Abstract
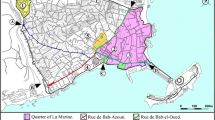
Calabria is one of the Italian regions mostly affected by mass movements. The case study of a densely populated neighborhood (Ianò) located in the central-western sector of Calabria is presented. The several landslides triggered in February 2010 caused heavy damages to the built area, infrastructures and productions of this neighborhood, and increased the risk for the inhabitants. The results obtained through field surveys, photo interpretation, analyses of rainfall data and of the urban fabric evolution, historical survey on the reports of the damages caused by landslides, have enabled to formulate hypotheses on the potential causes that triggered landslide events and produced severe consequences on the area. These results have revealed that almost all landslides of February 2010 are partial reactivations of pre-existing landslide deposits. Moreover, the analyses have indicated a critical role of cumulative rainfalls over an interval of 15 days. However, the severe damage framework is explained through an unplanned urbanization which took place across the years on an area characterized by a high level of instability per se. Some buildings have been erected in proximity of or within pre-existing landslide scarps; in other cases, buildings have been constructed even inside the landslide bodies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari P, Hong Y, Douglas KR, Kirschbaum DB, Gourley J (2010) A digitized global flood inventory (1998–2008): compilation and preliminary results. Nat Hazards 55z(2):405–422
Amodio-Morelli L, Bonard G, Colonna V, Dietrich D, Giunta G, Ippolito F, Liguori V, Lorenzoni S, Paglionico A, Perrone V, Piccarreta G, Russo M, Scandone P, Zanettin-Lorenzoni E, Zuppetta A (1976) L'Arco Calabro-peloritano nell'orogene appenninicomaghrebide. Soc Geol Ital Mem 17:1–60
Antronico L, Sorriso-Valvo M, Tansi C, Gullà G (2001) Carta litologico–strutturale e dei movimenti in massa della Stretta di Catanzaro (scala 1:50000). Selca, Firenze
Antronico L, Gullà G, Terranova O (2002) L'evento pluviometrico dell'8–10 settembre 2000 nella Caloria Ionica meridionale: dissesti sui versanti e processi in alveo. In: Atti del Convegno XIX Giornata dell'ambiente "Il rischio idrogeologico e la difesa del suolo" Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei. Roma, 5 giugno 2001
Antronico L, Borrelli L, Gullà G, Sorriso-Valvo M (2010) La frana di Maierato (Calabria, Italia meridionale) del febbraio 2010: caratteristiche geomorfologiche ed evoluzione. GEAM GEoingegneria Ambientale e Mineraria 2: 15–26, ISSN: 1121–9041
Ayalew L (1999) The effect of seasonal rainfall on landslides in the highlands of Ethiopia. Bull Eng Geol Environ 58:9–19
Brázdil R, Kundzewicz ZW, Zbigniew W, Benito G (2006) Historical hydrology for studying flood risk in Europe. Hydrol Sci J 51(5):739–764
Brunetti M, Buffoni L, Maugeri M, Nanni T (2006) Temperature and precipitation variability in Italy in the last two centuries from homogenised instrumental time series. Int J Climatol 26:345–381
Brunetti M, Caloiero T, Coscarelli R, Gullà G, Nanni T, Simolo C (2012) Precipitation variability and change in the Calabria region (Italy) from a high resolution daily data-set. Int J Climatol 32:57–73
Caloiero T, Coscarelli R, Ferrari E, Mancini M (2011) Trend detection of annual and seasonal rainfall in Calabria (Southern Italy). Int J Climatol 31:44–56
Copien C, Frank C, Becht M (2008) Natural hazards in the Bavarian Alps: a historical approach to risk assessment. Nat Hazards 45:173–181
Coscarelli R, Caloiero T (2012) Analysis of daily and monthly rainfall concentration in Southern Italy (Calabria region). J Hydrol 416(417):145–156
Craddock JM (1979) Methods of comparing annual rainfall records for climatic purposes. Weather 34:332–346
Crosta GB (1998) Regionalization of rainfall thresholds: an aid to landslide hazard evaluation. Environ Geol 35(2–3):131–145
Crosta GB, Frattini P (2001). Rainfall thresholds for triggering soil slips and debris flow. In: Proceedings of EGS 2nd Plinius conference 2000, Mediterranean storms, Siena, pp 463–488
Crozier M (1986) Landslides: causes, consequences and environment. Croom Helm, London, p 252
Ferrari E, Caloiero T, Coscarelli R (2013) Influence of the North Atlantic Oscillation on the winter rainfall in Calabria (southern Italy). Theor Appl Climatol. doi:10.1007/s00704-013-0856-6
FitzGerald G, Du W, Jamal A, Clark M, Hou X (2010) Flood fatalities in contemporary Australia (1997–2008). Emerg Med Australas 22:180–186
Glade T, Crozier MJ, Smith P (2000) Applying probability determination to refine landslide-triggering rainfall thresholds using an empirical "Antecedent Daily Rainfall Model". Pure Appl Geophys 157:1059–1079
Gullà G, Antronico L, Iaquinta P, Terranova O (2008) Susceptibility and triggering scenarios at a regional scale for shallow landslides. Geomorphology 99: 39–58, ISSN: 0169-555X
Gullà G, Antronico L, Borrelli L, Caloiero T, Coscarelli R, Iovine G, Nicoletti PG, Pasqua AA, Petrucci O, Terranova O (2009) Indicazioni conoscitive e metodologiche connesse all'evento idrogeologico dell'autunno-inverno 2008–2009 in Calabria. Geologi Calabria, anno 10, n.1
Gullà G, Caloiero T, Coscarelli R, Petrucci O (2012a) Rainfall–landslide scenarios: a methodological application in Calabria (Southern Italy). Nat Hazard Earth Syst Sci 12:165–173
Gullà G, Aceto L, Borrelli L, Maiorano S (2012b) Caratterizzazione geotecnica [Parte 5a – Azione A5]. In Gullà G. (Responsabile scientifico), L. Aceto, L. Antronico, L. Borrelli, R. Coscarelli, A.A. Pasqua, O. Petrucci, C. Reali, S. Guardia, E. Valente (2012) – RELAZIONI FINALI – Frazione Ianò del Comune di Catanzaro, Convenzione di consulenza tecnico-scientifica per "Studi ed indagini geologiche, geotecniche, idrologiche ed idrauliche nella frazione Ianò del comune di Catanzaro", CNR–IRPI, Commissario Delegato OPCM n. 3862/2010. Unpublished report, November 2012, 104 pp., (in Italian).
Hilker N, Badoux A, Hegg C (2009) The Swiss flood and landslide damage database 1972–2007. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 9:913–925
Kirschbaum DB, Adler R, Hong Y, Hill S, Lerner-Lam AL (2009) A global landslide catalogue for hazard applications: method, results and limitations. Nat Hazards 52(3):561–575. doi:10.1007/s11069-009-9401-4
Kuriakose SL, Sankar G, Muraleedharan C (2009) History of landslide susceptibility and a chorology of landslide-prone areas in the Western Ghats of Kerala. Indian Environ Geol 57:1553–1568
Llasat MC, Barriendos M, Barrera A (2006) The use of historical data in flood risk assessment, Application to Catalonia (NE Spain) 14th–20th centuries. In: Armiero M (ed) View from the South, Environmental stories from the Mediterranean Word, CNR. Istituto di Studi sulle Società del Mediterraneo, Naples, pp 95–111
Llasat MC, Llasat-Botija M, López L (2009) A press database on natural risks and its application in the study of floods in northeastern Spain. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 9:2049–2061
Maples LZ, Tiefenbacher JP (2009) Landscape, development, technology and drivers: the geography of drownings associated with automobiles in Texas floods, 1950–2004. Appl Geogr 29:224–234
Marques R, Zêezere J, Trigo R, Gaspar J, Trigo I (2008) Rainfall patterns and critical values associated with landslides in Povaҫão County (São Miguel Island, Azores): relationships with the North Atlantic Oscillation. Hydrol Process 22:478–494
Petrucci O (2012) Assessment of the impact caused by natural disasters: simplified procedures and open problems. In: Tiefenbacher JP (ed) Managing disasters, assessing hazards, emergencies and disaster impacts, INTECH, Open Access Publisher. http://www.intechopen.com/books/approaches-to-managing-disaster-assessing-hazards-emergencies-and-disaster-impacts
Petrucci O, Gullà G (2009) A Support Analysis Framework for mass movement damage assessment: applications to case studies in Calabria (Italy). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 9:315–326
Petrucci O, Gullà G (2010) A simplified method for landslide damage scenario assessment based on historical data. Nat Hazard 52(3):539–560
Petrucci O, Pasqua AA (2008) The study of past damaging hydrogeological events for damage susceptibility zonation. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 8:881–892
Petrucci O, Pasqua AA (2009) A methodological approach to characterise Landslide Periods based on historical series of rainfall and landslide damage. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 9:1655–1670
Petrucci O, Pasqua AA (2012) Damaging events along roads during bad weather periods: a case study in Calabria (Italy). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12:365–378
Petrucci O, Polemio M, Pasqua AA (2009) Analysis of damaging hydrogeological events: the case of the Calabria Region (Southern Italy). Environ Manag 43(3):483–495. doi:10.1007/s00267-008-9234-z, Springer
Petrucci O, Pasqua AA, Gullà G (2010) Landslide damage assessment using the Support Analysis Framework (SAF): the 2009 landsliding event in Calabria (Italy). ADGEO 26:13–17
Reneau SL, Dietrich WE (1987) The importance of hollows in debris flow studies. In: Costa and Wiezcorek (eds) Debris flows/avalanches: process, recognition and mitigation, reviews in engineering geology, Vol. VII, J.E. Geological Society of America, pp 165–180
Terranova O, Antronico L, Gulla' G (2007) Landslide triggering scenarios in homogeneous geological contexts: the area surrounding Acri (Calabria, Italy). Geomorphology 87:250–267
Varnes DJ (1978) Slope movements: type and processes. In: Eckel EB (ed) Landslides analysis and control. Transp Res Board Spec Rep 176:11–33
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out under the Commessa TA.P05.012 "Tipizzazione di eventi naturali e antropici ad elevato impatto sociale ed economico" of the CNR — Department "Scienze del sistema Terra e Tecnologie per l'Ambiente". Data and information used have been collected within the framework of the activities carried out for the action "Regione Calabria – Supporto tecnico-scientifico al Commissario delegato O.P.C.M. no. 3862/2010".
The authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewer for the precious remarks and comments which led to improve the initial version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antronico, L., Borrelli, L., Coscarelli, R. et al. Slope movements induced by rainfalls damaging an urban area: the Catanzaro case study (Calabria, southern Italy). Landslides 10, 801–814 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0431-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0431-3