Abstract
Many oak stands (Quercus spp.) have been managed as coppices for firewood production for centuries in the Mediterranean area. After the abandonment of firewood production during the 1980s, current management practices attempt to convert coppices into coppices-with-standards through thinning and promoting forest regeneration via sexual reproduction. In this work, we used long-term data from repeated forest inventories and dendrometers in a thinning trial to assess the effects of thinning and climate on the intra- and inter-annual growth dynamics of Quercus pyrenaica Willd. coppices. Our results revealed that thinning favored the growth of Q. pyrenaica trees, especially when the stand density reduction was high (ca. 50% of the basal area extracted). Unthinned plots displayed more natural mortality i.e., self-thinning. Growth was enhanced with low vapor pressure deficit. Intense thinning treatments displayed higher intra-annual growth rates and interacted positively with rainfall to induce higher growth. We conclude that thinning, especially intensive thinning, may alleviate the negative effects of dry years and thus could provide a potential measure to adapt these stands to the different climatic scenarios with higher temperatures and less precipitation within the framework of sustainable forest management.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adame P, Hynynen J, Cañellas I, del Río M (2008) Individual-tree diameter growth model for rebollo oak (Quercus pyrenaica Willd.) coppices. For Ecol Manag 255:1011–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2007.10.019
Ainalis AB, Platis PD, Meliadis IM (2010) Grazing effects on the sustainability of an oak coppice forest. For Ecol Manag 259:428–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.10.039
Aldea J, Bravo F, Bravo-Oviedo A et al (2017) Thinning enhances the species-specific radial increment response to drought in Mediterranean pine-oak stands. Agric For Meteorol 237:371–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.02.009
Aldea J, Bravo F, Vázquez-Piqué J et al (2018) Species-specific weather response in the daily stem variation cycles of Mediterranean pine-oak mixed stands. Agric For Meteorol 256–257:220–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.03.013
Ally D, Ritland K, Otto SP (2008) Can clone size serve as a proxy for clone age?An exploration using microsatellite divergence in Populus tremuloides. Mol Ecol 17:4897–4911. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03962.x
Bravo-Fernández JA (2003) Resalveos de conversión en montes bajos de la región central de la Península Ibérica. Technic University of Madrid
Cabon A, Mouillot F, Lempereur M et al (2018) Thinning increases tree growth by delaying drought-induced growth cessation in a Mediterranean evergreen oak coppice. For Ecol Manag 409:333–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2017.11.030
Campelo F, Gutiérrez E, Ribas M et al (2018) The facultative bimodal growth pattern in Quercus ilex—a simple model to predict sub-seasonal and inter-annual growth. Dendrochronologia 49:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dendro.2018.03.001
Cañellas I, Del Rio M, Roig S, Montero G (2004) Growth response to thinning in Quercus pyrenaica Willd. coppice stands in Spanish central mountain. Ann For Sci 61:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest
Cañellas I, Sánchez-González M, Bogino SM et al (2017) Carbon sequestration in Mediterranean oak forests. In: Bravo F, LeMay V, Jandl R (eds) Managing forest ecosystems: the challenge of climate change. Springer, Cham, pp 403–427
Ciancio O, Corona P, Lamonaca A et al (2006) Conversion of clearcut beech coppices into high forests with continuous cover: a case study in central Italy. For Ecol Manag 224:235–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2005.12.045
Corcuera L, Camarero JJ, Sisó S, Gil-Pelegrín E (2006) Radial-growth and wood-anatomical changes in overaged Quercus pyrenaica coppice stands: functional responses in a new Mediterranean landscape. Trees Struct Funct 20:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-005-0016-4
Cotillas M, Sabaté S, Gracia C, Espelta JM (2009) Growth response of mixed mediterranean oak coppices to rainfall reduction. Could selective thinning have any influence on it? For Ecol Manag 258:1677–1683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.07.033
De Cáceres M, Martin-StPaul N, Turco M et al (2018) Estimating daily meteorological data and downscaling climate models over landscapes. Environ Model Softw 108:186–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.08.003
Diaconu D, Kahle HP, Spiecker H (2017) Thinning increases drought tolerance of European beech: a case study on two forested slopes on opposite sides of a valley. Eur J For Res 136:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-017-1033-8
Fernández-de-Uña L, Cañellas I, Gea-Izquierdo G (2015) Stand competition determines how different tree species will wope with a warming climate. PLoS ONE 10:e0122255. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122255
Fernández-de-Uña L, Rossi S, Aranda I et al (2017) Xylem and leaf functional adjustments to drought in Pinus sylvestris and Quercus pyrenaica at their elevational boundary. Front Plant Sci 8:1200. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01200
Flannigan M, Krawchuk M, de Groot W et al (2009) Implications of changing climate for global wildland fire. Int J Wildl Fire 18:483–507
Gea-Izquierdo G, Cañellas I (2014) Local climate forces instability in long-term productivity of a Mediterranean oak along climatic gradients. Ecosystems 17:228–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-013-9719-3
Giorgi F, Lionello P (2008) Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Glob Planet Change 63:90–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.09.005
Hair J, Anderson R, Tatham R, Black W (1995) Multivariate data analysis, vol 3. Macmillan Publishers Limited, New York
Hastie T, Tibshirani R (1989) Generalized additive models. Stat Sci 10:297–318. https://doi.org/10.1214/ss/1177013604
Hernández-Santana V, Martínez-Fernández J, Morán C, Cano A (2008) Response of Quercus pyrenaica (melojo oak) to soil water deficit: a case study in Spain. Eur J For Res 127:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-008-0214-x
Hoff C, Rambal S, Joffre R (2002) Simulating carbon and water flows and growth in a Mediterranean evergreen Quercus ilex coppice using the FOREST-BGC model. For Ecol Manag 164:121–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(01)00605-3
Kirby KJ, Buckley GP, Mills J (2017) Biodiversity implications of coppice decline, transformations to high forest and coppice restoration in British woodland. Folia Geobot 52:5–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12224-016-9252-1
Lenth R (2019) emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means
Mäkinen H, Seo JW, Nöjd P et al (2008) Seasonal dynamics of wood formation: a comparison between pinning, microcoring and dendrometer measurements. Eur J For Res 127:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-007-0199-x
Marchi E, Picchio R, Mederski PS et al (2016) Impact of silvicultural treatment and forest operation on soil and regeneration in Mediterranean Turkey oak (Quercus cerris L.) coppice with standards. Ecol Eng 95:475–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.084
Menéndez-Miguélez M, Ávarez-Álvarez PA, Majada J, Canga E (2015) Effects of soil nutrients and environmental factors on site productivity in Castanea sativa Mill. coppice stands in NW Spain. New For 46:217–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-014-9456-2
Montserrat-Martí G, Camarero JJ, Palacio S et al (2009) Summer-drought constrains the phenology and growth of two coexisting Mediterranean oaks with contrasting leaf habit: implications for their persistence and reproduction. Trees Struct Funct 23:787–799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-009-0320-5
Moreno-Fernández D, Sánchez-González M, Álvarez-González JG et al (2014) Response to the interaction of thinning and pruning of pine species in Mediterranean mountains. Eur J For Res 133:833–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-014-0800-z
Nieto Quintano P, Caudullo G, de Rigo D (2016) Quercus pyrenaica in Europe: distribution, habitat, usage and threats. In: San-Miguel-Ayanz J, de Rigo D, Caudullo G, et al. (eds) European Atlas of Forest Tree Species. p e01f807+
Núñez V, Hernando A, Velázquez J, Tejera R (2012) Livestock management in Natura 2000: a case study in a Quercus pyrenaica neglected coppice forest. J Nat Conserv 20:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnc.2011.07.001
Oberhuber W, Gruber A, Kofler W, Swidrak I (2014) Radial stem growth in response to microclimate and soil moisture in a drought-prone mixed coniferous forest at an inner Alpine site. Eur J For Res 133:467–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-013-0777-z
Oliveira N, Rodríguez-Soalleiro R, Pérez-Cruzado C et al (2018) Above- and below-ground carbon accumulation and biomass allocation in poplar short rotation plantations under Mediterranean conditions. For Ecol Manag 428:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2018.06.031
Pacheco A, Camarero JJ, Ribas M et al (2018) Disentangling the climate-driven bimodal growth pattern in coastal and continental Mediterranean pine stands. Sci Total Environ 615:1518–1526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.133
Pedersen EJ, Miller DL, Simpson GL, Ross N (2019) Hierarchical generalized additive models in ecology: an introduction with mgcv. Peer J. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6876
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, R Core Team (2020). nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R package version 3.1–149
R Core Team (2020) R: a language and environment for statistical computing
Restaino CM, Peterson DL, Littell J (2016) Increased water deficit decreases Douglas fir growth throughout western US forests. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:9557–9562. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1602384113
Rodríguez-Calcerrada J, Pérez-Ramos IM, Ourcival JM et al (2011) Is selective thinning an adequate practice for adapting Quercus ilex coppices to climate change? Ann For Sci 68:575–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-011-0050-x
Salomón R, Valbuena-Carabaña M, Gil L, González-Doncel I (2013) Clonal structure influences stem growth in Quercus pyrenaica Willd. coppices: Bigger is less vigorous. For Ecol Manag 296:108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2013.02.011
Salomón R, Rodríguez-Calcerrada J, Zafra E et al (2016) Unearthing the roots of degradation of Quercus pyrenaica coppices: a root-to-shoot imbalance caused by historical management? For Ecol Manag 363:200–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FORECO.2015.12.040
Seidl R, Thom D, Kautz M et al (2017) Forest disturbances under climate change. Nat Clim Chang 7:395–402. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3303
Serrada R, Gómez-Sanz V, Aroca MJ et al (2017) Decline in holm oak coppices (Quercus ilex L. subsp. ballota (Desf.) Samp.): biometric and physiological interpretations. For Syst 26:6. https://doi.org/10.5424/fs/2017262-10583
Serrada-Hierro R, González I, Lopez C, et al (1994) Dasometric classification and alternative silvopastoral uses of rebollo oak (Quercus pyrenaica Willd.) stands in Madrid. Investig Agrar Sist Recur For Fuera de s:79–88
Siegmund JF, Sanders TGM, Heinrich I et al (2016) Meteorological drivers of extremes in daily stem radius variations of beech, oak, and pine in Northeastern Germany: an event coincidence analysis. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00733
Sohn JA, Saha S, Bauhus J (2016) Potential of forest thinning to mitigate drought stress: a meta-analysis. For Ecol Manag 380:261–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FORECO.2016.07.046
Stinziano JR, Way DA (2017) Autumn photosynthetic decline and growth cessation in seedlings of white spruce are decoupled under warming and photoperiod manipulations. Plant Cell Environ 40:1296–1316. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12917
Valbuena-Carabaña M, González-Martínez SC, Gil L (2008) Coppice forests and genetic diversity: a case study in Quercus pyrenaica Willd. from Central Spain. For Ecol Manag 254:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2007.08.001
Vanclay JK (1991) Mortality functions for North Queensland Rain forests. J Trop For Sci 4:15–36
Vaz M, Pereira JS, Gazarini LC et al (2010) Drought-induced photosynthetic inhibition and autumn recovery in two Mediterranean oak species (Quercus ilex and Quercus suber). Tree Physiol 30:946–956. https://doi.org/10.1093/TREEPHYS/TPQ044
Vázquez de la Cueva A, Quintana JR, Cañellas I (2012) Fire activity projections in the SRES A2 and B2 climatic scenarios in peninsular Spain. Int J Wildl Fire 21:653. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF11013
Vieira J, Campelo F, Rossi S et al (2015) Adjustment capacity of maritime pine cambial activity in drought-prone environments. PLoS ONE 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126223
Volkova L, Weston CJ (2019) Effect of thinning and burning fuel reduction treatments on forest carbon and bushfire fuel hazard in Eucalyptus sieberi forests of South-Eastern Australia. Sci Total Environ 694:133708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133708
Wood SN (2003) Thin-plate regression splines. J R Stat Soc 65:95–114. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9868.00374
Wood SN (2017) Generalized additive models: an introduction with R. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Second
Wykoff WR (1990) A basal area increment model for individual conifers in the northern Rocky Mountains. For Sci 36:1077–1104. https://doi.org/10.1093/forestscience/36.4.1077
Acknowledgements
We thank Adam Collins for revising and editing the English grammar. The authors recognize the work of Estrella Viscasillas and Ángel Bachiller, who collected most of the field data. This study has been funded through the Agreement EG17-042 between the Ministry of Agriculture and INIA. DMF was supported by Juan de la Cierva Formación Post-Doctoral program (FJC2018-037870-I) and DMB was funded by projects AGL2015-73190-JIN and RYC-2017-23389 from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments, which improved the quality of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Lluís Coll.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. SM1
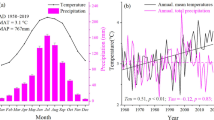
Average monthly trends of mean temperature (red) and average monthly rainfall (blue) from 2011 to 2019 (TIFF 109863 kb)
Fig. SM3
Annual trends of seasonal cumulative rainfall, seasonal mean temperature and seasonal mean vapor pressure deficit (VPD) from 2012 to 2019 (TIFF 175781 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreno-Fernández, D., Aldea, J., Gea-Izquierdo, G. et al. Influence of climate and thinning on Quercus pyrenaica Willd. coppices growth dynamics. Eur J Forest Res 140, 187–197 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-020-01322-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-020-01322-3