Abstract
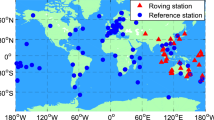
The Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) contains five geostationary earth orbit (GEO) satellites, which maintain almost stationary with respect to the earth. The accuracy of GEO orbit is very poor, which has negatively influenced multi-GNSS precise point positioning (PPP) integer ambiguity resolution (IAR). To overcome this problem, we estimate GEO orbit error corrections together with the narrow-lane fractional cycle bias (FCB), which is used to refine the orbit. We also estimate systematic bias in current GLONASS and BDS precise satellite clock products. Then, this solution is validated with combined GPS, GLONASS, and BDS PPP-IAR. A 7-day dataset of 45 stations was used in the experiment. It is demonstrated that, after considering GEO satellite orbit errors, the narrow-lane FCB estimates have comparable quality for each system. For kinematic PPP with an observation time of 6 min, only 14.7% of cases could be fixed by GPS alone, whereas the percentage decreased to 7.5% for GPS + GLONASS + BDS without considering GEO orbit errors. In contrast, if we consider that error, the percentage for GPS + GLONASS + BDS improved substantially to 96.9%.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beutler G, Moore AW, Mueller II (2009) The international global navigation satellite systems service (IGS): development and achievements. J Geod 83(3–4):297–307
Blewitt G (1989) Carrier phase ambiguity resolution for the global positioning system applied to geodetic baselines up to 2000 km. J Geophys Res 94(B8):10187–10203
Boehm J, Niell A, Tregoning P, Schuh H (2006) Global mapping function (GMF): a new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys Res Lett 33:L07304. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL025546
Chuang S, Wenting Y, Weiwei S, Yidong L, Rui Z (2013) GLONASS pseudorange inter-channel biases and their effects on combined GPS/GLONASS precise point positioning. GPS Solut 17(4):439–451
Dong D, Bock Y (1989) Global positioning system network analysis with phase ambiguity resolution applied to crustal deformation studies in California. J Geophys Res 94(B4):3949–3966
Dow JM, Neilan RE, Gendt G (2005) The international GPS service: celebrating the 10th anniversary and looking to the next decade. Adv Space Res 36(3):320–326
Dow JM, Neilan RE, Rizos C (2009) The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J Geod 83(3–4):191–198
Ge M, Gendt G, Rothacher M, Shi C, Liu J (2008) Resolution of GPS carrier phase ambiguities in precise point positioning(PPP) with daily observations. J Geod 82(7):389–399
Ge M, Chen J, Douša J, Gendt G, Wickert J (2012a) A computationally efficient approach for estimating high-rate satellite clock corrections in realtime. GPS Solut 16(1):9–17
Ge M, Zhang H, Jia X, Song S, Wickert L (2012b) What is achievable with the current COMPASS Constellations? In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2012, Institute of Navigation, Nashville, Tennessee, USA, 17–21 Sept, pp 331–339
Geng J, Shi C (2017) Rapid initialization of real-time PPP by resolving undifferenced GPS and GLONASS ambiguities simultaneously. J Geod 91(4):361–374
Geng J, Teferle FN, Shi C, Meng X, Dodson AH, Liu J (2009) Ambiguity resolution in precise point positioning with hourly data. GPS Solut 13(4):263–270
Geng J, Teferle FN, Meng X, Dodson AH (2011) Towards PPP-RTK: ambiguity resolution in real-time precise point positioning. Adv Space Res 47(10):1664–1673
Geng J, Zhao Q, Shi C, Liu J (2017) A review on the inter-frequency biases of GLONASS carrier-phase data. J Geod 91(3):329–340
Guo R, Hu X, Tang B, Huang Y, Liu L, Chen L, He F (2010a) Precise orbit determination for the geostationary satellite with multiple tracking technique. Chin Sci Bull 55(6):428–434
Guo R, Hu X, Liu L, Wu X, Huang Y, He F (2010b) Orbit determination for geostationary satellites with the combination of transfer ranging and pseudorange data. Sci China Ser G Phys Mech Astron 53(9):1746–1754
Han S (1997) Quality-control issues relating to instantaneous ambiguity resolution for real-time GPS kinematic positioning. J Geod 71(6):351–361
Hatch R (1982) The synergism of GPS code and carrier measurements. In: Proceedings of the third international symposium on satellite Doppler positioning at Physical Sciences Laboratory of New Mexico State University, 8–12 Feb, vol 2, pp 1213–1231
Kouba J (2009) A guide to using international GNSS service (IGS) products. http://igscb.jpl.nasa.gov/igscb/resource/pubs/UsingIGSProductsVer21.pdf
Kozlov D, Tkachenko M, Tochilin A (2000) Statistical characterization of hardware biases in GPS + GLONASS receivers. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2000, Institute of Navigation, Salt Lake City, UT, 19–22 Sept, pp 817–826
Laurichesse D, Mercier F, Berthias JP, Broca P, Cerri L (2009) Integer ambiguity resolution on undifferenced GPS phase measurements and its application to PPP and satellite precise orbit determination. Navigation 56(2):135–149
Li Y, Gao Y, Shi J (2016) Improved PPP ambiguity resolution by COES FCB estimation. J Geod 90(5):437–450
Liu J, Ge M (2003) PANDA Software and its preliminary result of positioning and orbit determination. Wuhan Univ J Nat Sci 8(2B):603–609
Liu Y, Ge M, Shi C, Lou Y, Wickert J, Schuh H (2016) Improving integer ambiguity resolution for GLONASS precise orbit determination. J Geod 90(8):715–726
Liu Y, Ye S, Song W, Lou Y, Chen D (2017a) Integrating GPS and BDS to shorten the initialization time for ambiguity-fixed PPP. GPS Solut 21(2):333–343
Liu Y, Ye S, Song W, Lou Y, Gu S, Li Q (2017b) Rapid PPP ambiguity resolution using GPS + GLONASS observations. J Geod 91(4):441–455
Liu Y, Lou Y, Ye S, Zhang R, Song W, Zhang X, Li Q (2017c) Assessment of PPP integer ambiguity resolution using GPS, GLONASS and BeiDou (IGSO, MEO) constellations. GPS Solut 21(4):1647–1659
Liu Y, Gu S, Li Q (2018) Calibration of GLONASS inter-frequency code bias for ppp ambiguity resolution with heterogeneous rover receivers. Remote Sens 10(3):399
Lou Y, Liu Y, Shi C, Yao X, Zheng F (2014) Precise orbit determination of BeiDou constellation based on bets and MGEX network. Sci Rep 4(8):4692
Lou Y, Liu Y, Shi C, Wang B, Yao X, Zheng F (2016) Precise orbit determination of BeiDou constellation: method comparison. GPS Solut 20(2):259–268
Lou Y, Gong X, Gu S, Zheng F, Feng Y (2017) Assessment of code bias variations of bds triple-frequency signals and their impacts on ambiguity resolution for long baselines. GPS Solut 21(1):177–186
Melbourne WG (1985) The case for ranging in GPS-based geodetic systems. In: Proceedings of the first international symposium on precise positioning with the global positioning system, Rockville, MD, USA, 15–19 April, pp 373–386
Montenbruck O, Rizos C, Weber R, Weber G, Neilan R, Hugentobler U (2013) Getting a grip on multi-GNSS: the international GNSS service MGEX campaign. GPS World 24(7):44–49
Montenbruck O, Steigenberger P, Prange L, Deng Z, Zhao Q, Perosanz F (2017) The multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) of the international GNSS service (IGS)—achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv Space Res 59(7):1671–1697
Parkinson BW, Spilker JJ (1996) Global positioning system: theory and applications, progress in astronautics and aerodynamics. American Institute of Astronautics, Washington, DC, pp 163–164
Petit G, Luzum B, Al E (2010) IERS conventions. IERS Tech Note 36:1–95
Qing Y, Lou Y, Dai X (2017) Orbit determination of BDS GEO and IGSO satellites using combined GNSS and SLR observations. J Geod Geodyn 37(5):467–471
Schmid R, Steigenberger P, Gendt G, Ge M, Rothacher M (2007) Generation of a consistent absolute phase-center correction model for GPS receiver and satellite antennas. J Geod 81(12):781–798
Shi C, Zhao Q, Li M, Tang W, Hu Z, Lou Y, Zhang H, Niu X, Liu J (2012) Precise orbit determination of BeiDou Satellites with precise positioning. Sci China Earth Sci 55(7):1079–1086
Sleewaegen J, Simsky A, Wilde W, Boon F, Willems T (2012) Demystifying GLONASS inter-frequency carrier phase biases. Inside GNSS 7:57–61
Song W, Yi W, Lou Y, Shi C, Yao Y, Liu Y, Mao Y, Xiang Y (2014) Impact of GLONASS pseudorange inter-channel biases on satellite clock corrections. GPS Solut 18(3):323–333
Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Hauschild A, Montenbruck O (2013a) Orbit and clock analysis of compass GEO and IGSO satellites. J Geod 87(6):515–525
Steigenberger P, Montenbruck O, Weber R, Hugentobler U (2013b) Status and perspective of the IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX). In: EGU general assembly conference abstracts, vol 15, p 2558
Teunissen PJG (1995) The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J Geod 70(1–2):65–82
Thaller D, Dach R, Seitz M, Beutler G, Mareyen M, Richter B (2011) Combination of GNSS and SLR observations using satellite co-locations. J Geod 85(5):257–272
Tian Y, Ge M, Neitzel F (2015) Particle filter-based estimation of inter-frequency phase bias for real-time GLONASS integer ambiguity resolution. J Geod 89(11):1145–1158
Urschl C, Beutler G, Gurtner W, Hugentobler U, Schaer S (2007) Contribution of SLR tracking data to GNSS orbit determination. Adv Space Res 39(10):1515–1523
Wanninger L (2012) Carrier phase inter-frequency biases of GLONASS receivers. J Geod 86(2):139–148
Wanninger L, Beer S (2015) BeiDou satellite-induced code pseudorange variations: diagnosis and therapy. GPS Solut 19(4):639–648
Wu JT, Wu SC, Hajj GA, Bertiger WI, Lichten SM (1993) Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscr Geod 18(2):91–98
Wübbena G (1985) Software developments for geodetic positioning with GPS using TI-4100 code and carrier measurements. In: Proceedings of the first international symposium on precise positioning with the global positioning system, Rockville, MD, 15–19 April, pp 403–412
Yamada H, Takasu T, Kubo N, Yasuda A (2010) Evaluation and calibration of receiver inter-channel biases for RTK-GPS/GLONASS. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2010, 21–24 Sept., Institute of Navigation, Portland, Oregon, pp 1580–1587
Ye S, Liu Y, Song W, Lou Y, Yi W, Zhang R, Jiang P, Xiang Y (2016) A cycle slip fixing method with GPS + GLONASS observations in real-time kinematic PPP. GPS Solut 20(1):101–110
Yi W, Song W, Lou Y, Shi C, Yao Y (2016) A method of undifferenced ambiguity resolution for GPS + GLONASS precise point positioning. Sci Rep 6:26334
Zhang R, Yao Y, Hu Y, Song W (2017) A two-step ionospheric modeling algorithm considering the impact of GLONASS pseudo-range inter-channel biases. J Geod 91:1435–1446
Zhao Q, Guo J, Li M, Qu L, Hu Z, Shi C, Liu J (2013) Initial results of precise orbit and clock determination for COMPASS navigation satellite system. J Geod 87(5):475–486
Zumberge JF, Heflin MB, Jefferson DC, Watkins MM, Webb FH (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res 102(B3):5005–5017
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (no. 2017YFB0503401), National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 41704033), Shenzhen Future Industry Development Funding Program (no. 201607281039561400), Shenzhen Scientific Research and Development Funding Program (no. JCYJ20170818092931604), and Research Program of Shenzhen S&T Innovation Committee (no. JCYJ20170412105839839).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Ye, S., Song, W. et al. Estimating the orbit error of BeiDou GEO satellites to improve the performance of multi-GNSS PPP ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut 22, 84 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-018-0751-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-018-0751-9