Abstract
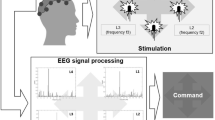
In this study flashing stimuli, such as digits or letters, are displayed on a LCD screen to induce flash visual evoked potentials (FVEPs). The aim of the proposed interface is to generate desired strings while one stares at target stimulus one after one. To effectively extract visually-induced neural activities with superior signal-to-noise ratio, independent component analysis (ICA) is employed to decompose the measured EEG and task-related components are subsequently selected for data reconstruction. In addition, all the flickering sequences are designed to be mutually independent in order to remove the contamination induced by surrounding non-target stimuli from the ICA-recovered signals. Since FVEPs are time-locked and phase-locked to flash onsets of gazed stimulus, segmented epochs from ICA-recovered signals based on flash onsets of gazed stimulus will be sharpen after averaging whereas those based on flash onsets of non-gazed stimuli will be suppressed after averaging. The stimulus inducing the largest averaged FVEPs is identified as the gazed target and corresponding digit or letter is sent out. Five subjects were asked to gaze at each stimulus. The mean detection accuracy resulted from averaging 15 epochs was 99.7%. Another experiment was to generate a specified string ‘0287513694E’. The mean accuracy and information transfer rates were 83% and 23.06 bits/min, respectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birbaumer N., Flor H., Ghanayim N., Hinterberger T., Iverson I., Taub E., Kotchoubey B., Kubler A., Perelmouter J., (1999) A spelling device for the paralyzed Nature 398:297–298
Cheng M., Gao X., Gao S., Xu D., (2002) Design and implementation of a brain-computer interface with high transfer rates IEEE T. Bio-Med Eng. 10: 1181–1186
Donchin E, Spencer K. M., Wilesinghe R., (2000) The mental prosthesis: Assessing the speed of a P300-based brain-computer interface IEEE T. Rehabil. Eng. 8:174–179
Duann J. R., Jung T. P., Kuo W. J., Yeh T. C., Makeig S., Hsieh J. C., Sejnowski T. J., (2002) Single-trial variability in event-related BOLD signals Neuroimage 15: 825–835
Hung C. I., Lee P. L., Wu Y. T., Chen L. F., Yeh T. C., Hsieh J. C. (2005) Recognition of motor imagery electroencephalography using independent component analysis and machine classifiers. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33: 1053–1070
Hyvarinen, A., J. Karhunen, and E. Oja. Independent component analysis. New York: Wiley, New York, 2001.
Hyvarinen A., Oja E., (1997) A fast fixed-point algorithm for independent component analysis Neural Comput. 9: 1483–1492
Jung T. P., Makeig S., Westerfield M., Townsend J., Courchesne E., Sejnowski J. T., (2001) Analysis and visualization of single-trial event-related potentials Hum. Brain Mapp. 14: 166–185
Kao Y. H., Guo W. Y., Wu Y. T., Liu K. C., Chai W. Y., Lin C. Y., Hwang Y. H., Liou A. J. K., Cheng H. C., Yeh T. C., Hsieh J. C., Teng M. M. H., (2003) Hemodynamic segmentation of MR brain perfusion images using independent component, thresholding and Bayesian estimation Magn. Reson. Med. 49: 885–894
Lee P. L., Wu Y. T., Chen L. F., Chen Y. S., Cheng C. M., Yeh T. C., Ho L. T., Chang M. S., Hsieh J. C., (2003) ICA-based spatiotemporal approach for signle-trial analysis of post-movement MEG beta synchronization Neuroimage 20: 2010–2030
Makeig S., Jung T. P., Bell A. J., Ghahremani D., Sejnowski T., (1997) Blind separation of auditory event-related brain responses into independent components Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94:10979–10984
Mason S. G., Birch G. E., (2000) A brain-controlled switch for asynchronous control applications IEEE T. Bio-Med Eng. 47: 1297–1307
McKeown M. J., Makeig S., Brown G. G., Jung T. P., Kindermann S. S., Bell A. J., Sejnowski T. J., (1998) Analysis of fMRI data by blind separation into independent spatial components Hum. Brain Mapp. 6: 160–188
McKeown M., Radtke R., (2001) Phasic and tonic coupling between EEG and EMG demonstrated with independent component analysis J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 18: 45–47
McSherry J. W., Walters C. L., Horbar J. D., (1982) Acute visual evoked potential changes in hydrocephalus Electroen. Clin. Neuro. 53: 331–333
Muller-Gerking J., Pfurtscheller G., Flyvbjerg H., (1999) Designing optimal spatial filters for single-trial EEG classification in a movement task Clin. Neurophysiol. 110: 787–798
Odom J. V., Bach M., Barber C., Brigell M., Marmor M. F., Tormene A. P., Holder G. E., (2004) Vaegan: Visual evoked potentials standard (2004). Doc. Ophthalmol. 108: 115–123
Pfurtscheller G., Neuper C., Guger C., Harkam W., Ramoser H., Schlogl A., Obermaier B., Pregenzer M., (2000) Current trends in Graz brain-computer interface (BCI) research IEEE T. Rehabil. Eng. 8: 216–219
Spehlmann, R. “Evoked potential primer.” In: The transient VEP to diffuse light simuli, edited by Misulis, K. E., and T. Fakhoury. Stoneham: Butterworth publishers, 1985, pp. 135–142.
Spehlmann, R. “Evoked potential primer.” In: VEPs to other stimuli, edited by Misulis, K. E., and T. Fakhoury. Stoneham: Butterworth publishers, 1985, pp. 144–158.
Sutter E. E., (1992) The brain response interface: Communication through visually-induced electrical brain responses J. Microcomput. Appl. 15: 31–45
Raitta C., Karhunene U., Seppalainen A. M., Naukkarinen M., (1979) Changes in the electroretinogram and visual evoked potentials during general anaesthesia. Albrecht von Graefes Arch Klin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 211: 139–144
Reilly E. L., Kondo C., Brunberg J. A., Doty D. B., (1978) Visual evoked potentials during hypothermia and prolonged circulatory arrest Electroen. Clin. Neuro. 45: 100–106
Tang A. C., Pearlmutter B. A., Malaszenko N. A., Phung D. B., (2002) Independent components of magnetoencephalography: Single-trial response onset times Neuroimage 17: 1773–1789
Tesche C. D., Unsitalo M. A., Ilmoniemi R. J., Huotilainen M., Kajola M., Salonen O., (1995) Signal-space projections of MEG data characterize both distributed and well-localized neuroal sources Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 95: 189–200
Trojaborg W., Jorgensen E. O., (1973) Evoked cortical potentials in patients with “isoelectric” EEGs Electroen. Clin. Neuro. 35: 301–309
Uhl R. R., Squires K. C., Bruce D. L., Starr A., (1980) Effect of halothane anesthesia on the human cortical visual evoked response Anesthesiology 53: 273–276
Wilson W. B. (1978) Visual-evoked response differentiation of ischemic optic neuritis from the optic neuritis of multiple sclerosis Am. J. Ophthalmol. 86: 530–535
Wolpaw J. R., Birbaumer N., McFarland D. J., Pfurtscheller G., Vaughan T. M., (2002) Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control Clin. Neurophysiol. 113: 767–791
York D. H., Pulliam M. W., Rosenfeld J. G., Watts C., (1981) Relationship between visual evoked potentials and intracranial pressure J. Neurosurg. 55: 909–916
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Central University, National Science Council (94-2218-E-008-013, 94-2218-E-010-004) and National Health Research Institutes (NHRI-EX94-CD9401) of Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, PL., Hsieh, JC., Wu, CH. et al. The Brain Computer Interface Using Flash Visual Evoked Potential and Independent Component Analysis. Ann Biomed Eng 34, 1641–1654 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-006-9175-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-006-9175-8