Abstract
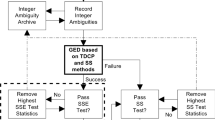
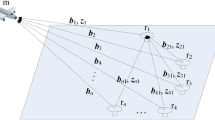
Usually, it is difficult to implement integer ambiguity resolution within a short amount of time for GNSS positioning in urban areas due to the contamination of non-line-of-sight signals and multipath. This study proposes a sequential ambiguity selection strategy for partial ambiguity resolution. First, the ambiguities are selected based on the filtered residuals of the phase and code measurements. In addition, the elevation angle and decorrelated variances are used as the metrics for selecting ambiguity subsets. Two kinematic experiments are carried out in urban areas to evaluate the performance of the strategy. Among the three independent strategies, the first one performs better than the others, as the dependency of observation quality on the elevation angle is low and the decorrelated variances are prone to be contaminated by biased ambiguities. When the proposed sequential ambiguity selection strategy is used, the percentage of correctly fixed epochs is increased by approximately 10–20%. The RMS of N/E/U is improved from the decimeter level (for full ambiguity resolution) to the centimeter level. The improvement is more obvious in the obstructed area and during the re-initialization phase.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The collected datasets for the two field experiments in the study are available from the corresponding author upon the request.
References
Castro-Arvizu JM, Medina D, Ziebold R, Vilà-Valls J, Chaumette E, Closas P (2021) Precision-aided partial ambiguity resolution scheme for instantaneous RTK positioning. Remote Sens 13(15):2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152904
Chai D, Sang W, Chen G, Ning Y, Xing J, Yu M, Wang S (2022) A novel method of ambiguity resolution and cycle slip processing for single-frequency GNSS/INS tightly coupled integration system. Adv Space Res 69(1):359–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.10.007
Euler H-J, Schaffrin B (1991) On a measure for the discernibility between different ambiguity solutions in the static-kinematic GPS-mode. In: IAG Symposia no 107, kinematic systems in geodesy, surveying, and remote sensing. Springer, New York, pp 285–295
Feng Y (2008) GNSS three carrier ambiguity resolution using ionosphere-reduced virtual signals. J Geod 82(12):847–862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-008-0209-x
Han S, Rizos C (1996) Integrated method for instantaneous ambiguity resolution using new generation GPS receivers. In: Proceedings of position, location and navigation symposium—PLANS '96. IEEE, Atlanta, GA, USA, pp 254–261
Henkel P, Günther C (2010) Partial integer decorrelation: optimum trade-off between variance reduction and bias amplification. J Geod 84(1):51–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-009-0343-0
Hou Y, Verhagen S, Wu J (2016) A data driven partial ambiguity resolution: two step success rate criterion, and its simulation demonstration. Adv Space Res 58(11):2435–2452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2016.07.029
Hsu L-T (2018) Analysis and modeling GPS NLOS effect in highly urbanized area. GPS Solut 22(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-017-0667-9
Leick A, Rapoport L, Tatarnikov D (2015) GPS satellite surveying. Wiley, Hoboken
Li B, Shen Y, Feng Y, Gao W, Yang L (2014) GNSS ambiguity resolution with controllable failure rate for long baseline network RTK. J Geod 88(2):99–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-013-0670-z
Li P, Zhang X (2015) Precise point positioning with partial ambiguity fixing. Sensors 15(6):13627–13643. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150613627
Liu W, Li J, Zeng Q, Guo F, Wu R, Zhang X (2019) An improved robust Kalman filtering strategy for GNSS kinematic positioning considering small cycle slips. Adv Space Res 63(9):2724–2734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.11.041
Liu X, Zhang S, Zhang Q, Zheng N, Zhang W, Ding N (2021) Theoretical analysis of the multi-GNSS contribution to partial ambiguity estimation and R-ratio test-based ambiguity validation. GPS Solut 25(2):52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-020-01080-0
Odolinski R, Teunissen PJG, Odijk D (2015) Combined BDS, Galileo, QZSS and GPS single-frequency RTK. GPS Solut 19(1):151–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0376-6
Parkins A (2011) Increasing GNSS RTK availability with a new single-epoch batch partial ambiguity resolution algorithm. GPS Solut 15(4):391–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-010-0198-0
Shi J, Gao Y (2012) A fast integer ambiguity resolution method for PPP. In: Proceedings of the 25th international technical meeting of the satellite division of the institute of navigation (ION GNSS 2012). pp 3728–3734
Shi J, Huang Y, Ouyang C (2019) A GPS relative positioning quality control algorithm considering both code and phase observation errors. J Geod 93(9):1419–1433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01254-w
Teunissen PJG (1995) The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J Geod 70(1–2):65–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00863419
Teunissen PJG (1997) A canonical theory for short GPS baselines. Part IV: precision versus reliability. J Geod 71(9):513–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900050119
Teunissen PJG, Joosten P, Tiberius C (1999) Geometry-free ambiguity success rates in case of partial fixing. In: Proceedings of the 1999 national technical meeting of the institute of navigation. pp 201–207
Teunissen PJG (2001) Integer estimation in the presence of biases. J Geod 75(7–8):399–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900100191
Teunissen PJG, Joosten P, Tiberius C (2002) A comparison of TCAR, CIR and LAMBDA GNSS ambiguity resolution. In: Proceedings of the 15th international technical meeting of the satellite division of the institute of navigation (ION GPS 2002). pp 2799–2808
Teunissen PJG, Verhagen S (2009) The GNSS ambiguity ratio-test revisited: a better way of using it. Surv Rev 41(312):138–151. https://doi.org/10.1179/003962609X390058
Teunissen PJG, Odolinski R, Odijk D (2014) Instantaneous BeiDou+GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J Geod 88(4):335–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-013-0686-4
Verhagen S, Li B, Teunissen PJG (2013) Ps-LAMBDA: ambiguity success rate evaluation software for interferometric applications. Comput Geosci 54:361–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2013.01.014
Wang J, Feng Y (2013) Reliability of partial ambiguity fixing with multiple GNSS constellations. J Geod 87(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-012-0573-4
Wei M, Schwarz K-P (1995) Fast ambiguity resolution using an integer nonlinear programming method. In: Proceedings of the 8th international technical meeting of the satellite division of the institute of navigation (ION GPS 1995). pp 1101–1110
Yang Y (1994) Robust estimation for dependent observations. Manuscr Geod 19(1):10–17
Yang Y, Song L, Xu T (2002) Robust estimator for correlated observations based on bifactor equivalent weights. J Geod 76(6):353–358
Acknowledgements
This study is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41974035, 42030109), and Yong Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by China Association of Science and Technology (2018QNRC001). The editor and reviewers are acknowledged for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Xu, G., Guo, J. et al. A sequential ambiguity selection strategy for partial ambiguity resolution during RTK positioning in urban areas. GPS Solut 26, 92 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01279-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01279-3