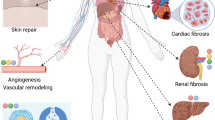
Abstract
Apoptosis is a highly conserved physiological process of programmed cell death which is critical for proper organism development, tissue maintenance, and overall organism homeostasis. Proper regulation of cell removal is crucial, as both excessive and reduced apoptotic rates can lead to the onset of a variety of diseases. Apoptosis can be induced in cells in response to biochemical, electrical, and mechanical stimuli. Here, we review literature on specific mechanical stimuli that regulate apoptosis and the current understanding of how mechanotransduction plays a role in apoptotic signaling. We focus on how insufficient or excessive mechanical forces may induce apoptosis in the cardiovascular system and thus contribute to cardiovascular disease. Although studies have demonstrated that a broad range of mechanical stimuli initiate and/or potentiate apoptosis, they are predominantly correlative, and no mechanisms have been established. In this review, we attempt to establish a unifying mechanism for how various mechanical stimuli initiate a single cellular response, i.e. apoptosis. We hypothesize that the cytoskeleton plays a central role in this process as it does in determining myriad cell behaviors in response to mechanical inputs. We also describe potential approaches of using mechanomedicines to treat various diseases by altering apoptotic rates in specific cells. The goal of this review is to summarize the current state of the mechanobiology field and suggest potential avenues where future research can explore.



(a–d) Images are adapted from Narula et al.96





Figure is adapted from Chan et al.11

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anesti, V., and L. Scorrano. The relationship between mitochondrial shape and function and the cytoskeleton. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1757:692–699, 2006.
Aragona, M., T. Panciera, A. Manfrin, S. Giulitti, F. Michielin, N. Elvassore, S. Dupont, and S. Piccolo. A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell 154:1047–1059, 2013.
Araki, S., Y. Shimada, K. Kaji, and H. Hayashi. Apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells by fibroblast growth factor deprivation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 168:1194–1200, 1990.
Arstall, M. A., D. B. Sawyer, R. Fukazawa, and R. A. Kelly. Cytokine-mediated apoptosis in cardiac myocytes. Circ. Res. 85:829–840, 1999.
Asakura, T., and T. Karino. Flow patterns and spatial distribution of atherosclerotic lesions in human coronary arteries. Circ. Res. 66:1045–1066, 1990.
Bailey, R. W., T. Nguyen, L. Robertson, E. Gibbons, J. Nelson, R. E. Christensen, J. P. Bell, A. M. Judd, and J. D. Bell. Sequence of physical changes to the cell membrane during glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in S49 lymphoma cells. Biophys. J. 96:2709–2718, 2009.
Banerjee, I., J. Zhang, T. Moore-Morris, E. Pfeiffer, K. S. Buchholz, A. Liu, K. Ouyang, M. J. Stroud, L. Gerace, S. M. Evans, A. McCulloch, and J. Chen. Targeted ablation of nesprin 1 and nesprin 2 from murine myocardium results in cardiomyopathy, altered nuclear morphology and inhibition of the biomechanical gene response. PLoS Genet. 10:e1004114, 2014.
Bing, O. H. L. Hypothesis: apoptosis may be a mechanism for the transition to heart failure with chronic Pressure overload. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 26:943–948, 1994.
Bortner, C. D., and J. A. Cidlowski. Ion channels and apoptosis in cancer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 369:1–9, 2014.
Califano, J. P., and C. A. Reinhart-King. Substrate stiffness and cell area predict cellular traction stresses in single cells and cells in contact. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 3:68–75, 2010.
Chan, D. D., W. S. Van Dyke, M. Bahls, S. D. Connell, P. Critser, J. E. Kelleher, M. A. Kramer, S. M. Pearce, S. Sharma, and C. P. Neu. Mechanostasis in apoptosis and medicine. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 106:517–524, 2011.
Chang, J., M. Xie, V. R. Shah, M. D. Schneider, M. L. Entman, L. Wei, and R. J. Schwartz. Activation of Rho-associated coiled-coil protein kinase 1 (ROCK-1) by caspase-3 cleavage plays an essential role in cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:14495–14500, 2006.
Chaudhuri, O., L. Gu, D. Klumpers, M. Darnell, S. A. Bencherif, J. C. Weaver, N. Huebsch, H.-P. Lee, E. Lippens, G. N. Duda, and D. J. Mooney. Hydrogels with tunable stress relaxation regulate stem cell fate and activity. Nat. Mater. 15:326–334, 2015.
Chen, B., G. Kumar, C. C. Co, and C.-C. Ho. Geometric control of cell migration. Sci. Rep. 3:2827, 2013.
Chen, C. S., M. Mrksich, S. Huang, G. M. Whitesides, and D. E. Ingber. Geometric control of cell life and death. Science 276:1425–1428, 1997.
Chiong, M., Z. V. Wang, Z. Pedrozo, D. J. Cao, R. Troncoso, M. Ibacache, A. Criollo, A. Nemchenko, J. Hill, and S. Lavandero. Cardiomyocyte death: mechanisms and translational implications. Cell Death Dis. 2:e244, 2011.
Cirka, H., M. Monterosso, N. Diamantides, J. Favreau, Q. Wen, and K. Billiar. Active traction force response to long-term cyclic stretch is dependent on cell pre-stress. Biophys. J. 110:1845–1857, 2016.
Cirka, H. A., J. Uribe, V. Liang, F. J. Schoen, and K. L. Billiar. Reproducible in vitro model for dystrophic calcification of cardiac valvular interstitial cells: insights into the mechanisms of calcific aortic valvular disease. Lab Chip 17:814–829, 2017.
Clark, R. S. B., P. M. Kochanek, M. Chen, S. C. Watkins, D. W. Marion, J. Chen, R. L. Hamilton, J. E. Loeffert, and S. H. Graham. Increases in Bcl-2 and cleavage of caspase-1 and caspase-3 in human brain after head injury. FASEB J. 13:813–821, 1999.
Clarke, M. C. H., N. Figg, J. J. Maguire, A. P. Davenport, M. Goddard, T. D. Littlewood, and M. R. Bennett. Apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells induces features of plaque vulnerability in atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 12:1075–1080, 2006.
Clarke, M. C. H., T. D. Littlewood, N. Figg, J. J. Maguire, A. P. Davenport, M. Goddard, and M. R. Bennett. Chronic apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells accelerates atherosclerosis and promotes calcification and medial degeneration. Circ. Res. 102:1529–1538, 2008.
Codelia, V. A., G. Sun, and K. D. Irvine. Regulation of YAP by mechanical strain through Jnk and Hippo signaling. Curr. Biol. 24:2012–2017, 2017.
Cui, Y., F. M. Hameed, B. Yang, K. Lee, C. Q. Pan, S. Park, and M. Sheetz. Cyclic stretching of soft substrates induces spreading and growth. Nat. Commun. 6:6333–6340, 2015.
Czabotar, P. E., G. Lessene, A. Strasser, and J. M. Adams. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15:49–63, 2014.
Darzynkiewicz, Z., D. Galkowski, and H. Zhao. Analysis of apoptosis by cytometry using TUNEL assay. Methods 44:250–254, 2008.
Darzynkiewicz, Z., and H. Zhao. Detection of DNA strand breaks in apoptotic cells by flow- and image-cytometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 682:91–101, 2011.
Desouza, M., P. W. Gunning, and J. R. Stehn. The actin cytoskeleton as a sensor and mediator of apoptosis. Bioarchitecture 2:75–87, 2012.
Dupont, S., L. Morsut, M. Aragona, E. Enzo, S. Giulitti, M. Cordenonsi, F. Zanconato, J. Le Digabel, M. Forcato, S. Bicciato, N. Elvassore, and S. Piccolo. Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature 474:179–183, 2011.
Dweck, M. R., N. A. Boon, and D. E. Newby. Calcific aortic stenosis: a disease of the valve and the myocardium. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 60:1854–1863, 2012.
Egerbacher, M., S. P. Arnoczky, O. Caballero, M. Lavagnino, and K. L. Gardner. Loss of homeostatic tension induces apoptosis in tendon cells: an in vitro study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 466:1562–1568, 2008.
Elosegui-Artola, A., I. Andreu, A. E. M. Beedle, A. Lezamiz, M. Uroz, A. J. Kosmalska, R. Oria, J. Z. Kechagia, P. Rico-Lastres, A.-L. L. Le Roux, C. M. Shanahan, X. Trepat, D. Navajas, S. Garcia-Manyes, and P. Roca-Cusachs. Force triggers YAP nuclear entry by regulating transport across nuclear pores. Cell 171:1397–1410.e14, 2017.
Fadeel, B. Plasma membrane alterations during apoptosis: role in corpse clearance. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 6:269–275, 2004.
Farrelly, N., Y.-J. Lee, J. Oliver, C. Dive, and C. H. Streuli. Extracellular matrix regulates apoptosis in mammary epithelium through a control on insulin signaling. Cell 144:1337–1347, 1999.
Flusberg, D. A., Y. Numaguchi, and D. E. Ingber. Cooperative control of Akt phosphorylation, bcl-2 expression, and apoptosis by cytoskeletal microfilaments and microtubules in capillary endothelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 12:3087–3094, 2001.
Freeman, R. V., and C. M. Otto. Spectrum of calcific aortic valve disease: pathogenesis, disease progression, and treatment strategies. Circulation 111:3316–3326, 2005.
Fu, R., Q. Liu, G. Song, A. Baik, M. Hu, S. Sun, X. E. Guo, M. Long, and B. Huo. Spreading area and shape regulate apoptosis and differentiation of osteoblasts. Biomed. Mater. 8:055005, 2013.
Galluzzi, L., M. C. Maiuri, I. Vitale, H. Zischka, M. Castedo, L. Zitvogel, and G. Kroemer. Cell death modalities: classification and pathophysiological implications. Cell Death Differ. 14:1237–1243, 2007.
Geske, F. J., R. Lieberman, R. Strange, and L. E. Gerschenson. Early stages of p53-induced apoptosis are reversible. Cell Death Differ. 8:182–191, 2001.
Goldblatt, Z. E., H. Ashouri Choshali, H. A. Cirka, V. Liang, Q. Wen, D. McCollum, N. Rahbar, and K. L. Billiar. Heterogeneity profoundly alters emergent stress fields in constrained multicellular systems. Biophys. J. 118:15–25, 2020.
Gottlieb, E., S. Armour, M. Harris, and C. Thompson. Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates matrix configuration and cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 10:709–717, 2003.
Gourlay, C. W., and K. R. Ayscough. The actin cytoskeleton: a key regulator of apoptosis and ageing? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6:583–589, 2005.
Gourlay, C. W., and K. R. Ayscough. A role for actin in aging and apoptosis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 33:1260–1264, 2005.
Gourlay, C. W., L. N. Carpp, P. Timpson, S. J. Winder, and K. R. Ayscough. A role for the actin cytoskeleton in cell death and aging in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 164:803–809, 2004.
Gu, X., and K. S. Masters. Role of the Rho pathway in regulating valvular interstitial cell phenotype and nodule formation. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 300:H448–H458, 2011.
Guilak, F., D. M. Cohen, B. T. Estes, J. M. Gimble, W. Liedtke, and C. S. Chen. Control of stem cell fate by physical interactions with the extracellular matrix. Cell Stem Cell 5:17–26, 2009.
Gurbanov, E., and X. Shiliang. The key role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. J. Cardio-thoracic Surg. 30:499–507, 2006.
Hanahan, D., and R. A. Weinberg. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674, 2011.
Hardwick, J. M. Apoptosis in viral pathogenesis. Cell Death Differ. 8:109–110, 2001.
Hinz, B., and D. Lagares. Evasion of apoptosis by myofibroblasts: a hallmark of fibrotic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 16:11–31, 2020.
Houben, F., F. C. S. Ramaekers, L. H. E. H. Snoeckx, and J. L. V. Broers. Role of nuclear lamina-cytoskeleton interactions in the maintenance of cellular strength. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1773:675–686, 2007.
Huang, X., H. D. Halicka, F. Traganos, T. Tanaka, A. Kurose, and Z. Darzynkiewicz. Cytometric assessment of DNA damage in relation to cell cycle phase and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 38:223–243, 2005.
Huang, S., and D. E. Ingber. Cell tension, matrix mechanics, and cancer development. Cancer Cell 8:175–176, 2005.
Huang, J., Y. Liu, P. Sun, X. Lv, K. Bo, and X. Fan. Novel strategy for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: enhancement of apoptosis. Lung 188:179–189, 2010.
Hughes-Fulford, M., R. Tjandrawinata, J. Fitzgerald, K. Gasuad, and V. Gilbertson. Effects of microgravity on osteoblast growth. Gravit. Space Biol. Bull. 11:51–60, 1998.
Humphrey, J. D., E. R. Dufresne, and M. A. Schwartz. Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15:802–812, 2014.
Igney, F. H., and P. H. Krammer. Death and anti-death: tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2:277–288, 2002.
Infanger, M., P. Kossmehl, M. Shakibaei, J. Bauer, S. Kossmehl-Zorn, A. Cogoli, F. Curcio, A. Oksche, M. Wehland, R. Kreutz, M. Paul, and D. Grimm. Simulated weightlessness changes the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix proteins in papillary thyroid carcinoma cells. Cell Tissue Res. 324:267–277, 2006.
Ingber, D. E. Can cancer be reversed by engineering the tumor microenvironment? Semin. Cancer Biol. 18:356–364, 2008.
Jaalouk, D. E., and J. Lammerding. Mechanotransduction gone awry. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10:63–73, 2009.
Jian, B., N. Narula, Q. Y. Li, E. R. Mohler, and R. J. Levy. Progression of aortic valve stenosis: TGF-β1 is present in calcified aortic valve cusps and promotes aortic valve interstitial cell calcification via apoptosis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 75:457–465, 2003.
Jordan, M. A., and L. Wilson. Microtubules and actin filaments: dynamic targets for cancer chemotherapy. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10:123–130, 1998.
Jurasz, P., D. Courtman, S. Babaie, and D. J. Stewart. Role of apoptosis in pulmonary hypertension: from experimental models to clinical trials. Pharmacol. Ther. 126:1–8, 2010.
Kaiser, D., M.-A. Freyberg, and P. Friedl. Lack of hemodynamic forces triggers apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 231:586–590, 1997.
Kannan, K., and S. K. Jain. Oxidative stress and apoptosis. Pathophysiology 7:153–163, 2000.
Kavallaris, M. Microtubules and resistance to tubulin-binding agents. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10:194–204, 2010.
Kerr, J. F. R., A. H. Wyllie, and A. R. Currie. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. J. Intern. Med. 258:479–517, 1972.
Kilian, K. A., B. Bugarija, B. T. Lahn, and M. Mrksich. Geometric cues for directing the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107:4872–4877, 2010.
Kim, N. H., and P. M. Kang. Apoptosis in cardiovascular diseases: mechanism and clinical implications. Korean Circ. J. 40:299–305, 2010.
Kim, D. H., S. B. Khatau, Y. Feng, S. Walcott, S. X. Sun, G. D. Longmore, and D. Wirtz. Actin cap associated focal adhesions and their distinct role in cellular mechanosensing. Sci. Rep. 2:1–13, 2012.
Klein, E. A., L. Yin, D. Kothapalli, P. Castagnino, F. J. Byfield, T. Xu, I. Levental, E. Hawthorne, P. A. Janmey, and R. K. Assoian. Cell-cycle control by physiological matrix elasticity and in vivo tissue stiffening. Curr. Biol. 19:1511–1518, 2009.
Konduri, S., Y. Xing, J. N. Warnock, Z. He, and A. P. Yoganathan. Normal physiological conditions maintain the biological characteristics of porcine aortic heart valves: an ex vivo organ culture study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33:1158–1166, 2005.
Kong, D., T. Zheng, M. Zhang, D. Wang, S. Du, X. Li, J. Fang, and X. Cao. Static mechanical stress induces apoptosis in rat endplate chondrocytes through MAPK and mitochondria-dependent caspase activation signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 8:1–10, 2013.
Kumar, S. Caspase function in programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ. 14:32–43, 2007.
Kusano, H., S. Shimizu, R. C. Koya, H. Fujita, S. Kamada, N. Kuzumaki, and Y. Tsujimoto. Human gelsolin prevents apoptosis by inhibiting apoptotic mitochondrial changes via closing VDAC. Oncogene 19:4807–4814, 2000.
Lagadic-Gossmann, D., L. Huc, and V. Lecureur. Alterations of intracellular pH homeostasis in apoptosis: origins and roles. Cell Death Differ. 11:953–961, 2004.
Leadsham, J. E., V. N. Kotiadis, D. J. Tarrant, and C. W. Gourlay. Apoptosis and the yeast actin cytoskeleton. Cell Death Differ. 17:754–762, 2010.
Leight, J. L., M. A. Wozniak, S. Chen, M. L. Lynch, and C. S. Chen. Matrix rigidity regulates a switch between TGF-β1-induced apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol. Biol. Cell 23:781–791, 2012.
Leopold, J. A. Cellular mechanisms of aortic valve calcification. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 5:605–614, 2012.
Li, Q., A. Kumar, E. Makhija, and G. V. Shivashankar. The regulation of dynamic mechanical coupling between actin cytoskeleton and nucleus by matrix geometry. Biomaterials 35:961–969, 2014.
Li, B., F. Li, K. M. Puskar, and J. H. C. Wang. Spatial patterning of cell proliferation and differentiation depends on mechanical stress magnitude. J. Biomech. 42:1622–1627, 2009.
Liao, X., X. Wang, Y. Gu, Q. Chen, and L. Y. Chen. Involvement of death receptor signaling in mechanical stretch-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Life Sci. 77:160–174, 2005.
Liu, X. M., D. Ensenat, H. Wang, A. I. Schafer, and W. Durante. Physiologic cyclic stretch inhibits apoptosis in vascular endothelium. FEBS Lett. 541:52–56, 2003.
Locksley, R. M., N. Killeen, and M. J. Lenardo. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell 104:487–501, 2001.
Loreto, C., G. Musumeci, A. Castorina, C. Loreto, and G. Martinez. Degenerative disc disease of herniated intervertebral discs is associated with extracellular matrix remodeling, vimentin-positive cells and cell death. Ann. Anat. 193:156–162, 2011.
Lotem, J., and L. Sachs. Cytokines as suppressors of apoptosis. Apoptosis 4:187–196, 1999.
Lunova, M., V. Zablotskii, N. M. Dempsey, T. Devillers, M. Jirsa, E. Sykova, S. Kubinova, O. Lunov, and A. Dejneka. Modulation of collective cell behaviour by geometrical constraints. Integr. Biol. 8:1093–1196, 2016.
Malek, A. M., S. L. Alper, and S. Izumo. Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis. Jama 282:2035–2042, 1999.
Mana-Capelli, S., M. Paramasivam, S. Dutta, and D. McCollum. Angiomotins link F-actin architecture to Hippo pathway signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 25:1676–1685, 2014.
Mayr, M., Y. Hu, P. Hainaut, and Q. Xu. Mechanical stress-induced DNA damage and rac- p38MAPK signal pathways mediate p53-dependent apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. FASEB J 16:1423–1425, 2002.
Mayr, M., C. Li, Y. Zou, U. Huemer, Y. Hu, and Q. Xu. Biomechanical stress-induced apoptosis in vein grafts involves p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. FASEB J 14:261–270, 2000.
McIlwain, D. R., T. Berger, and T. W. Mak. Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 7:1–28, 2015.
Mleynek, T., D. Li, J. Rosenblatt, M. J. Redd, A. Chan, and Y. Gu. Endothelia extrude apoptotic cells to maintain a constant barrier. BioRix2 2018. https://doi.org/10.1101/268946.
Mohler, E. R., F. Gannon, C. Reynolds, R. Zimmerman, M. G. Keane, and F. S. Kaplan. Bone formation and inflammation in cardiac valves. Circulation 103:1522–1528, 2001.
Morbidelli, L., M. Monici, N. Marziliano, A. Cogoli, F. Fusi, J. Waltenberger, and M. Ziche. Simulated hypogravity impairs the angiogenic response of endothelium by up-regulating apoptotic signals. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 334:491–499, 2005.
Musumeci, G., C. Loreto, M. L. Carnazza, I. Strehin, and J. Elisseeff. OA cartilage derived chondrocytes encapsulated in poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) for the evaluation of cartilage restoration and apoptosis in an in vitro model. Histol. Histopathol. 26:1265–1278, 2011.
Narula, J., N. Haider, R. Virmani, T. G. Disalvo, F. D. Kolodgie, R. J. Hajjar, U. Schmidt, M. J. Semigran, G. W. Dec, and B. Khaw. Apoptosis in myocytes in end-stage heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 335:1182–1189, 1996.
Nelson, C. M., R. P. Jean, J. L. Tan, W. F. Liu, N. J. Sniadecki, A. A. Spector, and C. S. Chen. Emergent patterns of growth controlled by multicellular form and mechanics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:11594–11599, 2005.
Norbury, C. J., and B. Zhivotovsky. DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 23:2797–2808, 2004.
Odaka, C., M. L. Sanders, and P. Crews. Jasplakinolide induces apoptosis in various transformed cell lines by a caspase-3-like protease-dependent pathway. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 7:947–952, 2000.
Ohsawa, S., J. Vaughen, and T. Igaki. Cell extrusion: a stress-responsive force for good or evil in epithelial homeostasis. Dev. Cell 44:284–296, 2018.
Ohtsu, M., N. Sakai, H. Fujita, M. Kashiwagi, S. Gasa, S. Shimizu, Y. Eguchi, Y. Tsujimoto, Y. Sakiyama, K. Kobayashi, and N. Kuzumaki. Inhibition of apoptosis by the actin-regulatory protein gelsolin. EMBO J. 16:4650–4656, 1997.
Olivetti, G., R. Abbi, and F. Quaini. Apoptosis in the failing human heart. N. Engl. J. Med. 336:1131–1141, 1997.
Olson, E. N., and A. Nordheim. Linking actin dynamics and gene transcription to drive cellular motile functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11:353–365, 2010.
Paoli, P., E. Giannoni, and P. Chiarugi. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 3481–3498:2013, 1833.
Parlato, S., A. M. Giammarioli, M. Logozzi, F. Lozupone, P. Matarrese, F. Luciani, M. Falchi, W. Malorni, and S. Fais. CD95 (APO-1/Fas) linkage to the actin cytoskeleton through ezrin in human T lymphocytes: a novel regulatory mechanism of the CD95 apoptotic pathway. EMBO J. 19:5123–5134, 2000.
Paul, C., F. Manero, S. Gonin, C. Kretz-Remy, S. Virot, and A.-P. Arrigo. Hsp27 as a negative regulator of cytochrome c release. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:816–834, 2002.
Peacock, A. J., N. F. Murphy, J. J. McMurray, L. Caballero, and S. Stewart. An epidemiological study of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 30:104–109, 2007.
Peitsch, M. C., B. Polzar, H. Stephan, T. Crompton, H. R. MacDonald, H. G. Mannherz, and J. Tschopp. Characterization of the endogenous deoxyribonuclease involved in nuclear DNA degradation during apoptosis (programmed cell death). EMBO J. 12:371–377, 1993.
Perry, S. W., J. P. Norman, J. Barbieri, E. B. Brown, and H. A. Gelbard. Mitochondrial membrane potential probes and the proton gradient: a practical usage guide. Biotechniques 50:98–115, 2011.
Peyronnet, R., J. M. Nerbonne, and P. Kohl. Cardiac mechano-gated ion channels and arrhythmias. Circ Res. 118:239–311, 2016.
Phrommintikul, A., L. Tran, A. Kompa, B. Wang, A. Adrahtas, D. Cantwell, D. J. Kelly, and H. Krum. Effects of a Rho kinase inhibitor on pressure overload induced cardiac hypertrophy and associated diastolic dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Hear. Circ. Physiol. 294:1804–1814, 2008.
Pickup, M. W., J. K. Mouw, and V. M. Weaver. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 15:1243–1253, 2014.
Porter, A. G., and R. U. Jänicke. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104, 1999.
Puthalakath, H., A. Villunger, L. A. O’Reilly, J. G. Beaumont, L. Coultas, R. E. Cheney, D. C. S. Huang, and A. Strasser. Bmf: a proapoptotic BH3-only protein regulated by interaction with the myosin V actin motor complex, activated by anoikis. Science 293:1829–1832, 2001.
Qiao, L., and G. C. Farrell. The effects of cell density, attachment substratum and dexamethasone on spontaneous apoptosis of rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Vitro. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 35:417–424, 1999.
Rikitake, Y., and J. K. Liao. Rho GTPases, statins, and nitric oxide. Circ. Res. 97:1232–1235, 2005.
Rodriguez, K. J., L. M. Piechura, A. M. Porras, and K. S. Masters. Manipulation of valve composition to elucidate the role of collagen in aortic valve calcification. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 14:1–10, 2014.
Roos, W. P., and B. Kaina. DNA damage-induced cell death by apoptosis. Trends Mol. Med. 12:440–450, 2006.
Rowe, V. L., S. L. Stevens, T. T. Reddick, M. B. Freeman, R. Donnell, R. C. Carroll, and M. H. Goldman. Vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis in aneurysmal, occlusive, and normal human aortas. J. Vasc. Surg. 31:567–576, 2000.
Roy, S., and D. W. Nicholson. Cross-talk in cell death signaling. J. Exp. Med. 192:F21–F25, 2000.
Sendoel, A., and M. O. Hengartner. Apoptotic cell death under hypoxia. Physiology 29:168–176, 2014.
Solon, J., I. Levental, K. Sengupta, P. C. Georges, and P. A. Janmey. Fibroblast adaptation and stiffness matching to soft elastic substrates. Biophys. J. 93:4453–4461, 2007.
Song, A. S. Thermally induced apoptosis, necrosis, and heat shock protein expression in 3D culture. J. Biomech. Eng. 136:1–10, 2014.
Song, Y., J. Fu, M. Zhou, L. Xiao, X. Feng, H. Chen, and W. Huang. Activated Hippo/Yes-associated protein pathway promotes cell proliferation and anti-apoptosis in endometrial stromal cells of endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 101:1552–1561, 2016.
Sotoudeh, M., Y.-S. Li, N. Yajima, C.-C. Chang, T.-C. Tsou, Y. Wang, S. Usami, A. Ratcliffe, S. Chien, and J. Y.-J. Shyy. Induction of apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells by mechanical stretch. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 282:H1709–H1716, 2002.
Steen, R. L., and P. Collas. Mistargeting of B-type lamins at the end of mitosis: implications on cell survival and regulation of lamins A/C expression. J. Cell Biol. 152:621–626, 2001.
Stournaras, C., E. Stiakaki, S. B. Koukouritaki, P. A. Theodoropoulos, M. Kalmanti, Y. Fostinis, and A. Gravanis. Altered actin polymerization dynamics in various malignant cell types: Evidence for differential sensitivity to cytochalasin B. Biochem. Pharmacol. 52:1339–1346, 1996.
Streichan, S. J., C. R. Hoerner, T. Schneidt, D. Holzer, and L. Hufnagel. Spatial constraints control cell proliferation in tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111:5586–5591, 2014.
Su, B. Y., K. M. Shontz, N. A. Flavahan, and P. T. Nowicki. The effect of phenotype on mechanical stretch-induced vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis. J. Vasc. Res. 43:229–237, 2006.
Suria, H., L. Chau, E. Negrou, D. Kelvin, and J. Madrenas. Cytoskeletal disruption induces T cell apoptosis by a caspase-3 mediated mechanism. Life Sci. 65:2697–2707, 1999.
Suzanne, M., and H. Steller. Shaping organisms with apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 20:669–675, 2013.
Tamada, M., M. P. Sheetz, and Y. Sawada. Activation of a signaling cascade by cytoskeleton stretch. Dev. Cell 7:709–718, 2004.
Tanaka, K., M. Sata, D. Fukuda, Y. Suematsu, N. Motomura, S. Takamoto, Y. Hirata, and R. Nagai. Age-associated aortic stenosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 46:134–141, 2005.
Tang, H. L., K. L. Yuen, H. M. Tang, and M. C. Fung. Reversibility of apoptosis in cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 100:118–122, 2009.
Tilghman, R. W., C. R. Cowan, J. D. Mih, Y. Koryakina, D. Gioeli, J. K. Slack-Davis, B. R. Blackman, D. J. Tschumperlin, and J. T. Parsons. Matrix rigidity regulates cancer cell growth and cellular phenotype. PLoS ONE 5:1–13, 2010.
Tomasek, J. J., G. Gabbiani, B. Hinz, C. Chaponnier, and R. A. Brown. Myofibroblasts and mechanoregulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3:349–363, 2002.
Tsujimoto, Y. Cell death regulation by the Bcl-2 protein family in the mitochondria. J. Cell. Physiol. 195:158–167, 2003.
Ulrich, T. A., E. M. de Juan Pardo, and S. Kumar. The mechanical rigidity of the extracellular matrix regulates the structure, motility, and proliferation of glioma cells. Cancer Res. 69:4167–4174, 2009.
Vidyasekar, P., P. Shyamsunder, R. Arun, R. Santhakumar, N. K. Kapadia, R. Kumar, and R. S. Verma. Genome wide expression profiling of cancer cell lines cultured in microgravity reveals significant dysregulation of cell cycle and MicroRNA gene networks. PLoS ONE 10:1–20, 2015.
Virani, S. S., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update. Circulation 141:139–596, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000000757.
Wada, T., and J. M. Penninger. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene 23:2838–2849, 2004.
Wang, K., J. J. Brems, R. L. Gamelli, and J. Ding. Reversibility of caspase activation and its role during glycochenodeoxycholate-induced hepatocyte apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 280:23490–23495, 2005.
Wang, G., W. Chen, H. Qu, and X. Li. The effect of cyclic stretch on apoptosis of human squamous carcinoma of tongue cell line Tca8113. Biomed. Eng. Inform. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1109/BMEI.2009.5303118.
Wang, H.-B., M. Dembo, and Y.-L. Wang. Substrate flexibility regulates growth and apoptosis of normal but not transformed cells. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 279:C1345–C1350, 2000.
Wang, Y. X., B. Martin-McNulty, V. Da Cunha, J. Vincelette, X. Lu, Q. Feng, M. Halks-Miller, M. Mahmoudi, M. Schroeder, B. Subramanyam, J. L. Tseng, G. D. Deng, S. Schirm, A. Johns, K. Kauser, W. P. Dole, and D. R. Light. Fasudil, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, attenuates angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by inhibiting apoptosis and proteolysis. Circulation 111:2219–2226, 2005.
Wang, P., A. J. Valentijn, A. P. Gilmore, and C. H. Streuli. Early events in the anoikis program occur in the absence of caspase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 278:19917–19925, 2003.
Watters, D. Molecular mechanisms of ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 77:263–271, 1999.
Wencker, D., M. Chandra, K. Nguyen, W. Miao, S. Garantziotis, S. M. Factor, J. Shirani, R. C. Armstrong, and R. N. Kitsis. A mechanistic role for cardiac myocyte apoptosis in heart failure. J. Clin. Invest. 111:1497–1504, 2003.
Wernig, F., M. Mayr, and Q. Xu. Mechanical stretch-induced apoptosis in smooth muscle cells is mediated by β1-integrin signaling pathways. Hypertension 41:903–911, 2003.
Wernig, F., and Q. Xu. Mechanical stress-induced apoptosis in the cardiovascular system. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 78:105–137, 2002.
Wu, C.-C., Y.-S. Li, J. H. Haga, R. Kaunas, J.-J. Chiu, F.-C. Su, S. Usami, and S. Chien. Directional shear flow and Rho activation prevent the endothelial cell apoptosis induced by micropatterned anisotropic geometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:1254–1259, 2007.
Wu, Y., D. Zhao, J. Zhuang, F. Zhang, and C. Xu. Caspase-8 and caspase-9 functioned differently at different stages of the cyclic stretch-induced apoptosis in human periodontal ligament cells. PLoS ONE 11:1–15, 2016.
Yamazaki, T., I. Komuro, S. Kudoh, Y. Zou, R. Nagai, R. Aikawa, H. Uozumi, and Y. Yazaki. Role of ion channels and exchangers in mechanical stretch-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circ. Res. 82:430–437, 1998.
Yeung, T., P. C. Georges, L. A. Flanagan, B. Marg, M. Ortiz, M. Funaki, N. Zahir, W. Ming, V. Weaver, and P. A. Janmey. Effects of substrate stiffness on cell morphology, cytoskeletal structure, and adhesion. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 60:24–34, 2005.
Zhang, T., F. Tian, J. Wang, J. Jing, S. S. Zhou, and Y. D. Chen. Atherosclerosis-associated endothelial cell apoptosis by MiR-429-mediated down regulation of Bcl-2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 37:1421–1430, 2015.
Zhang, Y. H., C. Q. Zhao, L. S. Jiang, and L. Y. Dai. Substrate stiffness regulates apoptosis and the mRNA expression of extracellular matrix regulatory genes in the rat annular cells. Matrix Biol. 30:135–144, 2011.
Zhao, T., X. Tang, C. S. Umeshappa, H. Ma, H. Gao, Y. Deng, A. Freywald, and J. Xiang. Simulated microgravity promotes cell apoptosis through suppressing Uev1A/TICAM/TRAF/NF-κB-regulated anti-apoptosis and p53/PCNA- and ATM/ATR-Chk1/2-controlled DNA-damage response pathways. J. Cell. Biochem. 2148:2138–2148, 2016.
Acknowledgments
This work was funding in part by Grants from the National Science Foundation (CMMI 1761432), the American Heart Association (Grant No. 14PRE18310016) to H.A.C., and the National Science Foundation IGERT (Grant No. DGE 1144804) to Z.E.G. and H.A.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Debra T. Auguste oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldblatt, Z.E., Cirka, H.A. & Billiar, K.L. Mechanical Regulation of Apoptosis in the Cardiovascular System. Ann Biomed Eng 49, 75–97 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02659-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02659-x