Abstract
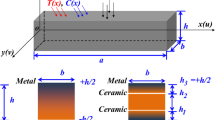
In the present study, the vibration behavior of laminated sandwich plate resting on a two-parameter elastic foundation, containing embedded magnetostrictive actuating layers and homogeneous core, is investigated. The plate is subjected to three different types of hygrothermal environments: uniform, linear and nonlinear distributions. The system associated with the vibration problem for the simply supported rectangular plate under the hygrothermal effect is derived based on Hamilton’s principle. The system solutions are obtained depending on Navier’s technique. Parametric effects due to the elastic foundation, smart layer location, lamination schemes, mode numbers, feedback gain control value, thickness ratio, aspect ratio, core thickness-to-fiber reinforced layer thickness ratio, magnetostrictive layer thickness to fiber-reinforced layer thickness ratio, temperature and moisture factors on vibration characteristics of the structure, are analyzed and discussed in detail. Numerical results can be useful as a benchmark for future studies of hygro-thermo-dynamic influences on structural applications in various fields as well as the suggested model can be contributed to the development of vibration control of advanced structural applications.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not Applicable.
References
Daniel, I.M., Ishai, O.: Engineering mechanics of composite materials. Oxford University Press, New York (1994)
Kapania, R.K., Raciti, S.: Recent advances in analysis of laminated beams and plates, part I: shear effects and buckling. AIAA J. 27, 923–934 (1989)
Kapania, R.K., Raciti, S.: Recent advances in analysis of laminated beams and plates, part II: vibration and wave propagation. AIAA J. 27, 935–946 (1989)
King, T.R., Blackketter, D.M., Walrath, D.E., Adams, D.F.: Micromechanics prediction of the shear strength of carbon fiber/epoxy matrix composites: the influence of the matrix and interface strengths. J. Compos. Mater. 26(4), 558–573 (1992)
Zenkour, A.M., Radwan, A.F.: Analysis of multilayered composite plates resting on elastic foundations in thermal environment using a hyperbolic model. J. Brazilian Society Mech. Sci. Eng. 39(7), 2801–2816 (2017)
Arefi, M., Zenkour, A.M.: Electro-magneto-elastic analysis of a three-layer curved beam. Smart Struct. Sys. 19(6), 695–703 (2017)
Kolahchi, R., Zarei, M.S., Hajmohammad, M.H., Nouri, A.: Wave propagation of embedded viscoelastic FG-CNT-reinforced sandwich plates integrated with sensor and actuator based on refined zigzag theory. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 130, 534–545 (2017)
Anjanappa, M., Bi, J.: Modelling, design and control of embedded Terfenol-D actuator. Smart Struct. Intel. Sys. 908–918, 1993 (1917)
Anjanappa, M., Bi, J.: A theoretical and experimental study of magnetostrictive mini actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 1, 83–91 (1994)
Reddy, J.N.: Mechanics of laminated composite plates: Theory and analysis, Boca Raton. CRC Press, FL (1997)
Hiller, M.W., Bryant, M.D., Umegaki, J.: Attenuation and transformation of vibration through active control of magnetostrictive Terfenol. J. Sound Vib. 134, 507–519 (1989)
Reddy, J.N., Barbosa, J.I.: On vibration suppression of magnetostrictive beams. Smart Mater. Struct. 9, 49–58 (2000)
Pradhan, S.C., Ng, T.Y., Lam, K.Y., Reddy, J.N.: Control of laminated composite plates using magnetostrictive layers. Smart Mater. Struct. 10, 657–667 (2001)
Zhang, Y., Zhou, H., Zhou, Y.: Vibration suppression of cantilever laminated composite plate with nonlinear giant magnetostrictive material layers. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 28, 50–60 (2015)
Subramanian, P.: Vibration suppression of symmetric laminated composite beams. Smart Mater. Struct. 11(6), 880–885 (2002)
Bhattacharya, B., Vidyashankar, B.R., Patsias, S., Tomlinson, G.R.: Active and passive vibration control of flexible structures using a combination of magnetostrictive and ferro-magnetic alloys. Proc. SPIE, Smart Struct. Mater. 4073, 204–214 (2000)
Kumar, J.S., Ganesan, N., Swarnamani, S., Padmanabhan, C.: Active control of beam with magnetostrictive layer. Comput. Struct. 81(13), 1375–1382 (2003)
Ghosh, D.P., Gopalakrishnan, S.: Coupled analysis of composite laminate with embedded magnetostrictive patches. Smart Mater. Struct. 14(6), 1462–1473 (2005)
Zhou, H.M., Zhou, Y.H.: Vibration suppression of laminated composite beams using actuators of giant magnetostrictive materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 16(1), 198–206 (2007)
Murty, A.V.K., Anjanappa, M., Wu, Y.-F.: The use of magnetostrictive particle actuators for vibration attenuation of flexible beams. J. Sound Vib. 206(2), 133–149 (1997)
Kumar, J.S., Ganesan, N., Swarnamani, S., Padmanabhan, C.: Active control of simply supported plates with a magnetostrictive layer. Smart Mater. Struct. 13(3), 487–492 (2004)
Suman, S.D., Hirwani, C.K.A.: Chaturvedi, S. K. Panda, Effect of magnetostrictive material layer on the stress and deformation behaviour of laminated structure. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 178, 012026 (2017)
Reddy, J.N.: On laminated composite plates with integrated sensors and actuators. Eng. Struct. 21(7), 568–593 (1999)
Koconis, D.B., Kollar, L.P., Springer, G.S.: Shape control of composite plates and shells with embedded actuators I: voltage specified. J. Compos. Mater. 28, 415–458 (1994)
Lee, S.J., Reddy, J.N., Rostamabadi, F.: Transient analysis of laminated composite plates with embedded smart-material layers. Fin. Elem. Anal. Des. 40, 463–483 (2004)
Zenkour, A.M., El-Shahrany, H.D.: Vibration suppression analysis for laminated composite beams contain actuating magnetostrictive layers. J. Computat. Appl. Mech. 50(1), 69–75 (2019)
Zenkour, A.M., El-Shahrany, H.D.: Control of a laminated composite plate resting on Pasternak’s foundations using magnetostrictive layers. Arch. Appl. Mech. 90, 1943–1959 (2020)
Zenkour, A.M., El-Shahrany, H.D.: Hygrothermal vibration of adaptive composite magnetostrictive laminates supported by elastic substrate medium. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids. 85, 104140 (2021)
Santapuri, S., Scheidler, J.J., Dapino, M.J.: Two-dimensional dynamic model for composite laminates with embedded magnetostrictive materials. Compos. Struct. 132, 737–745 (2015)
Anjanappa, M., Bi, J.: Magnetostrictive mini actuators for smart structural application. Smart Mater. Struct. 3, 383–390 (1994)
Pradhan, S.C.: Vibration suppression of FGM shells using embedded magnetostrictive layers. Int. J. Solids Struct. 42, 2465–2488 (2005)
Shankar, G., Kumar, S.K., Mahato, P.K.: Vibration analysis and control of smart composite plates with delamination and under hygrothermal environment. Thin-Walled Struct. 116, 53–68 (2017)
Hong, C.C.: Transient responses of magnetostrictive plates without shear effects. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 47(3), 355–362 (2009)
Hong, C.C.: Transient responses of magnetostrictive plates by using the GDQ method. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids. 29(6), 1015–1021 (2010)
Xiao, Y., Gou, X.-F., Zhang, D.-G.: A one-dimension nonlinear hysteretic constitutive model with elasto-thermo-magnetic coupling for giant magnetostrictive materials. J. Magnetism Magnetic Mater. 441, 642–649 (2017)
Zenkour, A.M., Sobhy, M.: Nonlocal piezo-hygrothermal analysis for vibration characteristics of a piezoelectric Kelvin-Voigt viscoelastic nanoplate embedded in a viscoelastic medium. Acta Mech. 229(1), 3–19 (2018)
Zenkour, A.M.: Bending analysis of piezoelectric exponentially graded fiber reinforced composite cylinders in hygrothermal environments. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Design 13(4), 515–529 (2017)
Arefi, M., Zenkour, A.M.: Employing sinusoidal shear deformation plate theory for transient analysis of three layers sandwich nanoplate integrated with piezo-magnetic face-sheets. Smart Mater. Struct. 25, 115040 (2016)
Zenkour, A.M., El-Shahrany, H.D.: Hygrothermal effect on vibration of magnetostrictive viscoelastic sandwich plates supported by Pasternak’s foundations. Thin-Walled Struct. 157, 107007 (2020)
Acknowledgements
Not Applicable.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception or design of the work – Dr. H. D. El-Shahrany, Prof. A. M. Zenkour.
Data collection – Dr. H. D. El-Shahrany.
Data analysis and interpretation – Prof. A. M. Zenkour.
Drafting the article – Dr. H. D. El-Shahrany.
Critical revision of the article – Prof. A. M. Zenkour.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The authors disclose that this manuscript is not submitted to any other journal and is an unpublished work.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
As a corresponding author, I give my consent for the publication of identifiable details within the text to be published in the above Journal and Article.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix A
The coefficients \({\overline{Q} }_{ij}^{\left(r\right)}\), \({\overline{q} }_{ij}\), \({\stackrel{\sim }{\alpha }}_{l}\) and \({\stackrel{\sim }{\beta }}_{l}\), \(l=xx,yy, xy\) appeared in Eq. (7) and Eq. (9) are described as.
in which \({E}_{i}\), \({v}_{ij}\), \({G}_{ij}\), \({\alpha }_{ij}\) and \({\beta }_{ij}\) are Young’s moduli, Poisson’s ratios, shear moduli, the thermal and hygroscopic expansion coefficients, respectively. Besides, the coefficients \({q}_{ij}\) are the magnetostrictive modules.
Appendix B
The coefficients \({\widehat{S}}_{ij},{\widehat{M}}_{ij}\) and \({\widehat{C}}_{ij}\) (\(i=1, 2, 3\)) appeared in Eq. (35) are obtained as the following.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zenkour, A.M., El-Shahrany, H.D. Hygrothermal Vibration and Damping Behavior of Magnetostrictive Sandwich Plate Resting On Pasternak’s Foundations. Appl Compos Mater 29, 803–828 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-021-09970-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-021-09970-3