Abstract
Purpose
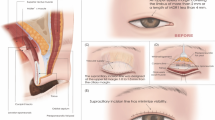
To report intraoperative quantification using finger force for involutional blepharoptosis, which helps in the prevention of postoperative lagophthalmos.
Methods
We carried out levator resection on 20 involutional blepharoptic eyelids. Fissure height was examined intraoperatively to evaluate the extent of resection. If a patient presented more than 3 mm of lagophthalmos in voluntary eyelid closure but could fully open the eye, we forcibly closed the eyelid, using a finger, after voluntary eyelid closure. If more than 3 mm of lagophthalmos was still observed after forced eyelid closure, we corrected eyelid tension until lagophthalmos became less than 2 mm.
Results
Six of the ten patients (20 eyelids) presented with full eyelid opening but more than 3 mm of lagophthalmos in voluntary eyelid closure. After the upper eyelids were forcibly lowered, all six eyelids showed less than 2 mm of lagophthalmos. There were no cases of lagophthalmos 1 month postoperatively.
Conclusions
Additional finger force makes precise quantification of blepharoptosis surgery possible and prevents postoperative lagophthalmos. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2006;50:135–140 © Japanese Ophthalmological Society 2006
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JA Nerad (2001) Oculoplastic surgery: the requisites in ophthalmology Mosby St. Louis 157–192
JJ Older (1983) ArticleTitleLevator aponeurosis surgery for the correction of acquired ptosis: analysis of 113 procedures Ophthalmology 90 1056–1059 Occurrence Handle6646644 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiuD28bht1A%3D
JV Linberg RJ Vasquez G-M Chao (1988) ArticleTitleAponeurotic ptosis repair under local anesthesia: prediction of results from operative lid height Ophthalmology 95 1046–1052 Occurrence Handle3231442 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaC2MbpsVI%3D
RG Small NR Sabates D Burrows (1989) ArticleTitleThe measurement and definition of ptosis Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 5 171–175 Occurrence Handle2487216 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6C38%2FltVQ%3D
M Landa EH Bedrossian SuffixJr (2002) Blepharoptosis RC Della Rocca EH Beddrossian SuffixJr BP Arthus (Eds) Ophthalmic plastic surgery: decision making and techniques McGraw-Hill New York 77–89
JRO Collin BA O'Donnell (1994) ArticleTitleAdjustable sutures in eyelid surgery for ptosis and lid retraction Br J Ophthalmol 78 167–174 Occurrence Handle8148331 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuC1MfisVY%3D
H Borman (2001) ArticleTitleNew adjustable suture technique for managing eyelid ptosis Ann Plast Surg 47 673–677 Occurrence Handle11756841 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FjvFGrtQ%3D%3D
MA Meltzer E Elahi P Taupeka et al. (2001) ArticleTitleA simplified technique of ptosis repair using a single adjustable suture Ophthalmology 108 1889–1892 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0161-6420(01)00712-6 Occurrence Handle11581067 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MrjsVGkuw%3D%3D
Y Tanabe (1989) ArticleTitleBlepharoptosis Atarashii Ganka (J Eye) 6 513–519
N Kubota (1995) ArticleTitleComplications of ptosis surgery Ganka Shujutsu (J Jpn Ophthalmic Surg) 8 605–609
Beard C. Ptosis, ed 2. St. Louis: Mosby; 1976. p. 79–86
S Dresner (2001) Ptosis management: a practical approach WP Chen (Eds) Oculoplastic surgery: the essentials Thieme New York 75–88
AG Tyers JRO Collin (2001) Colour atlas of ophthalmic plastic surgery EditionNumbered 2. Butterworth-Heineman Oxford 148–154
U Haramoto T Kubo M Tamatani et al. (2001) ArticleTitleAnatomic study of the insertions of the levator aponeurosis and Müller's muscle in Oriental eyelids Ann Plast Surg 47 528–533 Occurrence Handle11716265 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MnntVWjtA%3D%3D
H Kakizaki M Zako T Nakano et al. (2005) ArticleTitleThe levator aponeurosis consists of two layers that include smooth muscle Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 21 379–382 Occurrence Handle16234705
H Kakizaki M Zako H Mito et al. (2004) ArticleTitleA guide to making a natural eyelid margin curvature in blepharoptosis surgery Acta Ophthalmol Scand 82 240–241 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1600-0420.2004.00150b.x Occurrence Handle15043552
BR Frueh AS Hasaan DC Musch (2005) ArticleTitleHorizontal eyelid movement on eyelid closure Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 21 109–111 Occurrence Handle15778663
CA Sierra FA Nesi (2003) External levator advancement BG Brazzo (Eds) Complications in ophthalmic plastic surgery Springer New York 77–90
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kakizaki, H., Zako, M., Mito, H. et al. Intraoperative Quantification Using Finger Force for Involutional Blepharoptosis without Postoperative Lagophthalmos. Jpn J Ophthalmol 50, 135–140 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-005-0297-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-005-0297-6