Abstract
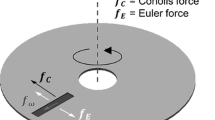
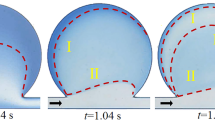
In order to predict the time-dependent behaviors of the moving front in lab-on-a-CD systems or centrifugal pumping, an analytical expression and experimental methods of centrifugal-force-driven transient filling flow into a rectangular microchannel in centrifugal microfluidics are presented in this paper. Considering the effect of surface tension, and neglecting the effect of Coriolis force, the velocity profile, flow rate, the moving front displacement and the pressure distribution along the microchannel are characterized. Experiments are carried out using the image-capturing unit to measure the shift of the flow in rectangular microchannels. The flow characteristics in rectangular microchannels with different cross-sectional dimensions (200, 300 and 400 μm in width and 140, 240 and 300 μm in depth) and length (18 and 25 mm) under different rotational speed are investigated. According to the experimental data, the model can be more reasonable to predict the flow displacement with time, and the errors between theoretical and the experimental will decrease with increasing the cross-section size of the microchannel.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner T, Glatzel T, Zengerle R et al (2005) Frequency-dependent transversal flow control in centrifugal microfluidics. Lab Chip 5(2):146–150
Chen JM, Huang PC, Lin MG (2008) Analysis and experiment of capillary valves for microfluidics on a rotating disk. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:427–437
Cho H, Kim HY, Kang JY et al (2007) How the capillary burst microvalve works. J Colloid Interface Sci 306(2):379–385
Ducrée J, Haeberle S, Brenner T et al (2006) Patterning of flow and mixing in rotating radial microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 2(2):97–105
Ducrée J, Haeberle S, Lutz S et al (2007) The centrifugal microfluidic bio-disk platform. J Micromech Microeng 17(7):S103
Duffy DC, Gillis HL, Lin J et al (1999) Microfabricated centrifugal microfluidic systems: characterization and multiple enzymatic assays. Anal Chem 71(20):4669–4678
Garcia-Cordero JL, Basabe-Desmonts L, Ducrée J et al (2010) Liquid recirculation in microfluidic channels by the interplay of capillary and centrifugal forces. Microfluid Nanofluid 9(4–5):695–703
Geschke O, Klank H, Telleman P (2004) Microsystem engineering of lab-on-a-chip devices[M]. Wiley-vch, Weinheim
Gorkin R, Park J, Siegrist J et al (2010) Centrifugal microfluidics for biomedical applications. Lab Chip 10(14):1758–1773
Haeberle S, Brenner T, Schlosser HP et al (2005) Centrifugal micromixery. Chem Eng Technol 28(5):613–616
Kim DS, Kwon TH (2006a) Modeling, analysis and design of centrifugal force driven transient filling flow into rectangular microchannel. Microsyst Technol 12(9):822–838
Kim DS, Kwon TH (2006b) Modeling, analysis and design of centrifugal force-driven transient filling flow into a circular microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 2(2):125–140
Kim J, Kido H, Rangel RH et al (2008) Passive flow switching valves on a centrifugal microfluidic platform. Sens Actuators B Chem 128(2):613–621
Leu TS, Chang PY (2004) Pressure barrier of capillary stop valves in micro sample separators. Sens Actuators A 115(2):508–515
Liu M, Zhang J, Liu Y et al (2008) Modeling of flow burst, flow timing in lab-on-a-CD systems and its application in digital chemical analysis. Chem Eng Technol 31(9):1328–1335
Madou MJ, Lee LJ, Daunert S et al (2001) Design and fabrication of CD-like microfluidic platforms for diagnostics: microfluidic functions. Biomed Microdevices 3(3):245–254
Madou M, Zoval J, Jia G et al (2006) Lab on a CD. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:601–628
Man PE, Mastrangelo CH, Burns MA et al (1998) Microfabricated capillarity-driven stop valve and sample injector. In: Proceedings of the eleventh annual international workshop on micro electro mechanical systems. MEMS 98. IEEE, pp 45–50
Marliani G, Matzkeit M, Ram VIV (1997) Visualisation studies of the transition regime flow in a channel of varying cross section under the influence of Coriolis force. Exp Fluids 23(1):64–75
Maruyama T, Maeuchi T (2008) Centrifugal-force driven flow in cylindrical micro-channel. Chem Eng Sci 63(1):153–156
Moles DR (2002) Electroosmotic flow controlled microfluidic devices: US Patent 6,406,605
Oh KW, Lee K, Ahn B et al (2012) Design of pressure-driven microfluidic networks using electric circuit analogy. Lab Chip 12(3):515–545
Zeng J, Deshpande M, Greiner KB, Gilbert JR (2000) Fluidic capacitance model of capillary-driven stop valve. In: MEMS proceedings of ASME international mechanical engineering congress and exposition, Orlando
Zoval JV, Madou MJ (2004) Centrifuge-based fluidic platforms. Proc IEEE 92(1):140–153
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51175265) and the Postgraduate Scientific Innovation Research Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. KYLX15_0339).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, T., Huang, L. & Wang, J. Analysis and experiment of transient filling flow into a rectangular microchannel on a rotating disk. Microfluid Nanofluid 20, 52 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1687-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1687-9