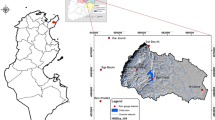
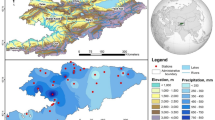
Abstract
Soil erosion by water is a common environmental problem which can affect the sustainable development and the agriculture of developing countries especially. Therefore, several countries, threatened by this phenomenon, adopt different measures to preserve and protect their natural resources. The main purpose of this study was to identify vulnerable areas to establish a soil erosion risk map in Tunisia. In order to do so, an approach based on a combination of the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) as an erosion model, Geographic Information System (GIS) and Remote Sensing was applied. RUSLE, which is a model to predict soil loss, is composed of five factors. Erosivity factor (R factor), erodibility factor (K factor), topography factor (LS factor), crop management factor (C factor), and supporting practices factor (P factor). Furthermore, in order to get the most accurate C factor for each land use, times series Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Enhanced Vegetation index (MODIS-EVI) were used. MODIS-EVI time series was helpful for distinguishing vegetation dynamics with taking into account phenological variation of the crops. The results indicated that Tunisia has a serious risk of soil erosion. Indeed, about 24.57% of our study area had a soil loss rate more than 30 t/ha. In these areas, suitable and urgent measures and treatments should be required. Finally, this approach which is based on remote sensing techniques, GIS and erosion model can be useful for planning appropriate environmental decision-making policy in a global scale.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Arnoldus HM (1980) An approximation of the rainfall factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. In: De Boodt M, Gabriel D (eds) Assessment of erosion. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., Chichester, West Sussex, UK, pp 127–132
Aster GDEM validation team: METI/ERSDAC, NASA/LPDAAC, USGS/EROS (2009) ASTER Global DEM Validation. Summary Report. p 28
Bakker MM, Govers G, Van Doorn A, Quetier F, Chouvardas D, Rounsevell M (2008) The response of soil erosion and sediment export to land-use change in four areas of Europe: the importance of landscape pattern. Geomorphology 98:213–226
Baskan O, Cebel H, Akgul S, Erpul G (2010) Conditional simulation of USLE/RUSLE soil erodibility factor by geostatistics in a Mediterranean Catchment, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 60:1179–1187
Belkhodja K, Bortoli L, Cointepas JP, Dimanche P, Fournet A, Jacquinet JC, Mori A (1973) Les sols de la Tunisie Septentrionale. Sol de Tunisie, Bulletin de la Division des sols n°5, Ministère de l’agriculture de Tunisie
Ben Mammou A, Louati MH (2007) Evolution temporelle de l’envasement des retenues de barrages de Tunisie. Revue des sciences de l’eau 20:201–210
Benkobi L, Trlica MJ, Smith JL (1994) Evaluation of a refined surface cover subfactor for use in RUSLE. J Range Manag 47:74–78
Cormary Y, Masson J (1964) Etude de conservation des eaux et du sol au centre de recherches du génie rural de tunisie. Application à un projet-type de la formule de pertes de sols de Wischmeier. Cahiers ORSTOM. Série Pédologie 2:3–26
Cyr L, Bonn F, Pesant A (1995) Vegetation indices derived from remote sensing for an estimation of soil protection against water erosion. Ecol Model 79:277–285
Da Silva AM (2004) Rainfall erosivity map for Brazil. Catena 57:251–259
Dabral PP, Baithuri N, Pandey A (2008) Soil erosion assessment in a hilly catchment of north eastern India USLE, GIS and remote sensing. Water Resour Manag 22:1783–1798
De Asis AM, Omasa K (2007) Estimation of vegetation parameter for modeling soil erosion using linear spectral mixture analysis of Landsat ETM data. J Photogramm Remote Sens 62:309–324
De Jong Van Lier Q, Spavorek G, Flanagan DC, Bloem EM, Schnug E (2005) Runoff mapping using WEPP erosion model and GIS tools. Comput Geosci 31:1270–1276
De Jong SM, Paracchini ML, Bertolo F, Folving S, Megier J, De Roo APJ (1999) Regional assessment of soil erosion using the distributed model SEMMED and remotely sensed data. Catena 37:291–308
Direction General des Barrages et des Grands Travaux Hydraulique (DG/BGTH) (2010) Bulletin de suivie de la situation hydraulique des barrages. Ministère de l’Agriculture, des ressources hydrauliques et de la pêche
Direction Générale de l’aménagement et de la conservation des terres Agricoles (DG/ACTA) (2002) Second strategy of soil and water conservation (2002–2011). Ministry of Agriculture of Tunisia
Direction Générale de la Planification et du Développement des investissements Agricoles (DG/PDIA) (2007) Investigation results of the agricultural campaign 2005/2006. Technical report, Ministry of Agriculture of Tunisia
Dunjo G, Pardini G, Gispert M (2004) The role of land use—land cover on runoff generation and sediment yield a microplot scale, in a small Mediterranean catchment. J Arid Environ 57:239–256
Duran ZVH, Francia MJR, Martinez RA (2004) Impact of vegetative cover on Runoff and soil erosion at hillslope scale in Lanjaron, Spain. Environmentalist 24:39–48
Ferro V, Porto P, Bofu Y (1999) A comparative study of rainfall erosivity estimation for southern Italy and southeastern Australia. Hydrol Sci J Sci Hydrol 44:3–24
Fistikoglu O, Harmancioglu NB (2002) Integration of GIS with USLE in assessment of soil erosion. Water Resour Manag 16:447–467
Flanagan DC, Nearing MA (1995) USDA-Water Erosion Prediction Project: Hillslope Profile and watershed model documentation. NSERL Report n 10, USDA-ARS National Soil Erosion Research Laboratory. West Lafayette, IN, USA
Folly A, Bronsveld MC, Clavaux M (1996) A knowledge-based approach for C-factor mapping in Spain using Landsat TM and GIS. Int J Remote Sens 17:2401–2415
Foster GR, McCool DK, Renard KG, Moldenhauer WC (1981) Conversion of the universal soil loss equation to SI metric units. J Soil Water Conserv 36:355–359
Ganguly S, Friedl MA, Tan B, Zhang X, Verma M (2010) Land surface phenology from MODIS: characterization of the collection 5 global land cover dynamics product. Remote Sens Environ 114:1805–1816
Groupe de recherche sur la Variabilité du Climat et l’homme en Tunisie de l’université de Tunis (Grevachot) (2008) Atlas de l’eau en Tunisie. Faculté des sciences Humaines et Sociales de Tunis
Hochschild V, Marker M, Rodolfi G, Staudenrausch H (2003) Delineation of erosion classes in semi-arid southern African grasslands using vegetation indices from optical remote sensing data. Hydrol Process 17:917–928
Huete AR (1988) A soil-adjusted vegetation index. Remote Sens Environ 25:295–309
Huete A, Didan K, Miura T, Rodriguez EP, Gao X, Ferreira LG (2002) Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens Environ 83:195–213
Irvem A, Topaloglu F, Uygur V (2007) Estimating spatial distribution of soil loss over Seyhan River Basin in Turkey. J Hydrol 336:30–37
Ismail J, Ravichandran S (2008) RUSLE2 model application for soil erosion assessment using remote sensing and GIS. Water Resour Manag 22:83–102
Jabbar MT (2003) Application of GIS to estimate soil erosion using RUSLE. Geo-spatial information. Science 6:34–37
Karaburun A (2010) Estimation of C factor for soil erosion modeling using NDVI in Buyukcekmece watershed. Ozean J Appl Sci 3:77–85
Kefi M, Yoshino K, Zayani K, Isoda H (2009) Estimation of Soil Loss by using combination of Erosion Model and GIS: case of study watersheds in Tunisia. J Arid Land Stud 19:287–290
Kouli M, Sopios P, Vallianatos F (2009) Soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in a GIS framework, Chania, Northwestern Crete, Greece. Environ Geol 57:483–497
Laflen JM, Moldenhauer WC (2003) Pioneering soil erosion prediction: the USLE story. In: Zoebisch MA (ed) Special publication n 1. World Association of Soil and water Conservation (WASWC), China
Lal R (2001) Soil degradation by erosion. Land Degrad Dev 12:519–539
Land Processes DAAC (2008) MODIS Reprojection Tool User’s Manual, Release 4.0. USGS Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center in Collaboration with the Department of Mathematics and Computer Science South Dakota School of Mines and Technology. p 61
Lillesand TM, Kiefer RW (1994) Remote sensing and image interpretation, 3rd edn. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York
Lin CY, Lin WT, Chou WC (2002) Soil erosion prediction and sediment yield estimation: the Taiwan experience. Soil Tillage Res 68:143–152
Lu D, LI G, Valladares S, Batistella M (2004) Mapping soil erosion risk in Rondônia, Brazilian Amazonia: using RUSLE, remote sensing and GIS. Land Degrad Dev 15:499–512
Mati BC, Morgan RPC, Gichuki FN, Quiton JN, Brewer TR, Liniger HP (2000) Assessment of erosion hazard with USLE and GIS: a case of study of the Upper Ewaso Ng’iro North basin of Kenya. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinformation (JAG) 2:78–86
Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development (MESD) (2007) National report: The State of the Environment in 2007. Republic of Tunisia
Mondiale B (2007) République Tunisienne: Evaluation du coût de la dégradation de l’eau. Bureau Régional Moyen-Orient & Afrique du Nord, Département Développement Durable
Moore ID, Burch GJ (1986) Physical basis of the length-slope factor in the universal soil loss equation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:1294–1298
Morgan RPC (2005) Soil erosion and conservation, 3rd edn. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford
Mtimet A (2001) Soils of Tunisia. In: Zdruli P, Steduto P, Lacirignola C, Montanarella L (eds) Soil resources of Southern and Eastern Mediterranean countries. Options Méditerranéennes, Série B n 34. CIHEAM-IAMB, Bari, pp 243–268
Nam PT, Yang D, Kanae S, Oki T, Musiake K (2003) Global soil loss estimate using rusle model: the use of Global spatial datasets on estimating erosive parameters. Geoinformatics 14:49–53
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290
Ozhan S, Balci AN, Ozyuvaci N, Hizai A, Gokbulak F, Serengil Y (2005) Cover and management factors for the Universal Soil Loss Equation for forest ecosystem in the Marmara region, Turkey. Forest Ecol Manag 214:118–123
Pimentel D, Harvey C, Resosudarmo P, Sinclair K, Kurz D, McNair M, Crist S, Shpritz L, Fitton L, Saffouri R, Blair R (1995) Environmental and economic costs of soil erosion and conservation benefits. Science 61:1117–1123
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, McCool DK, Yoder DC (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the revised universal soil loss equation. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook, p 703
Rouse JW, Haas R H, Schell J A, Deering DW (1973) Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. In: Third ERTS Symposium, NASA SP-351 I: 309–317
Sakamoto T, Yokozawa M, Toritani H, Shibayama M, Ishitsuka N, Ohno H (2005) A crop phenology detection method using time-series MODIS data. Remote Sens Environ 96:366–374
Schmidt F, Persson A (2003) Comparison of DEM data capture and topographic wetness indices. Precision Agric 4:179–192
Sedano F, Gong P, Ferrao M (2005) Land cover assessment with MODIS imagery in southern African Miombo ecosystems. Remote Sens Environ 98:429–441
Van Rompaey AJJ, Viellefont V, Jones RJA, Montanarella L, Verstraeten G, Bazzoffi P, Dostal T, Krasa J, De Vente J, Poesen J (2003) Validation of Soil erosion estimates at European Scale. European Commission, Joint Research Center. EUR 20827
Vigiak O, Newham LTH, Whitford J, Robert AM, Rattray D, Melland AR (2011) Integrating farming systems and landscape processes to assess management impacts on suspended sediment loads. Environ Model Softw 26:144–162
Vrieling A (2006) Satellite remote sensing for water erosion assessment: a review. Catena 65:2–18
Vrieling A (2007) Mapping erosion from space. Doctoral Thesis, Wageningen University
Wang G, Wente S, Gertner GZ, Anderson A (2002) Improvement in mapping vegetation cover factor for the universal soil loss equation by geostatistical methods with Landsat Thematic Mapper Images. Int J Remote Sens 23:3649–3667
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses: a guide to conservation planning. Agriculture Handbook No. 537. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC
Yoshino K, Ishioka Y (2005) Guidelines for soil conservation towards integrated basin management for sustainable development: a new approach based on the assessment of soil loss risk using remote sensing and GIS. Paddy Water Environ 3:234–247
Yue-qing X, Jian P, Xiao-mei S (2009) Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: a case of study of Maotiao River watershed, Guizhou Province, China. Environ Geol 56:1643–1652
Zante P, Collinet J, Leclerc G (2003) Carthographie des risques érosifs sur le bassin versant de la retenue collinaires d’Abdessadok (Dorsal Tunisienne). IRD, INGREF
Zhang X, Friedl MA, Schaaf CB, Strahler AH, Hodges JCF, Gao F, Reed BC, Huete A (2003) Monitoring vegetation phenology using MODIS. Remote Sens Environ 84:471–475
Zhang KL, Shu AP, Xu XL, Yang QK, Yu B (2008) Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soils in China. J Arid Environ 72:1002–1011
Zheng FL (2006) Effect of vegetation changes on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau. Pedosphere 16:420–427
Zhou P, Luukkanen O, Tokola T, Nieminen J (2008) Effect of vegetation cover on soil erosion in a mountainous watershed. Catena 75:319–325
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the General Directorate for Water and Soil Conservation and the General Directorate of Water Resources in Tunisia for their help and providing data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kefi, M., Yoshino, K. & Setiawan, Y. Assessment and mapping of soil erosion risk by water in Tunisia using time series MODIS data. Paddy Water Environ 10, 59–73 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-011-0265-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-011-0265-3