Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the role of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography in the detection of renal parenchymal damage in kidneys with and without ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO).
Methods
Twenty-five pediatric patients with a diagnosis of UPJO who underwent surgery and 15 pediatric patients with conservatively managed UPJO were prospectively evaluated with ARFI elastography. Sixteen healthy volunteers constituted the control group. Shear wave velocity (SWV) measurements in the upper, mid, and lower poles of the affected kidney were performed. SWV values of kidneys based on presence of UPJO and hydronephrosis grade were compared. The correlation of SWV values with residual renal function obtained from diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid or mercaptoacetyltriglycine-3 renal scan was evaluated.
Results
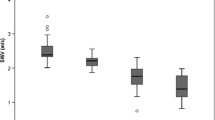
Significantly, higher SWV values were found in control kidneys compared to kidneys affected by UPJO. The median SWVs were 2.82 (2.51–3.07) m/s for the control kidneys and 2.36 (2.09–2.53) m/s for the kidneys in the UPJO group (p < 0.001). When UPJO patients were grouped according to the grade of hydronephrosis, grade 0 hydronephrotic kidneys [2.35 (2.11–2.50) m/s] and grade 3–4 hydronephrotic kidneys [1.86 (1.96–2.25) m/s] had significantly lower SWV values compared to grade 1–2 hydronephrotic kidneys [2.62 (2.37–2.90) m/s] (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
ARFI as a noninvasive, radiation-free procedure for evaluating parenchymal stiffness may prove useful in the diagnostic work-up and follow-up of children with UPJO-induced renal disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dias CS, Silva JM, Pereira AK, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of renal pelvic dilatation for detecting surgically managed ureteropelvic junction obstruction. J Urol. 2013;190:661–6.
Hashim H, Christopher RJ. Ureteropelvic junction obstruction. Eur Urol. 2012;11:25–32.
Sohn B, Kim MJ. Shear wave velocity measurements using acoustic radiation force impulse in young children with normal kidneys versus hydronephrotic kidneys. Ultrasonography. 2014;33:116–21.
Guo LH, Xu HX, Fu HJ, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for noninvasive evaluation of renal parenchyma elasticity: preliminary findings. PLoS One. 2013;8:e68925.
Lee MJ, Kim MJ, Han KH, et al. Age-related changes in liver, kidney, and spleen stiffness in healthy children measured with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:e290–4.
Goya C, Hamidi C, Ece A, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography for detection of renal damage in children. Pediatr Radiol. 2015;45:55–61.
Bruno C, Caliari G, Zaffanello M, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) in the evaluation of the renal parenchymal stiffness in paediatric patients with vesicoureteral reflux: preliminary results. Eur Radiol. 2013;23:3477–84.
Asano K, Ogata A, Tanaka K, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography of the kidneys: is shear wave velocity affected by tissue fibrosis or renal blood flow? J Ultrasound Med. 2014;33:793–801.
Kim SY, Kim MJ, Yoon CS, et al. Comparison of the reliability of two hydronephrosis grading systems: the Society for Foetal Urology grading system vs. the Onen grading system. Clin Radiol. 2013;68:e484–90.
Chertin B, Pollack A, Koulikov D, et al. Conservative treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction in children with antenatal diagnosis of hydronephrosis: lessons learned after 16 years of follow-up. Eur Urol. 2006;49:734–8.
Kelley JC, White JT, Goetz JT, et al. Sonographic renal parenchymal measurements for the evaluation and management of ureteropelvic junction obstruction in children. Front Pediatr. 2016;4:42.
Bob F, Bota S, Sporea I, et al. Relationship between the estimated glomerular filtration rate and kidney shear wave speed values assessed by acoustic radiation force impulse elastography: a pilot study. J Ultrasound Med. 2015;34:649–54.
Gennisson JL, Grenier N, Combe C, et al. Supersonic shear wave elastography of in vivo pig kidney: influence of blood pressure, urinary pressure and tissue anisotropy. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38:1559–67.
Grenier N, Gennisson JL, Cornelis F, et al. Renal ultrasound elastography. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2013;94:545–50.
Bota S, Bob F, Sporea I, et al. Factors that influence kidney shear wave speed assessed by acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in patients without kidney pathology. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:1–6.
Yang C, Hu M, Zhu T, et al. Evaluation of kidney allograft status using novel ultrasonic technologies. Asian J Urol. 2015;2:142–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statements
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Conflict of interest
All authors state that they have no conflict of interest to declare.
About this article
Cite this article
Habibi, H.A., Cicek, R.Y., Kandemirli, S.G. et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography in the evaluation of renal parenchymal stiffness in patients with ureteropelvic junction obstruction. J Med Ultrasonics 44, 167–172 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-016-0760-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-016-0760-7