo M, Zachary I (2001) Src mediates stimulation by vascular endothelial growth factor of the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase at tyrosine 861, and migration and anti-apoptosis in endothelial cells. Biochem J 360(Pt 1):255–264
Pyun BJ, Choi S, Lee Y, Kim TW, Min JK, Kim Y, Kim BD, Kim JH, Kim TY, Kim YM, Kwon YG (2008) Capsiate, a nonpungent capsaicin-like compound, inhibits angiogenesis and vascular permeability via a direct inhibition of Src kinase activity. Cancer Res 68(1):227–235. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2799
Somanath PR, Razorenova OV, Chen J, Byzova TV (2006) Akt1 in endothelial cell and angiogenesis. Cell Cycle 5(5):512–518. doi:10.4161/cc.5.5.2538
Berra E, Milanini J, Richard DE, Le Gall M, Vinals F, Gothie E, Roux D, Pages G, Pouyssegur J (2000) Signaling angiogenesis via p42/p44 MAP kinase and hypoxia. Biochem Pharmacol 60(8):1171–1178. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(00)00423-8
Pages G, Milanini J, Richard DE, Berra E, Gothie E, Vinals F, Pouyssegur J (2000) Signaling angiogenesis via p42/p44 MAP kinase cascade. Ann N Y Acad Sci 902:187–200
Cabebe E, Wakelee H (2006) Sunitinib: a newly approved small-molecule inhibitor of angiogenesis. Drugs Today (Barc) 42(6):387–398. doi:10.1358/dot.2006.42.6.985633
Kane RC, Farrell AT, Saber H, Tang S, Williams G, Jee JM, Liang C, Booth B, Chidambaram N, Morse D, Sridhara R, Garvey P, Justice R, Pazdur R (2006) Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 12(24):7271–7278. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1249
Cocchietto M, Skert N, Nimis PL, Sava G (2002) A review on usnic acid, an interesting natural compound. Naturwissenschaften 89(4):137–146
Guo L, Shi Q, Fang JL, Mei N, Ali AA, Lewis SM, Leakey JE, Frankos VH (2008) Review of usnic acid and usnea barbata toxicity. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 26(4):317–338. doi:10.1080/10590500802533392
O’Neill MA, Mayer M, Murray KE, Rolim-Santos HM, Santos-Magalhaes NS, Thompson AM, Appleyard VC (2010) Does usnic acid affect microtubules in human cancer cells? Braz J Biol 70(3):659–664. doi:10.1590/S1519-69842010005000013
Einarsdottir E, Groeneweg J, Bjornsdottir GG, Harethardottir G, Omarsdottir S, Ingolfsdottir K, Ogmundsdottir HM (2010) Cellular mechanisms of the anticancer effects of the lichen compound usnic acid. Planta Med 76(10):969–974. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1240851
da Silva Santos NP, Nascimento SC, Wanderley MS, Pontes-Filho NT, da Silva JF, de Castro CM, Pereira EC, da Silva NH, Honda NK, Santos-Magalhaes NS (2006) Nanoencapsulation of usnic acid: an attempt to improve antitumour activity and reduce hepatotoxicity. Euro J Pharm Biopharm 64(2):154–160. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2006.05.018
Mayer M, O’Neill MA, Murray KE, Santos-Magalhaes NS, Carneiro-Leao AM, Thompson AM, Appleyard VC (2005) Usnic acid: a non-genotoxic compound with anti-cancer properties. Anticancer Drugs 16(8):805–809. doi:10.1097/01.cad.0000175588.09070.77
Gupta GP, Nguyen DX, Chiang AC, Bos PD, Kim JY, Nadal C, Gomis RR, Manova-Todorova K, Massague J (2007) Mediators of vascular remodelling co-opted for sequential steps in lung metastasis. Nature 446(7137):765–770. doi:10.1038/nature05760
Ye H, Jin L, Hu R, Yi Z, Li J, Wu Y, Xi X, Wu Z (2006) Poly(gamma,l-glutamic acid)-cisplatin conjugate effectively inhibits human breast tumor xenografted in nude mice. Biomaterials 27(35):5958–5965. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.08.016
Cho SG, Yi Z, Pang X, Yi T, Wang Y, Luo J, Wu Z, Li D, Liu M (2009) Kisspeptin-10, a KISS1-derived decapeptide, inhibits tumor angiogenesis by suppressing Sp1-mediated VEGF expression and FAK/Rho GTPase activation. Cancer Res 69(17):7062–7070. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0476
Yi ZF, Cho SG, Zhao H, Wu YY, Luo J, Li D, Yi T, Xu X, Wu Z, Liu M (2009) A novel peptide from human apolipoprotein(a) inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth by targeting c-Src phosphorylation in VEGF-induced human umbilical endothelial cells. Int J Cancer 124(4):843–852. doi:10.1002/ijc.24027
Pang X, Yi Z, Zhang X, Sung B, Qu W, Lian X, Aggarwal BB, Liu M (2009) Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid inhibits prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis. Cancer Res 69(14):5893–5900. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0755
Dong Y, Lu B, Zhang X, Zhang J, Lai L, Li D, Wu Y, Song Y, Luo J, Pang X, Yi Z, Liu M (2010) Cucurbitacin E, a tetracyclic triterpenes compound from Chinese medicine, inhibits tumor angiogenesis through VEGFR2-mediated Jak2-STAT3 signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis 31(12):2097–2104. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq167
Yi T, Yi Z, Cho SG, Luo J, Pandey MK, Aggarwal BB, Liu M (2008) Gambogic acid inhibits angiogenesis and prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 signaling. Cancer Res 68(6):1843–1850. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5944
Ribatti D, Vacca A, Roncali L, Dammacco F (1996) The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane as a model for in vivo research on angiogenesis. Int J Dev Biol 40(6):1189–1197
Tozer GM, Kanthou C, Baguley BC (2005) Disrupting tumour blood vessels. Nat Rev Cancer 5(6):423–435. doi:10.1038/nrc1628
Rousseau S, Houle F, Landry J, Huot J (1997) p38 MAP kinase activation by vascular endothelial growth factor mediates actin reorganization and cell migration in human endothelial cells. Oncogene 15(18):2169–2177. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201380
Patan S (2004) Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Cancer Treat Res 117:3–32
Lynch CN, Wang YC, Lund JK, Chen YW, Leal JA, Wiley SR (1999) TWEAK induces angiogenesis and proliferation of endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 274(13):8455–8459
Strasser A, O’Connor L, Dixit VM (2000) Apoptosis signaling. Annu Rev Biochem 69:217–245. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.217
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA, Lowe SW (2002) Apoptosis: a link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell 108(2):153–164. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00625-6
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC (1997) A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 3(8):917–921
Yang D, Welm A, Bishop JM (2004) Cell division and cell survival in the absence of survivin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(42):15100–15105. doi:10.1073/pnas.0406665101
Kawasaki H, Toyoda M, Shinohara H, Okuda J, Watanabe I, Yamamoto T, Tanaka K, Tenjo T, Tanigawa N (2001) Expression of survivin correlates with apoptosis, proliferation, and angiogenesis during human colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer 91(11):2026–2032. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(20010601)91:11<2026:AID-CNCR1228>3.0.CO;2-E
Conway EM, Zwerts F, Van Eygen V, DeVriese A, Nagai N, Luo W, Collen D (2003) Survivin-dependent angiogenesis in ischemic brain: molecular mechanisms of hypoxia-induced up-regulation. Am J Pathol 163(3):935–946
Tu SP, Jiang XH, Lin MC, Cui JT, Yang Y, Lum CT, Zou B, Zhu YB, Jiang SH, Wong WM, Chan AO, Yuen MF, Lam SK, Kung HF, Wong BC (2003) Suppression of survivin expression inhibits in vivo tumorigenicity and angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Cancer Res 63(22):7724–7732
Li QX, Zhao J, Liu JY, Jia LT, Huang HY, Xu YM, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Wang CJ, Yao LB, Chen SY, Yang AG (2006) Survivin stable knockdown by siRNA inhibits tumor cell growth and angiogenesis in breast and cervical cancers. Cancer Biol Ther 5(7):860–866. doi:10.4161/cbt.5.7.2893
Caldas H, Fangusaro JR, Boue DR, Holloway MP, Altura RA (2007) Dissecting the role of endothelial SURVIVIN DeltaEx3 in angiogenesis. Blood 109(4):1479–1489. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-02-003749
Botto S, Streblow DN, Defilippis V, White L, Kreklywich CN, Smith PP, Caposio P (2010) IL-6 in human cytomegalovirus secretome promotes angiogenesis and survival of endothelial cells through the stimulation of survivin. Blood. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-06-291245
Lohela M, Bry M, Tammela T, Alitalo K (2009) VEGFs and receptors involved in angiogenesis versus lymphangiogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21(2):154–165. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2008.12.012
Risau W (1997) Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 386(6626):671–674. doi:10.1038/386671a0
Yap TA, Garrett MD, Walton MI, Raynaud F, de Bono JS, Workman P (2008) Targeting the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway: progress, pitfalls, and promises. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8(4):393–412. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2008.08.004
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129(7):1261–1274. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.009
Olszewska-Pazdrak B, Hein TW, Olszewska P, Carney DH (2009) Chronic hypoxia attenuates VEGF signaling and angiogenic responses by downregulation of KDR in human endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296(5):C1162–C1170. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00533.2008
Surh YJ (2003) Cancer chemoprevention with dietary phytochemicals. Nat Rev Cancer 3(10):768–780. doi:10.1038/nrc1189
Tufan AC, Satiroglu-Tufan NL (2005) The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane as a model system for the study of tumor angiogenesis, invasion and development of anti-angiogenic agents. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 5(4):249–266
Schwartz S, George J, Ben-Shoshan J, Luboshits G, Avni I, Levkovitch-Verbin H, Ziv H, Rosner M, Barak A (2008) Drug modification of angiogenesis in a rat cornea model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49(1):250–254. doi:10.1167/iovs.06-1337
Jablonska J, Leschner S, Westphal K, Lienenklaus S, Weiss S (2010) Neutrophils responsive to endogenous IFN-beta regulate tumor angiogenesis and growth in a mouse tumor model. J Clin Investig 120(4):1151–1164. doi:10.1172/JCI37223
Wedge SR, Ogilvie DJ, Dukes M, Kendrew J, Chester R, Jackson JA, Boffey SJ, Valentine PJ, Curwen JO, Musgrove HL, Graham GA, Hughes GD, Thomas AP, Stokes ES, Curry B, Richmond GH, Wadsworth PF, Bigley AL, Hennequin LF (2002) ZD6474 inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor signaling, angiogenesis, and tumor growth following oral administration. Cancer Res 62(16):4645–4655
Murphy DA, Makonnen S, Lassoued W, Feldman MD, Carter C, Lee WM (2006) Inhibition of tumor endothelial ERK activation, angiogenesis, and tumor growth by sorafenib (BAY43-9006). Am J Pathol 169(5):1875–1885. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.050711
Acknowledgments
We thank all members in the laboratory of Dr.Mingyao Liu’s lab at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences and School of Life Sciences, East China Normal University. This study was partially sponsored by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (2012CB910400, 2009CB918402). National Natural Science Foundation of China (30930055, 30971523, 81071807) and The Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (11DZ2260300).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., Dai, F., Zhai, D. et al. Usnic acid inhibits breast tumor angiogenesis and growth by suppressing VEGFR2-mediated AKT and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Angiogenesis 15, 421–432 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9270-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9270-4