Abstract
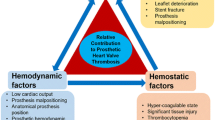
We investigate the potential of prosthetic heart valves to generate abnormal flow and stress patterns, which can contribute to platelet activation and lysis according to blood damage accumulation mechanisms. High-resolution velocity measurements of the unsteady flow field, obtained with a standard particle image velocimetry system and a scaled-up model valve, are used to estimate the shear stresses arising downstream of the valve, accounting for flow features at scales less than one order of magnitude larger than blood cells. Velocity data at effective spatial and temporal resolution of 60 μm and 1.75 kHz, respectively, enabled accurate extraction of Lagrangian trajectories and loading histories experienced by blood cells. Non-physiological stresses up to 10 Pa were detected, while the development of vortex flow in the wake of the valve was observed to significantly increase the exposure time, favouring platelet activation. The loading histories, combined with empirical models for blood damage, reveal that platelet activation and lysis are promoted at different stages of the heart cycle. Shear stress and blood damage estimates are shown to be sensitive to measurement resolution.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemu, Y., and D. Bluestein. Flow-induced platelet activation and damage accumulation in a mechanical heart valve: numerical studies. Artif. Organs 31(9):677–688, 2007.
Apel, J., R. Paul, S. Klaus, T. Siess, and H. Reul. Assessment of hemolysis related quantities in a microaxial blood pump by computational fluid dynamics. Artif. Organs 25(5):341–347, 2001.
Balducci, A., M. Grigioni, G. Querzoli, G. P. Romano, C. Daniele, G. D’Avenio, and V. Barbaro. Investigation of the flow field downstream of an artificial heart valve by means of PIV and PTV. Exp. Fluids 36(1):204–213, 2004.
Baldwin, J. T., S. Deutsch, D. B. Geselowitz, and J. M. Tarbell. LDA measurements of mean velocity and Reynolds stress fields within an artificial heart ventricle. J. Biomech. Eng. 116(2):190–200, 1994.
Bellofiore, A., E. M. Donohue, and N. J. Quinlan. Scale-up of an unsteady flow-field for enhanced spatial and temporal resolution of PIV measurements: application to leaflet wake flow in a mechanical heart valve. Exp. Fluids. doi:10.1007/s00348-010-1038-2, 2011.
Bluestein, D., K. B. Chandran, and K. B. Manning. Towards non-thrombogenic performance of blood recirculating devices. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38(3):1236–1256, 2010.
Bluestein, D., Y. M. Li, and I. B. Krukenkamp. Free emboli formation in the wake of bi-leaflet mechanical heart valves and the effects of implantation techniques. J. Biomech. 35(12):1533–1540, 2002.
Bluestein, D., E. Rambod, and M. Gharib. Vortex shedding as a mechanism for free emboli formation in mechanical heart valves. J. Biomech. Eng. 122(2):125–134, 2000.
Brown, C. H., L. B. Leverett, C. W. Lewis, C. P. Alfrey, and J. D. Hellums. Morphological, biochemical, and functional changes in human platelets subjected to shear stress. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 86(3):462–471, 1975.
Brucker, C., U. Steinseifer, W. Schroder, and H. Reul. Unsteady flow through a new mechanical heart valve prosthesis analysed by digital particle image velocimetry. Meas. Sci. Technol. 13(7):1043–1049, 2002.
Cannegieter, S. C., F. R. Rosendaal, and E. Brit. Thromboembolic and bleeding complications in patients with mechanical heart valve prostheses. Circulation 89(2):635–641, 1994.
Dasi, L. P., L. Ge, H. Simon, F. Sotiropoulos, and A. P. Yoganathan. Vorticity dynamics of a bileaflet mechanical heart valve in an axisymmetric aorta. Phys. Fluids 19(6):067105, 2007.
De Tullio, M. D., A. Cristallo, E. Balaras, and R. Verzicco. Direct numerical simulation of the pulsatile flow through an aortic bileaflet mechanical heart valve. J. Fluid Mech. 622:259–290, 2009.
Dumont, K., J. Vierendeels, R. Kaminsky, G. van Nooten, P. Verdonck, and D. Bluestein. Comparison of the hemodynamic and thrombogenic performance of two bileaflet mechanical heart valves using a CFD/FSI model. J. Biomech. Eng. 129(4):558–565, 2007.
Ellis, J. T., T. M. Wick, and A. P. Yoganathan. Prosthesis-induced hemolysis: mechanisms and quantification of shear stress. J. Heart Valve Dis. 7(4):376–386, 1998.
Ge, L., L. P. Dasi, F. Sotiropoulos, and A. P. Yoganathan. Characterization of hemodynamic forces induced by mechanical heart valves: Reynolds vs. viscous stresses. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 36(2):276–297, 2008.
Giersiepen, M., L. J. Wurzinger, R. Opitz, and H. Reul. Estimation of shear stress-related blood damage in heart valve prostheses—in vitro comparison of 25 aortic valves. Int. J. Artif. Organs 13(5):300–306, 1990.
Goubergrits, L. Numerical modeling of blood damage: current status, challenges and future prospects. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices 3(5):527–531, 2006.
Goubergrits, L., and K. Affeld. Numerical estimation of blood damage in artificial organs. Artif. Organs 28(5):499–507, 2004.
Grigioni, M., C. Daniele, G. D’Avenio, and V. Barbaro. The influence of the leaflets’ curvature on the flow field in two bileaflet prosthetic heart valves. J. Biomech. 34(5):613–621, 2001.
Grigioni, M., C. Daniele, U. Morbiducci, G. D’Avenio, G. Di Benedetto, and V. Barbaro. The power-law mathematical model for blood damage prediction: analytical developments and physical inconsistencies. Artif. Organs 28(5):467–475, 2004.
Grigioni, M., U. Morbiducci, G. D’Avenio, G. Di Benedetto, and C. Del Gaudio. A novel formulation for blood trauma prediction by a modified power-law mathematical model. Biomech. Model Mechanobiol. 4(4):249–260, 2005.
Guivier-Curien, C., V. Deplano, and E. Bertrand. Validation of a numerical 3-D fluidstructure interaction model for a prosthetic valve based on experimental PIV measurements. Med. Eng. Phys. 31(8):986–993, 2009.
Kaminsky, R., S. Kallweit, M. Rossi, U. Morbiducci, L. Scalise, P. Verdonck, and E. Tomasini. PIV measurements of flows in artificial heart valves. In: Particle Image Velocimetry: New Developments, Recent Applications, edited by A. Schroder. Berlin: Springer, 2008, pp. 55–72.
Kroll, M. H., J. D. Hellums, L. V. McIntire, A. I. Schafer, and J. L. Moake. Platelets and shear stress. Blood 88(5):1525–1541, 1996.
Leverett, L. B., J. D. Hellums, C. P. Alfrey, and E. C. Lynch. Red blood cell damage by shear stress. Biophys. J. 12(3):257–273, 1972.
Li, C. P., C. W. Lo, and P. C. Lu. Estimation of viscous dissipative stresses induced by a mechanical heart valve using PIV data. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38(3):903–916, 2010.
Liu, J. S., P. C. Lu, and S. H. Chu. Turbulence characteristics downstream of bileaflet aortic valve prostheses. J. Biomech. Eng. 122(2):118–124, 2000.
Luff, J. D., T. Drouillard, A. M. Rompage, M. A. Linne, and J. R. Hertzberg. Experimental uncertainties associated with particle image velocimetry (PIV) based vorticity algorithms. Exp. Fluids 26(1):36–54, 1999.
Manning, K. F., V. Kini, A. A. Fontaine, S. Deutsch, and J. M. Tarbell. Regurgitant flow field characteristics of the St. Jude bileaflet mechanical heart valve under physiologic pulsatile flow using particle image velocimetry. Artif. Organs 27(9):840–846, 2003.
Mecozzi, G., A. D. Milano, M. De Carlo, F. Sorrentino, S. Pratali, C. Nardi, and U. Bortolotti. Intravascular hemolysis in patients with new-generation prosthetic heart valves: a prospective study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 123(3):550–556, 2002.
Morbiducci, U., R. Ponzini, M. Nobili, D. Massai, F. M. Montevecchi, D. Bluestein, and A. Redaelli. Blood damage safety of prosthetic heart valves. Shear-induced platelet activation and local flow dynamics: a fluid–structure interaction approach. J. Biomech. 42(12):1952–1960, 2009.
Nobili, M., J. Sheriff, U. Morbiducci, A. Redaelli, and D. Bluestein. Platelet activation due to hemodynamic shear stresses: damage accumulation model and comparison to in vitro measurements. ASAIO J. 54(1):64–72, 2008.
Paul, R., J. Apel, S. Klaus, F. Schügner, P. Schwindke, and H. Reul. Shear stress related blood damage in laminar couette flow. Artif. Organs 27(6):517–529, 2003.
Quinlan, N. J., and P. Dooley. Models of flow-induced loading on blood cells in laminar and turbulent flow, with application to cardiovascular device flow. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 35(8):1347–1356, 2007.
Raz, S., S. Einav, Y. Alemu, and D. Bluestein. DPIV prediction of flow induced platelet activation—comparison to numerical predictions. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 35(4):493–504, 2007.
Shadden, S. C., M. Astorino, and J. F. Gerbeau. Computational analysis of an aortic valve jet with Lagrangian coherent structures. Chaos 20(1):017512, 2010.
Sheriff, J., D. Bluestein, G. Girdhar, and J. Jesty. High-shear stress sensitizes platelets to subsequent low-shear conditions. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38(4):1442–1450, 2010.
Steegers, A., R. Paul, H. Reul, and G. Rau. Leakage flow at mechanical heart valve prostheses: improved washout or increased blood damage? J. Heart Valve Dis. 8(3):312–323, 1999.
Vongpatanasin, W., L. D. Hillis, and R. A. Lange. Prosthetic heart valves. N. Engl. J. Med. 335(6):407–416, 1996.
Wurzinger, L. J., R. Opitz, P. Blasberg, and H. Schmid-Schönbein. Platelet and coagulation parameters following millisecond exposure to laminar shear stress. Thromb. Haemost. 54(2):381–386, 1985.
Yeung, P. K. Lagrangian investigations of turbulence. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 34(1):115–142, 2002.
Yoganathan, A. P., T. M. Wick, and H. Reul. The influence of flow characteristics of prosthetic valves on thrombus formation. In: Thrombosis, Embolism and Bleeding, edited by E. Buchart. London: IRC Publishers, 1992, pp. 123–148.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) under the Research Frontiers Programme (grant code 07/RFP/ENMF450).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Kerry Hourigan oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellofiore, A., Quinlan, N.J. High-Resolution Measurement of the Unsteady Velocity Field to Evaluate Blood Damage Induced by a Mechanical Heart Valve. Ann Biomed Eng 39, 2417–2429 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0329-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0329-y