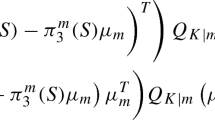Abstract
A commonly used procedure for reduction of the number of variables in linear discriminant analysis is the stepwise method for variable selection. Although often criticized, when used carefully, this method can be a useful prelude to a further analysis. The contribution of a variable to the discriminatory power of the model is usually measured by the maximum likelihood ratio criterion, referred to as Wilks’ lambda. It is well known that the Wilks’ lambda statistic is extremely sensitive to the influence of outliers. In this work a robust version of the Wilks’ lambda statistic will be constructed based on the Minimum Covariance Discriminant (MCD) estimator and its reweighed version which has a higher efficiency. Taking advantage of the availability of a fast algorithm for computing the MCD a simulation study will be done to evaluate the performance of this statistic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chork CY, Rousseeuw PJ (1992) Integrating a high breakdown option into discriminant analysis in exploration geochemistry. J Geochem Explor 43:191–203
Croux C, Dehon C (2001) Robust linear discriminant analysis using S-estimators. Can J Statisti 29:473–492
Croux C, Joossens K (2005) Influence of observations on the misclassification probability in quadratic discriminant analysis. J Multivar Anal 96:384–403
Fish Catch Data Set (2006) Journal of Statistical Education [http://www.amstat.org/publications/jse/datasets/fishcatch.txt] accessed January 2006
He X, Fung WK (2000) High breakdown estimation for multiple populations with applications to discriminant analysis. J Multivar Anal 72:151–162
Hawkins DM, McLachlan GJ (1997) High-breakdown linear discriminant analysis. J Amer Statist Assoc 92(437):136–143
Hubert M, Van Driessen K (2004) Fast and robust discriminant analysis. Computat Statist Data Anal 45:301–320
Jennrich R (1977) Stepwise discriminant analysis. In: Enslein KAR, Wilf HS (eds) Statistical methods for digital computers. Wiley, New York, pp 76–95
Johnson RA, Wichern DW (2002) Applied multivariate statistical analysis, 5th edn. Prentice Hall, International Editions
Krusinska E, Liebhart J (1988) Robust selection of the most discriminative variables in the dichotomous problem with application to some respiratory desease data. Biometric J 30(2):295–304
Krusinska E (1988) Robust methods in discriminant analysis. Rivista di Statistica Applicada 21(3):239–253
Krusinska E, Liebhart J (1989) Some further remarks on the robust selection of variables in discriminant analysis. Biometric J 31(2):227–233
Lachenbruch PA (1975) Discriminant analysis. Hafner Press, New York
McLachlan GJ (1992) Discriminant analysis and statistical pattern recognition. Wiley, New York
Pison G, Van Aelst S, Willems G (2002) Small sample corrections for LTS and MCD. Metrika 55:111–123
R Development Core Team (2005) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org
Ronchetti E (1985) Robust model selection in regression. Statist Probab Lett 3:21–23
Rousseeuw PJ (1984) Least median of squares regression. J Am Statist Assoc 79:851–857
Rousseeuw PJ, Van Driessen K (1999) A Fast algorithm for the Minimum Covariance Determinant Estimator. Technometrics 41:212–223
Rousseeuw PJ, van Zomeren BC (1991) Robust distances: simulation and cutoff values. In: Stahel W, Weisberg S (eds) Directions in robust statistics, Part II. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Todorov V, Neykov N, Neytchev P (1990) Robust selection of variables in the discriminant analysis based on MVE and MCD estimators. In: Proceedings in Computational statistics, COMPSTAT’90. Physica Verlag, Heidelberg
Todorov V, Neykov N, Neytchev Pl (1994) Robust two-group discrimination by bounded influence regression. Computat Statist Data Anal 17:289–302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The presentation of material in this article does not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of Austro Control GmbH and is the sole responsibility of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Todorov, V. Robust selection of variables in linear discriminant analysis. Stat. Meth. & Appl. 15, 395–407 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260-006-0032-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260-006-0032-6