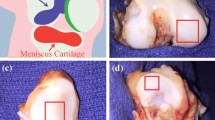
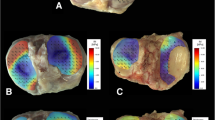
Abstract
Articular cartilage is a multicomponent, poroviscoelastic tissue with nonlinear mechanical properties vital to its function. A consequent goal of repair or replacement of injured cartilage is to achieve mechanical properties in the repair tissue similar to healthy native cartilage. Since fresh healthy human articular cartilage (HC) is not readily available, we tested whether swine cartilage (SC) could serve as a suitable substitute for mechanical comparisons. To a first approximation, cartilage tissue and surgical substitutes can be evaluated mechanically as viscoelastic materials. Stiffness measurements (dynamic modulus, loss angle) are vital to function and are also a non-destructive means of evaluation. Since viscoelastic material stiffness is strongly strain rate dependent, stiffness was tested under different loading conditions related to function. Stiffness of healthy HC and SC specimens was determined and compared using two non-destructive, mm-scale indentation test modes: fast impact and slow sinusoidal deformation. Deformation resistance (dynamic modulus) and energy handling (loss angle) were determined. For equivalent anatomic locations, there was no difference in dynamic modulus. However, the HC loss angle was ~35% lower in fast impact and ~12% higher in slow sinusoidal mode. Differences seem attributable to age (young SC, older HC) but also to species anatomy and biology. Test mode-related differences in human-swine loss angle support use of multiple function-related test modes. Keeping loss angle differences in mind, swine specimens could serve as a standard of comparison for mechanical evaluation of e.g. engineered cartilage or synthetic repair materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleyard R (2003) Topographical analysis of the structural, biochemical and dynamic biomechanical properties of cartilage in an ovine model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 11(1): 65–77
Ardura Garcia H, Daniels AU, Wirz D (2008) Dual-mode dynamic functional stiffness of articular cartilage. Eur Cells Mater 16(1): 7
Arnold MP, Daniels AU, Ronken S, García HA, Friederich NF, Kurokawa T et al (2011) Acrylamide polymer double-network hydrogels: candidate cartilage repair materials with cartilage-like dynamic stiffness and attractive surgery-related attachment mechanics. Cartilage: accepted for publication 1/2011
Athanasiou KA, Agarwal A, Dzida FJ (1994) Comparative study of the intrinsic mechanical properties of the human acetabular and femoral head cartilage. J Orthop Res 12(3): 340–349
Brown KL, Cruess RL (1982) Bone and cartilage transplantation in orthopaedic surgery. A review. J Bone Joint Surg 64(2): 270–279
Bueckle H (1973) Use of the hardness test to determine other material properties. In: Westbrook JW, Conrad H (eds) The science of hardness testing and its research applications. American Society for Metals, Materials Park, pp 453–491
Cs-Szabó G, Melching LI, Roughley PJ, Glant TT (1997) Changes in messenger rna and protein levels of proteoglycans and link protein in human osteoarthritic cartilage samples. Arthr Rheum 40(6): 1037–1045
Ficklin T, Thomas G, Barthel JC, Asanbaeva A, Thonar EJ, Masuda K et al (2007) Articular cartilage mechanical and biochemical property relations before and after in vitro growth. J Biomech 40(16): 3607–3614
Fortin PR, Penrod JR, Clarke AE, St-Pierre Y, Joseph L, Bélisle P et al (2002) Timing of total joint replacement affects clinical outcomes among patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. Arthr Rheum 46(12): 3327–3330
Franke O, Durst K, Maier V, Göken M, Birkholz T, Schneider H et al (2007) Mechanical properties of hyaline and repair cartilage studied by nanoindentation. Acta Biomater 3(6): 873–881
Hollander AP, Pidoux I, Reiner A, Rorabeck C, Bourne R, Poole AR (1995) Damage to type II collagen in aging and osteoarthritis starts at the articular surface, originates around chondrocytes, and extends into the cartilage with progressive degeneration. J Clin Invest 96(6): 2859–2869
Hunziker EB (2002) Articular cartilage repair: basic science and clinical progress. A review of the current status and prospects. Osteoarthr Cartil 10(6): 432–463
Jurvelin J, Buschmann M, Hunziker E (1997) Optical and mechanical determination of poisson’s ratio of adult bovine humeral articular cartilage. J Biomech 30(3): 235–241
Jurvelin J, Kiviranta I, Säämänen A-M, Tammi M, Helminen HJ (1990) Indentation stiffness of young canine knee articular cartilage—influence of strenuous joint loading. J Biomech 23(12): 1239–1246
Kääb MJ, Gwynn IA, Nötzli HP (1998) Collagen fibre arrangement in the tibial plateau articular cartilage of man and other mammalian species. J Anat 193(1): 23–34
Kleemann RU, Krocker D, Cedraro A, Tuischer J, Duda GN (2005) Altered cartilage mechanics and histology in knee osteoarthritis: relation to clinical assessment (ICRS Grade). Osteoarthr Cartil 13(11): 958–963
Korhonen RK et al (2002a) Comparison of the equilibrium response of articular cartilage in unconfined compression, confined compression and indentation. J Biomech 35(7): 903–909
Korhonen RK, Laasanen MS, Töyräs J, Rieppo J, Hirvonen J, Helminen HJ et al (2002b) Importance of the superficial tissue layer for the indentation stiffness of articular cartilage. Med Eng Phys 24(2): 99–108
Kren AP, Rudnitskii VA, Deikun IG (2005) Determining the viscoelastic parameters of vulcanisates by the dynamic indentation method using a non-linear deformation model. Int Polym Sci Tech 32(7): 19–23
Lakes RS (1999) Viscoelastic solids. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Lippiello L, Hall D, Mankin HJ (1977) Collagen synthesis in normal and osteoarthritic human cartilage. J Clin Invest 59(4): 593–600
Loeser RF (2004) Aging cartilage and osteoarthritis—what’s the link? Science of aging knowledge environment : SAGE KE 2004(29):31
Lyyra T, Kiviranta I, Väätäinen U, Helminen HJ, Jurvelin J (1999) In vivo characterization of indentation stiffness of articular cartilage in the normal human knee. J Biomed Mater Res 48(4): 482–487
Mow V, Gibbs M, Lai W, Zhu W, Athanasiou KA (1989) Biphasic indentation of articular cartilage—II. A numerical algorithm and an experimental study. J Biomech 22(8/9): 853–861
Niederauer GG, Niederauer GM, Cullen LC, Athanasiou KA, Thomas JB, Niederauer MQ (2004) Correlation of cartilage stiffness to thickness and level of degeneration using a handheld indentation probe. Ann Biomed Eng 32(3): 352–359
Nieminen MT, Töyräs J, Laasanen MS, Silvennoinen J, Helminen HJ, Jurvelin J (2004) Prediction of biomechanical properties of articular cartilage with quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. J Biomech 37(3): 321–328
Nugent GE, Law AW, Wong EG, Temple MM, Bae WC, Chen AC et al (2004) Site- and exercise-related variation in structure and function of cartilage from equine distal metacarpal condyle. Osteoarthr Cartil 12(10): 826–833
Oakley SP, Lassere MN, Portek I, Szomor Z, Ghosh P, Kirkham BW et al (2004) Biomechanical, histologic and macroscopic assessment of articular cartilage in a sheep model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 12(8): 667–679
O’Hara BP, Urban JPG, Maroudas A (1990) Influence of cyclic loading articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis 49: 536–539
Park S, Hung C, Ateshian G (2004) Mechanical response of bovine articular cartilage under dynamic unconfined compression loading at physiological stress levels. Osteoarthr Cartil 12: 65–73
Peterson L, Brittberg M, Kiviranta I, Åkerlund EL, Lindahl A (2002) Autologous chondrocyte transplantation: biomechanics and long-term durability. Am J Sport Med 30(1): 2–12
Pullig O, Weseloh G, Swoboda B (1999) Expression of type VI collagen in normal and osteoarthritic human cartilage. Osteoarthr Cartil 7(2): 191–202
Schinagl RM, Gurskis D, Chen AC, Sah RL (1997) Depth-dependent confined compression modulus of full-thickness bovine articular cartilage. J Orthop Res 15(4): 499–506
Stolz M, Raiteri R, Daniels AU, VanLandingham MR, Baschong W, Aebi U (2004) Dynamic elastic modulus of porcine articular cartilage determined at two different levels of tissue organization by indentation-type atomic force microscopy. Biophys J 86(5): 3269–3283
Stolz M, Gottardi R, Raiteri R, Miot S, Martin I, Imer R et al (2009) Early detection of osteoarthritis and articular cartilage aging in mice and patient biopsies using atomic force microscopy. Nat Nanotechnol 4(3): 186–192
Wells T, Davidson C, Mörgelin M, Bird JLE, Bayliss MT, Dudhia J (2003) Age-related changes in the composition, the molecular stoichiometry and the stability of proteoglycan aggregates extracted from human articular cartilage. Biochem J 370(1): 69–79
Wirz D, Kohler K, Keller B, Göpfert B, Hudetz D, Daniels AU (2008) Dynamic stiffness of articular cartilage by single impact micro-indentation (SIMI). J Biomech 41(Supplement 1): S172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ronken, S., Arnold, M.P., Ardura García, H. et al. A comparison of healthy human and swine articular cartilage dynamic indentation mechanics. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 11, 631–639 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-011-0338-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-011-0338-7