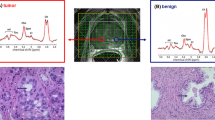
Abstract
Introduction
Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the leading causes of death among men worldwide. The current methods utilized to screen for prostate cancer may not have sufficient sensitivity in distinguishing aggressive from indolent diseases, which affect the quality of life of patients in the short and long term. The overdiagnosis of cases and overtreatment are prevalent due to the heterogeneity of the disease in terms of latent and progressive variants, as well as in the tissue types present in biopsy samples.
Methods
The purpose of this review is to discuss the potential clinical benefits of incorporating high-resolution magic angle spinning (HRMAS) magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) modalities to overcome the current challenges in the diagnosis, prognostication, and monitoring of PCa.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leslie SW, Soon-Sutton TL, Sajjad H, Siref LE. Prostate Cancer. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL) 2021.
Gomez-Cebrian N, Rojas-Benedicto A, Albors-Vaquer A, Lopez-Guerrero JA, Pineda-Lucena A, Puchades-Carrasco L (2019) Metabolomics contributions to the discovery of prostate cancer biomarkers. Metabolites. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9030048
Vandergrift LA, Decelle EA, Kurth J, Wu S, Fuss TL, DeFeo EM et al (2018) Metabolomic prediction of human prostate cancer aggressiveness: magnetic resonance spectroscopy of histologically benign tissue. Sci Rep 8:4997
Trock BJ (2011) Application of metabolomics to prostate cancer. Urol Oncol 29:572–581
Burns MA, He W, Wu CL, Cheng LL (2004) Quantitative pathology in tissue MR spectroscopy based human prostate metabolomics. Technol Cancer Res Treat 3:591–598
Braadland PR, Giskeodegard G, Sandsmark E, Bertilsson H, Euceda LR, Hansen AF et al (2017) Ex vivo metabolic fingerprinting identifies biomarkers predictive of prostate cancer recurrence following radical prostatectomy. Br J Cancer 117:1656–1664
van Asten JJ, Cuijpers V, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa C, Soede-Huijbregts C, Witjes JA, Verhofstad A, et al. High resolution magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy for metabolic assessment of cancer presence and Gleason score in human prostate needle biopsies. MAGMA. 2008;21:435–42.
Cheng LL, Burns MA, Taylor JL, He W, Halpern EF, McDougal WS et al (2005) Metabolic characterization of human prostate cancer with tissue magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Can Res 65:3030–3034
Tessem MB, Swanson MG, Keshari KR, Albers MJ, Joun D, Tabatabai ZL et al (2008) Evaluation of lactate and alanine as metabolic biomarkers of prostate cancer using 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy of biopsy tissues. Magn Reson Med 60:510–516
Cheng LL, Lean CL, Bogdanova A, Wright SC Jr, Ackerman JL, Brady TJ et al (1996) Enhanced resolution of proton NMR spectra of malignant lymph nodes using magic-angle spinning. Magn Reson Med 36:653–658
Cheng LL, Ma MJ, Becerra L, Ptak T, Tracey I, Lackner A et al (1997) Quantitative neuropathology by high resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6408–6413
Dinges SS, Vandergrift LA, Wu S, Berker Y, Habbel P, Taupitz M et al (2019) Metabolomic prostate cancer fields in HRMAS MRS-profiled histologically benign tissue vary with cancer. NMR Biomed 32:e4038
Wu CL, Taylor JL, He W, Zepeda AG, Halpern EF, Bielecki A et al (2003) Proton high-resolution magic angle spinning NMR analysis of fresh and previously frozen tissue of human prostate. Magn Reson Med 50:1307–1311
Smith R, Litwin M, Lu Y, Zetter B (1995) Identification of an endogenous inhibitor of prostate carcinoma cell growth. Nature Med 1:1040–1045
Cheng LL, Wu C, Smith MR, Gonzalez RG (2001) Non-destructive quantitation of spermine in human prostate tissue samples using HRMAS 1H NMR spectroscopy at 9.4 T. FEBS Lett 494:112–116
Andersen MK, Rise K, Giskeodegard GF, Richardsen E, Bertilsson H, Storkersen O et al (2018) Integrative metabolic and transcriptomic profiling of prostate cancer tissue containing reactive stroma. Sci Rep 8:14269
Swanson MG, Zektzer AS, Tabatabai ZL, Simko J, Jarso S, Keshari KR et al (2006) Quantitative analysis of prostate metabolites using 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 55:1257–1264
Swanson MG, Keshari KR, Tabatabai ZL, Simko JP, Shinohara K, Carroll PR et al (2008) Quantification of choline- and ethanolamine-containing metabolites in human prostate tissues using 1H HR-MAS total correlation spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 60:33–40
Albers MJ, Bok R, Chen AP, Cunningham CH, Zierhut ML, Zhang VY et al (2008) Hyperpolarized 13C lactate, pyruvate, and alanine: noninvasive biomarkers for prostate cancer detection and grading. Cancer Res 68:8607–8615
Levin YS, Albers MJ, Butler TN, Spielman D, Peehl DM, Kurhanewicz J (2009) Methods for metabolic evaluation of prostate cancer cells using proton and (13)C HR-MAS spectroscopy and [3-(13)C] pyruvate as a metabolic substrate. Magn Reson Med 62:1091–1098
Bancroft Brown J, Sriram R, VanCriekinge M, Delos Santos R, Sun J, Delos Santos J et al (2019) NMR quantification of lactate production and efflux and glutamate fractional enrichment in living human prostate biopsies cultured with [1,6-(13) C2 ]glucose. Magn Reson Med 82:566–576
Perez-Rambla C, Puchades-Carrasco L, Garcia-Flores M, Rubio-Briones J, Lopez-Guerrero JA, Pineda-Lucena A (2017) Non-invasive urinary metabolomic profiling discriminates prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia. Metabolomics 13:52
Lima AR, Pinto J, Barros-Silva D, Jeronimo C, Henrique R, Bastos ML et al (2020) New findings on urinary prostate cancer metabolome through combined GC-MS and (1)H NMR analytical platforms. Metabolomics 16:70
Yang B, Zhang C, Cheng S, Li G, Griebel J, Neuhaus J (2021) Novel metabolic signatures of prostate cancer revealed by (1)H-NMR metabolomics of urine. Diagnostics (Basel). 11:149
Stenman K, Stattin P, Stenlund H, Riklund K, Grobner G, Bergh A (2011) H HRMAS NMR derived bio-markers related to tumor grade, tumor cell fraction, and cell proliferation in prostate tissue samples. Biomark Insights 6:39–47
Dittrich R, Kurth J, Decelle EA, DeFeo EM, Taupitz M, Wu S et al (2012) Assessing prostate cancer growth with citrate measured by intact tissue proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 15:278–282
Giskeodegard GF, Bertilsson H, Selnaes KM, Wright AJ, Bathen TF, Viset T et al (2013) Spermine and citrate as metabolic biomarkers for assessing prostate cancer aggressiveness. PLoS ONE 8:e62375
Dudka I, Thysell E, Lundquist K, Antti H, Iglesias-Gato D, Flores-Morales A et al (2020) Comprehensive metabolomics analysis of prostate cancer tissue in relation to tumor aggressiveness and TMPRSS2-ERG fusion status. BMC Cancer 20:437
Santos CF, Kurhanewicz J, Tabatabai ZL, Simko JP, Keshari KR, Gbegnon A et al (2010) Metabolic, pathologic, and genetic analysis of prostate tissues: quantitative evaluation of histopathologic and mRNA integrity after HR-MAS spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 23:391–398
Bertilsson H, Tessem MB, Flatberg A, Viset T, Gribbestad I, Angelsen A et al (2012) Changes in gene transcription underlying the aberrant citrate and choline metabolism in human prostate cancer samples. Clin Cancer Res 18:3261–3269
Swanson MG, Vigneron DB, Tabatabai ZL, Males RG, Schmitt L, Carroll PR et al (2003) Proton HR-MAS spectroscopy and quantitative pathologic analysis of MRI/3D-MRSI-targeted postsurgical prostate tissues. Magn Reson Med 50:944–954
Massie CE, Lynch A, Ramos-Montoya A, Boren J, Stark R, Fazli L et al (2011) The androgen receptor fuels prostate cancer by regulating central metabolism and biosynthesis. EMBO J 30:2719–2733
Chetta P, Zadra G (2020) Metabolic reprogramming as an emerging mechanism of resistance to endocrine therapies in prostate cancer. Cancer Drug Resistance J 4:143–162
Madhu B, Shaw GL, Warren AY, Neal DE, Griffiths JR (2016) Response of Degarelix treatment in human prostate cancer monitored by HR-MAS (1)H NMR spectroscopy. Metabolomics 12:120
Selnaes KM, Gribbestad IS, Bertilsson H, Wright A, Angelsen A, Heerschap A et al (2013) Spatially matched in vivo and ex vivo MR metabolic profiles of prostate cancer – investigation of a correlation with Gleason score. NMR Biomed 26:600–606
Patel SK, George B, Rai V (2020) Artificial Intelligence to Decode Cancer Mechanism: Beyond Patient Stratification for Precision Oncology. Front Pharmacol 11:1177
Acknowledgements
NIH Grants: R01CA115746, R01CA115746S1, R01AG070257-01, S10OD023406, T32EB025823-02 (SAS). MGH Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging. Mass spectrometry data were acquired using instrumentation in the UMass Amherst Mass Spectrometry Core Facility, RRID:SCR_019063.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanchez-Dahl Gonzalez, M., Muti, I.H. & Cheng, L.L. High resolution magic angle spinning MRS in prostate cancer. Magn Reson Mater Phy 35, 695–705 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-022-01005-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-022-01005-7