Abstract
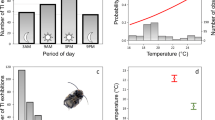
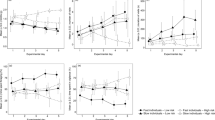
Significant between-individual variation in resting metabolic rate (RMR) of animals is a widespread phenomenon that may have important implications for our understanding of variation in behavior and animal personality. By using wild caught mealworm beetles, Tenebrio molitor, we examined the relationships among survival rate under predator tests, individual response latency time to become immobile under the risk of predation, duration of immobility time, and RMR. Individuals with higher levels of RMR were bold, and bold individuals were found to be more exposed to the risk of bird predation. We found that RMR was positively correlated with the latency of immobility response and negatively correlated with the total duration of immobility. The correlation between behavioral responses suggests a behavioral syndrome in the anti-predator behavior of T. molitor. The results indicate that energy metabolism may be part of a syndrome that involves behavior and life history traits in animals.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcock J (2001) Animal behavior: an evolutionary approach. Sinauer, Sunderland
Alvarez D, Nicieza AG (2005) Is metabolic rate a reliable predictor of growth and survival of brown trout (Salmo trutta) in the wild? Can J Fish Aquat Sci 62:643–649
Artacho P, Nespolo RF (2009) Natural selection reduces energy metabolism in the garden snail, Helix aspersa (Cornu aspersum). Evolution 63:1044–1050
Barnard C (2007) Ethical regulation and animal science: why animal behaviour is special. Anim Behav 74:5–13
Bell AM, Sih A (2007) Exposure to predation generates personality in threespined sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Ecol Lett 10:828–834
Bell AM, Hankison SJ, Laskowski KL (2009) The repeatability of behaviour: a meta-analysis. Anim Behav 77:771–783
Bhattacharya AK, Ameel JJ, Waldbaue GP (1970) Method for sexing living pupal and adult yellow mealworms. Ann Entomol Soc Am 63:1783
Biro PA, Stamps JA (2008) Are animal personality traits linked to life-history productivity? Trends Ecol Evol 23:361–368
Biro PA, Stamps JA (2010) Do consistent individual differences in metabolic rate promote consistent individual differences in behavior? Trends Ecol Evol 25:653–659
Biro PA, Abrahams MV, Post JR, Parkinson EA (2006) Behavioural trade-offs between growth and mortality explain evolution of submaximal growth rates. J Anim Ecol 75:1165–1171
Biro PA, Beckmann C, Stamps JA (2010) Small within-day increases in temperature affects boldness and alters personality in coral reef fish. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 277:71–77
Boratynski Z, Koteja P (2009) The association between body mass, metabolic rates and survival of bank voles. Funct Ecol 23:330–339
Burton T, Killen SS, Armstrong JD, Metcalfe NB (2011) What causes intraspecific variation in resting metabolic rate and what are its ecological consequences? Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 278:3465–3473
Butler SJ, Whittingham MJ, Quinn JL, Cresswell W (2005) Quantifying the interaction between food density and habitat structure in determining patch selection. Anim Behav 69:337–343
Candolin U (1998) Reproduction under predation risk and the trade-off between current and future reproduction in the threespine stickleback. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 265:1171–1175
Careau V, Thomas D, Humphries MM, Réale D (2008) Energy metabolism and animal personality. Oikos 117:641–653
Castañeda LE, Figueroa CC, Bacigalupe LD, Nespolo RF (2010) Effects of wing polyphenism, aphid genotype and host plant chemistry on energy metabolism of the grain aphid, Sitobion avenae. J Insect Physiol 56:1920–1924
Chappell MA, Garland T, Rezende EL, Gomes FR (2004) Voluntary running in deer mice: speed, distance, energy costs and temperature effects. J Exp Biol 207:3839–3854
Cuthill IC (2007) Ethical regulation and animal science: why animal behaviour is not so special. Anim Behav 74:15–22
Daan S, Masman D, Strijkstra AM, Kenagy GJ (1990) Daily energy turnover during reproduction in birds and mammals: its relationships to basal metabolic rate. Acta XX Congr Int Ornithol IV:1976–1987
Dall SRX, Witter MS (1998) Feeding interruptions, diurnal mass changes and daily routines of behaviour in the zebra finch. Anim Behav 55:715–725
Dall SRX, Houston AI, McNamara JM (2004) The behavioural ecology of personality: consistent individual differences from an adaptive perspective. Ecol Lett 7:734–739
Daukste J, Kivleniece I, Krama T, Rantala MJ, Krams I (2012) Senescence in immune priming and attractiveness in a beetle. J Evol Biol 25:1298–1304
Dingemanse NJ, Réale D (2005) Natural selection and animal personality. Behaviour 142:1159–1184
Dingemanse NJ, Wolf M (2010) Recent models for adaptive personality differences: a review. Philos Trans R Soc B 365:3947–3958
Dohm MR (2002) Repeatability estimates do not always set an upper limit to heritability. Funct Ecol 16:273–280
Duncan FD (2003) The role of the subelytral cavity in respiration in a tenebrionid beetle, Onymacris multistriata (Tenebrionidae: Adesmiini). J Insect Physiol 49:339–346
Duncan FD, Byrne MJ (2005) The role of the mesothoracic spiracles in respiration in flighted and flightless dung beetles. J Exp Biol 208:907–914
Earle M, Lavigne DM (1990) Intraspecific variation in body size, metabolic rate, and reproduction of deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus). Can J Zool 68:381–388
Fedigan LM (2010) Ethical issues faced by field primatologists: asking the relevant questions. Am J Primatol 72:754–771
Finerty SE, Wolt RC, Davis RW (2009) Summer activity pattern and field metabolic rate of adult male sea otters (Enhydra lutris) in a soft sediment habitat in Alaska. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 377:36–42
Fu SJ, Xie XJ, Cao ZD (2005) Effect of fasting and repeat feeding on metabolic rate in southern catfish, Silurus meridionalis Chen. Mar Freshw Behav Physiol 38:191–198
Fu SJ, Cao ZD, Peng JL, Wang YX (2008) Is peak postprandial oxygen consumption positively related to growth rate and resting oxygen consumption in a sedentary catfish Silurus meridionalis? J Fish Biol 73:692–701
Gilliam JF, Fraser DF (1987) Habitat selection under predation hazard—test of a model with foraging minnows. Ecology 68:1856–1862
Godin JGJ (1995) Predation risk and alternative mating tactics in male Trinidadian guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Oecologia 103:224–229
Godin JGJ (1997) Evading predators. In: Godin JGJ (ed) Behavioural ecology of teleost fishes. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 191–236
Godin JGJ, Dugatkin LA (1996) Female mating preference for bold males in the guppy, Poecilia reticulata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10262–10267
Gray EM, Bradley TJ (2006) Evidence from mosquitoes suggests that cyclic gas exchange and discontinuous gas exchange are two manifestations of a single respiratory pattern. J Exp Biol 209:1603–1611
Groothuis TGG, Carere C (2005) Avian personalities: characterization and epigenesis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:137–150
Gyuris E, Feró O, Tartally A, Barta Z (2011) Individual behaviour in firebugs (Pyrrhocoris apterus). Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 278:628–633
Hammond KA, Diamond J (1997) Maximal sustained energy budgets in humans and animals. Nature 386:457–462
Hammond KA, Wunder BA (1995) Effect of cold temperatures on the morphology of gastrointestinal tracts of two microtine rodents. J Mammal 76:232–239
Hammond KA, Lam M, Lloyd KCK, Diamond J (1996) Simultaneous manipulation of intestinal capacities and nutrient loads in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver 271:G969–G979
Hayes JP, Garland T, Dohm MR (1992) Individual variation in metabolism and reproduction of Mus: are energetics and life history linked? Funct Ecol 6:5–14
Hedrick AV, Kortet R (2006) Hiding behaviour in two cricket populations that differ in predation pressure. Anim Behav 72:1111–1118
Hetz SK (1994) Untersuchung zu Atmung, Kreislauf und Säure-Basen-Regulation an Puppen der tropischen Schmetterlingsgattungen Ornithoptera, Troides and Attacus. Dissertation at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität, Erlangen-Nürnberg, p 216
Hollander FA, van Overveld T, Tokka I, Matthysen E (2008) Personality and nest defence in the great tit (Parus major). Ethology 114:405–412
Hõrak P, Lauri S, Ots I, Kollist H (2002) Repeatability of condition indices in captive greenfinches (Carduelis chloris). Can J Zool 80:636–643
Jackson DM, Trayhurn P, Speakman JR (2001) Associations between energetics and over-winter survival in the short-tailed field vole Microtus agrestis. J Anim Ecol 70:633–640
Jones KA, Godin J-GJ (2010) Are fast explorers slow reactors? Linking personality type and anti-predator behaviour. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 277:625–632
Karise R, Kuusik A, Mänd M, Metspalu L, Williams IH, Hiiesaar K, Luik A, Muljar R, Liiv K (2010) Gas exchange patterns of bumble bee foragers before and after exposing to lowered temperature. J Insect Physiol 56:529–535
Kivleniece I, Krams I, Daukste J, Krama T, Rantala MJ (2010) Sexual attractiveness of immune-challenged male mealworm beetles suggests terminal investment in reproduction. Anim Behav 80:1015–1021
Kortet R, Hedrick ANN (2007) A behavioural syndrome in the field cricket Gryllus integer: intrasexual aggression is correlated with activity in a novel environment. Biol J Linn Soc 91:475–482
Kortet R, Härkönen L, Hokkanen P, Härkönen S, Kaitala A, Kaunisto S, Laaksonen S, Kekäläinen J, Ylönen H (2010) Experiments on the ectoparasitic deer ked that often attacks humans; preferences for body parts, colour and temperature. Bull Entomol Res 100:279–285
Koteja P (2000) Energy assimilation, parental care and the evolution of endothermy. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 267:479–484
Kotiaho JS, Alatalo RV, Mappes J, Nielsen MG, Parri S, Rivero A (1998) Energetic costs of size and sexual signalling in a wolf spider. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 265:2203–2209
Krams I, Daukste J, Kivleniece I, Krama T, Rantala MJ (2013a) Previous encapsulation response enhances within individual protection against fungal parasite in the mealworm beetle Tenebrio molitor. Insect Science, doi:10.1111/j.1744-7917.2012.01574.x
Krams I, Daukste J, Kivleniece I, Kaasik A, Krama T, Freeberg TM, Rantala MJ (2013b) Trade-off between cellular immunity and life span in mealworm beetles Tenebrio molitor. Current Zoology 59 in press
Krause J, Ruxton GD (2002) Living in groups. Oxford University Press, New York
Lantovį P, Zub K, Koskela E, Sķchovį K, Borowski Z (2011) Is there a linkage between metabolism and personality in small mammals? The root vole (Microtus oeconomus) example. Physiol Behav 104:378–383
Larivee ML, Boutin S, Speakman JR, McAdam AG, Humphries MM (2010) Associations between over-winter survival and resting metabolic rate in juvenile North American red squirrels. Funct Ecol 24:597–607
Lessells CM, Boag PT (1987) Unrepeatable repeatabilities: a common mistake. Auk 104:116–121
Lighton JRB (2008) Measuring metabolic rate: a manual for scientists. Oxford University Press, New York
Lima SL, Dill LM (1990) Behavioral decisions made under the risk of predation—a review and prospectus. Can J Zool 68:619–640
Luttbeg B, Sih A (2010) Risk, resources and state-dependent adaptive behavioural syndromes. Philos Trans R Soc B 365:3977–3990
Lynch M, Walsh B (1998) Genetics and analysis of quantitative traits. Sinauer, Sunderland
Macleod R, Gosler AG, Cresswell W (2005) Diurnal mass gain strategies and perceived predation risk in the great tit Parus major. J Anim Ecol 74:956–964
Magnhagen C (1990) Reproduction under predation risk in the sand goby, Pomatoschistus minutus, and the black goby, Gobius niger, the effect of age and longevity. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 26:331–335
Mänd M, Kuusik A, Martin AJ, Williams IH, Luik A, Karise R, Metspalu L, Hiiesaar K (2005) Discontinuous gas exchange cycles and active ventilation in pupae of the bumblebee Bombus terrestris. Apidologie 36:561–570
Mänd M, Kuusik A, Martin AJ, Williams IH, Luik A, Karise R (2006) Regular periods of abdominal contractions recorded from larvae of the bumblebee, Bombus terrestris (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Eur J Entomol 103:319–322
McLean JA, Speakman JR (2000) Effects of body mass and reproduction on the basal metabolic rate of brown long-eared bats (Plecotus auritus). Physiol Biochem Zool 73:112–121
Metcalfe NB, Taylor AC, Thorpe JE (1995) Metabolic rate, social status and life-history strategies in Atlantic salmon. Anim Behav 49:431–436
Metspalu L, Kuusik A, Hiiesaar K, Tartes U (2002) Tonic immobility in adult Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) evoked by mechanical and optical stimuli. Eur J Entomol 99:215–219
Miyatake T, Katayama K, Takeda Y, Nakashima A, Sugita A, Mizumoto M (2004) Is death-feigning adaptive? Heritable variation in fitness difference of death-feigning behaviour. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 271:2293–2296
Miyatake T, Nakayama S, Nishi Y, Nakajima S (2009) Tonically immobilized selfish prey can survive by sacrificing others. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 276:2763–2767
Moret Y (2006) ‘Trans-generational immune priming’: specific enhancement of the antimicrobial immune response in the mealworm beetle, Tenebrio molitor. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 273:1399–1405
Mueller P, Diamond J (2001) Metabolic rate and environmental productivity: well-provisioned animals evolved to run and idle fast. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 98:12550–12554
Muljar R, Karise R, Viik E, Kuusik A, Williams I, Metspalu L, Hiiesaar K, Must A, Luik A, Mänd M (2012) Effects of Fastac 50 EC on bumble bee Bombus terrestris L. respiration: DGE disappearance does not lead to increasing water loss. J Insect Physiol 58:1469–1476
Nespolo RF, Franco M (2007) Whole-animal metabolic rate is a repeatable trait: a meta-analysis. J Exp Biol 210:2000–2005
Nespolo RF, Roff DA, Fairbairn DJ (2008) Energetic trade-off between maintenance costs and flight capacity in the sand cricket (Gryllus firmus). Funct Ecol 22:624–631
Niemelä PT, Vainikka A, Lahdenperä S, Kortet R (2012) Nymphal density, behavioural development, and life history in a field cricket. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 66:645–652
Niemelä PT, Vainikka A, Forsman JT, Loukola OJ, Kortet R (2013) How does variation in the environment and individual cognition explain the existence of consistent behavioural differences? Ecol Evol 3:457–464
Niewiarowski PH, Balk ML, Londraville RL (2000) Phenotypic effects of leptin in an ectotherm: a new tool to study the evolution of life histories and endothermy? J Exp Biol 203:295–300
Quinlan MC, Lighton JRB (1999) Respiratory physiology and water relations of three species of Pogonomyrmex harvester ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Physiol Entomol 24:293–302
Quinn JL, Cresswell W (2005) Personality, anti-predation behaviour and behavioural plasticity in the chaffinch Fringilla coelebs. Behaviour 142:1377–1402
Réale D, Reader SM, Sol D, McDougall PT, Dingemanse NJ (2007) Integrating animal temperament within ecology and evolution. Biol Rev 82:291–318
Réale D, Dingemanse NJ, Kazem AJN, Wright J (2010) Evolutionary and ecological approaches to the study of personality. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 365:3937–3946
Rezende EL, Chappell MA, Gomes FR, Malisch JL, Garland T (2005) Maximal metabolic rates during voluntary exercise, forced exercise, and cold exposure in house mice selectively bred for high wheel-running. J Exp Biol 208:2447–2458
Rezende EL, Gomes FR, Chappell MA, Garland T (2009) Running behavior and its energy cost in mice selectively bred for high voluntary locomotor activity. Physiol Biochem Zool 82:662–679
Ruxton GD, Sherratt TN, Speed MP (2004) Avoiding attack: the evolutionary ecology of crypsis, aposematism and mimicry. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Sadd B, Holman L, Armitage H, Lock F, Marland R, Siva-Jothy MT (2006) Modulation of sexual signalling by immune challenged male mealworm beetles (Tenebrio molitor, L.): evidence for terminal investment and dishonesty. J Evol Biol 19:321–325
Sadowska ET, Labocha MK, Baliga K, Stanisz A, Wroblewska AK, Jagusiak W, Koteja P (2005) Genetic correlations between basal and maximum metabolic rates in a wild rodent: consequences for evolution of endothermy. Evolution 59:672–681
Schmidt-Nielsen K (1991) Animal physiology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Schmitz A (2005) Metabolic rates in harvestmen (Arachnida, Opiliones): the influence of running activity. Physiol Entomol 30:75–81
Sih A, Bell AM (2008) Insights for behavioral ecology from behavioral syndromes, chapter 5. In: Brockmann HJ, Roper TJ, Naguib M, Wynne-Edwards K, Barnard C, Mitani JC (eds) Advances in the study of behavior, vol 38. Academic, New York, pp 227–281
Smith BR, Blumstein DT (2008) Fitness consequences of personality: a meta-analysis. Behav Ecol 19:448–455
Smith BR, Blumstein DT (2010) Behavioral types as predictors of survival in Trinidadian guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Behav Ecol 21:919–926
Speakman JR, Ergon T, Cavanagh R, Reid K, Scantlebury DM, Lambin X (2003) Resting and daily energy expenditures of free-living field voles are positively correlated but reflect extrinsic rather than intrinsic effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:14057–14062
Speakman JR, Krol E, Johnson MS (2004) The functional significance of individual variation in basal metabolic rate. Physiol Biochem Zool 77:900–915
Stamps JA (2007) Growth-mortality tradeoffs and ‘personality traits’ in animals. Ecol Lett 10:355–363
Szafranska PA, Zub K, Konarzewski M (2007) Long-term repeatability of body mass and resting metabolic rate in free-living weasels, Mustela nivalis. Funct Ecol 21:731–737
Tartes U, Kuusik A, Vanatoa A (1999) Diversity in gas exchange and muscular activity patterns in insects studied by a respirometer-actograph. Physiol Entomol 24:150–157
Vainikka A, Seppala O, Loytynoja K, Rantala MJ (2006) Fitness consequences of female preference for male pheromones in Tenebrio molitor. Evol Ecol Res 8:943–957
Van Oers K, Drent PJ, de Goede P, van Noordwijk AJ (2004) Realized heritability and repeatability of risk-taking behaviour in relation to avian personalities. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 271:65–73
Vezina F, Speakman JR, Williams TD (2006) Individually variable energy management strategies in relation to energetic costs of egg production. Ecology 87:2447–2458
West-Eberhard MJ (2003) Developmental plasticity and evolution. Oxford University Press, New York
Wolf M, Weissing FJ (2010) An explanatory framework for adaptive personality differences. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 365:3959–3968
Wolf M, van Doorn GS, Leimar O, Weissing FJ (2007) Life-history trade-offs favour the evolution of animal personalities. Nature 447:581–584
Wone B, Sears MW, Labocha MK, Donovan ER, Hayes JP (2009) Genetic variances and covariances of aerobic metabolic rates in laboratory mice. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 276:3695–3704
Worden BD, Parker PG (2001) Polyandry in grain beetles, Tenebrio molitor, leads to greater reproductive success: material or genetic benefits? Behav Ecol 12:761–767
Worden B, Skemp A, Papaj D (2005) Learning in two contexts: the effects of interference and body size in bumblebees. J Exp Biol 208:2045–2053
Yamamoto T, Ueda H, Higashi S (1998) Correlation among dominance status, metabolic rate and otolith size in masu salmon. J Fish Biol 52:281–290
Yeates LC, Williams TM, Fink TL (2007) Diving and foraging energetics of the smallest marine mammal, the sea otter (Enhydra lutris). J Exp Biol 210:1960–1970
Ylonen H (1994) Vole cycles and antipredatory behavior. Trends Ecol Evol 9:426–430
Zera AJ, Zhao ZW (2006) Intermediary metabolism and life-history trade-offs: differential metabolism of amino acids underlies the dispersal–reproduction trade-off in a wing-polymorphic cricket. Am Nat 167:889–900
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the Academy of Finland to M.J.R. and I.K., by the Estonian Ministry of Education and Science to R.M. (target-financing project number 0180004s09) and to M.M. and A.K. (target-financing project number SF0170057s09), by the Estonian Science Foundation Grant No. 7391 to M.M. and A.K., and by the European Social Fund within the project “Support for the implementation of doctoral studies at Daugavpils University” (agreement number 2009/0140/1DP/1.1.2.1.2./09/IPIA/ VIAA/015) to I.K. and J.V. T.M.F. acknowledges the support of a Fulbright award during Spring 2012, which helped make his work on this manuscript possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krams, I., Kivleniece, I., Kuusik, A. et al. Predation selects for low resting metabolic rate and consistent individual differences in anti-predator behavior in a beetle. acta ethol 16, 163–172 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10211-013-0147-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10211-013-0147-3