Abstract
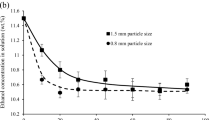
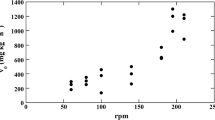
The objective of this manuscript was to elucidate the main mechanism of mass transport involved in intraparticle diffusion during the adsorption of phenol, methylene blue (MB), and methyl blue (MTB) on granular activated carbon (AC F400) by using three diffusional models: (i) pore volume diffusion model (PVDM), (ii) pore volume and surface diffusion model (PVSDM), and (iii) surface diffusion model (SDM). Results revealed that the molecular size of the organic compounds as well as its adsorption capacity considerably affect their overall adsorption rate as well as controlling the mass transfer mechanism. The PVSDM model, which assumes that pore volume and surface diffusion are both important in intraparticle diffusion, satisfactorily fitted the experimental data. The percentage contribution of surface diffusion to overall intraparticle diffusion was >82 % for phenol, 19 % for MTB and 5–95 % for MB. These results confirmed that the controlling mechanism of the overall adsorption rate on AC F400 is surface diffusion for phenol and pore volume diffusion for MTB, while both diffusion mechanisms are important in the adsorption of MB. The SDM modeled reasonably well the concentration decay data for phenol adsorption under different experimental conditions. Furthermore, it was found that surface diffusion coefficient values augmented as the amount of phenol adsorbed at equilibrium increased. The PVDM model fitted the experimental MTB decay data reasonably well, showing that the tortuosity factor of AC F400 ranged from 3 to 5. The external mass transport did not affect the overall rate of phenol, MB and MTB adsorption on AC F400.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Abbreviations
- a:
-
Prausnitz–Radke isotherm constant (L/g)
- b:
-
Prausnitz–Radke isotherm constant (mmol−βLβ)
- CA :
-
Concentration of adsorbate in aqueous solution (mmol/L)
- CA0 :
-
Initial concentration of adsorbate in aqueous solution (mmol/L)
- CAr :
-
Concentration of adsorbate within the particle at distance r (mmol/L)
- CAr∣r=Rp :
-
Concentration of adsorbate at the external surface of the particle at r = Rp (mmol/L)
- dp :
-
Average pore diameter (nm)
- DAB :
-
Molecular diffusion coefficient at infinite dilution (cm2/s)
- Dep :
-
Effective pore volume diffusion coefficient (cm2/s)
- Ds :
-
Surface diffusion coefficient (cm2/s)
- kL :
-
External mass transfer coefficient in liquid phase (cm/s)
- m:
-
Mass of adsorbent (g)
- qe :
-
Amount of adsorbate adsorbed at equilibrium (mmol/g)
- qexp :
-
Experimental amount of solute adsorbed (mmol/g)
- qpred :
-
Amount of solute adsorbed predicted with the isotherm model (mmol/g)
- r:
-
Radial distance (cm)
- Rp :
-
Radius of the particle (cm)
- S:
-
External surface area per mass of adsorbent (cm2/g)
- V:
-
Volume of the solution (mL)
- β:
-
Prausnitz–Radke isotherm constant
- εp :
-
Void fraction of AC F400 particles
- ρp :
-
Density of adsorbent particles (g/mL)
- τ:
-
Tortuosity factor
- ϕA :
-
Dimensionless concentration of adsorbate in the solution
- ϕexp :
-
Experimental dimensionless concentration of adsorbate in the solution
- ϕpred :
-
Dimensionless concentration of adsorbate in the solution predicted with the diffusional models
References
Al Duri, B., Mckay, G.: Basic dye adsorption on carbon using a solid-phase diffusion model. Chem. Eng. J. 38, 23–31 (1988)
Cañizares, P., Carmona, M., Baraza, O., Delgado, A., Rodrigo, M.A.: Adsorption equilibrium of phenol onto chemically modified activated carbon F400. J. Hazard. Mater. 131, 243–248 (2006)
Chiang, Y., Chiang, P., Huang, C.: Effects of pore structure and temperature on VOC adsorption on activated carbon. Carbon 39, 523–534 (2001)
Choong, T.S.Y., Wong, T.N., Chuah, T.G., Idris, A.: Film-pore-concentration-dependent surface diffusion model for the adsorption of dye onto palm kernel shell activated carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 301, 436–440 (2006)
Choy, K.K.H., Porter, J.F., McKay, G.: Film-surface diffusion during the adsorption of acid dyes onto activated carbon. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 79, 1181–1188 (2004)
Diaz-Flores, P.E., Leyva-Ramos, R., Guerrero-Coronado, R.M., Mendoza-Barron, J.: Adsorption of pentachlorophenol from aqueous solution onto activated carbon fiber. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45, 330–336 (2006)
Do, D.D.: Adsorption Analysis: Equilibria and Kinetics. Imperial College Press, London (1998)
El Qada, E.N., Allen, S.J., Walker, G.M.: Adsorption of basic dyes from aqueous solution onto activated carbons. Chem. Eng. J. 135, 174–184 (2008)
Fulazzaky, M.A.: Determining the resistance of mass transfer for adsorption of the surfactants onto granular activated carbons from hydrodynamic column. Chem. Eng. J. 166, 832–840 (2011)
Furusawa, T., Smith, J.M.: Fluid-particle and intraparticle mass transport rates in slurries. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 12, 197–203 (1973)
Gil, A., Grange, P.: Application of the Dubinin–Radushkevich and Dubinin–Astakhov equations in the characterization of microporous solids. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 113, 39–50 (1996)
Karimi-Jashni, A., Narbaitz, R.M.: Impact of pH on the adsorption and desorption kinetics of 2-nitrophenol on activated carbons. Water Res. 31, 3039–3044 (1997)
Kim, S.J., Kim, S.J., Kim, T.Y., Cho, S.Y.: A study of adsorption behavior of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid onto various GACs. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 19, 1050–1058 (2002)
Leyva-Ramos, R., Geankoplis, C.J.: Diffusion in liquid-filled pores of activated carbon. I. Pore volume diffusion. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 72, 262–271 (1994)
Leyva-Ramos, R., Bernal-Jacome, L.A., Mendoza-Barron, J., Hernandez-Orta, M.M.G.: Kinetic modeling of pentachlorophenol adsorption onto granular activated carbon. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 40, 622–629 (2009)
Mahmudov, R., Huang, C.P.: Selective adsorption of oxyanions on activated carbon exemplified by Filtrasorb 400 (F400). Sep. Purif. Technol. 77, 294–300 (2011)
Mohan, D., Pittman Jr, C.U., Bricka, M., Smith, F., Yancey, B., Mohammad, J., Steele, P.H., Alexandre-Franco, M.F., Gómez-Serrano, V., Gong, H.: Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 310, 57–73 (2007)
Ocampo-Perez, R., Leyva-Ramos, R., Alonso-Davila, P., Rivera-Utrilla, J., Sanchez-Polo, M.: Modeling adsorption rate of pyridine onto granular activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 165, 133–141 (2010)
Poling, B.E., Prausnitz, M., O’Connell, J.P.: The Properties of Gases and Liquids. McGraw-Hill, USA (2006)
Rivera-Utrilla, J., Sánchez-Polo, M., Gómez-Serrano, V., Álvarez, P.M., Alvim-Ferraz, M.C.M., Dias, J.M.: Activated carbon modifications to enhance its water treatment applications. An overview. J. Hazard. Mater. 187, 1–23 (2011)
Sotelo, J.L., Ovejero, G., Delgado, J.A., Martínez, I.: Adsorption of lindane from water onto GAC: Effect of carbon loading on kinetic behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 87, 111–120 (2002)
Suzuki, M.: Adsorption Engineering. Elsevier, Japan (1990)
Sze, M.F.F., McKay, G.: Enhanced mitigation of para-chlorophenol using stratified activated carbon adsorption columns. Water Res. 46, 700–710 (2012)
Traegner, U.K., Suidan, M.T.: Parameter evaluation for carbon adsorption. J. Environ. Eng. 115, 109–128 (1989)
Verma, Y.: Toxicity assessment of dye containing industrial effluents by acute toxicity test using Daphnia magna. Toxicol. Ind. Health 27, 41–49 (2011)
Wibowo, N., Setyadhi, L., Wibowo, D., Setiawan, J., Ismadji, S.: Adsorption of benzene and toluene from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon and its acid and heat treated forms: Influence of surface chemistry on adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 146, 237–242 (2007)
Yang, X., Al-Duri, B.: Kinetic modeling of liquid-phase adsorption of reactive dyes on activated carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 287, 25–34 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ocampo-Pérez, R., Leyva-Ramos, R., Sanchez-Polo, M. et al. Role of pore volume and surface diffusion in the adsorption of aromatic compounds on activated carbon. Adsorption 19, 945–957 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-013-9502-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-013-9502-y