Abstract
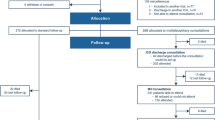
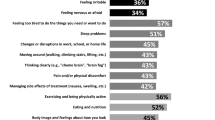
The psychometric properties of the EQ-5D-Y have not been widely tested in severely ill children. The aim of this study was to assess and compare the validity and responsiveness of the EQ-5D-Y-3L and EQ-5D-Y-5L in paediatric inpatients with haematological malignancies and caregivers. Respondents completed the interviewer-administered self-complete or proxy version of the EQ-5D-Y-3L and EQ-5D-Y-5L and an overall health assessment twice on different days. Known-groups validity was assessed by comparing patients who differed in overall health and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance. Responsiveness to worsened health was assessed using standardised effect size (SES) for patients with worsened ECOG grade, self-reported rating, or chemotherapy initiation. Ninety-six dyads completed the baseline questionnaires. A smaller proportion of patients reported “no problems” on the EQ-5D-Y-5L compared to EQ-5D-Y-3L for most of the five dimensions. Patients in poor health reported more problems in all dimensions and had higher EQ-5D-Y-5L level sum score, lower EQ VAS and EQ-5D-Y-3L index scores (Cohen’s d ES: 0.32–1.38 for patients; 0.50–2.05 for caregivers). There was a mild to good responsiveness to worsened health condition based on ECOG (SES: 0.14–0.61 for patients; 0.40–0.96 for caregivers), suggesting the proxy version was slightly responsive than the self-complete version of both instruments. The results demonstrated validity and responsiveness for both the self-complete and proxy versions of the EQ-5D-Y-3L and EQ-5D-Y-5L. The proxy and 5-level versions of the instrument were more sensitive than the self-complete and 3-level versions in this patient group.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in ‘Mendeley’ at: http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.17632/bdnrj3fsyx.1. http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.17632/793w7k59c3.1.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Devlin, N.J., Brooks, R.: EQ-5D and the EuroQol Group: past, present and future. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 15(2), 127–137 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40258-017-0310-5
Wille, N., Badia, X., Bonsel, G., Burström, K., Cavrini, G., Devlin, N., Egmar, A.C., Greiner, W., Gusi, N., Herdman, M., Jelsma, J., Kind, P., Scalone, L., Ravens-Sieberer, U.: Development of the EQ-5D-Y: a child-friendly version of the EQ-5D. Qual. Life Res. 19(6), 875–886 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-010-9648-y
Kreimeier, S., Greiner, W.: EQ-5D-Y as a health-related quality of life instrument for children and adolescents: the instrument’s characteristics, development, current use, and challenges of developing its value set. Value Health. 22(1), 31–37 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2018.11.001
Feng, Y., Devlin, N., Herdman, M.: Assessing the health of the general population in England: how do the three- and five-level versions of EQ-5D compare? Health Qual. Life Outcomes 13, 171 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-015-0356-8
Buchholz, I., Janssen, M.F., Kohlmann, T., Feng, Y.S.: A systematic review of studies comparing the measurement properties of the three-level and five-level versions of the EQ-5D. Pharmacoeconomics 36(6), 645–661 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-018-0642-5
Janssen, M.F., Bonsel, G.J., Luo, N.: Is EQ-5D-5L better than EQ-5D-3L? A head-to-head comparison of descriptive systems and value sets from seven countries. Pharmacoeconomics 36(6), 675–697 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-018-0623-8
Jin, X., Al Sayah, F., Ohinmaa, A., Marshall, D.A., Smith, C., Johnson, J.A.: The EQ-5D-5L Is superior to the -3L version in measuring health-related quality of life in patients awaiting THA or TKA. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 477(7), 1632–1644 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1097/CORR.0000000000000662
Kreimeier, S., Åström, M., Burström, K., Egmar, A.C., Gusi, N., Herdman, M., Kind, P., Perez-Sousa, M.A., Greiner, W.: EQ-5D-Y-5L: developing a revised EQ-5D-Y with increased response categories. Qual. Life Res. 28(7), 1951–1961 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-019-02115-x
Scott, D., Scott, C., Jelsma, J., Abraham, D., Verstraete, J.: Validity and feasibility of the self-report EQ-5D-Y as a generic health-related quality of life outcome measure in children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Western Cape. South Africa. S. Afr. J. Physiother. 75(1), 1335 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4102/sajp.v75i1.1335
Kim, S.K., Jo, M.W., Kim, S.H.: Health-related quality of life by allergy symptoms in elementary school students. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 16(1), 93 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-018-0922-y
Burström, K., Bartonek, Å., Broström, E.W., Sun, S., Egmar, A.C.: EQ-5D-Y as a health-related quality of life measure in children and adolescents with functional disability in Sweden: testing feasibility and validity. Acta Paediatr. 103(4), 426–435 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.12557
Perez Sousa, M.Á., Olivares Sánchez-Toledo, P.R., Gusi Fuerte, N.: Parent-child discrepancy in the assessment of health-related quality of life using the EQ-5D-Y questionnaire. Arch. Argent. Pediatr.Pediatr. 115(6), 541–546 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5546/aap.2017.eng.541. (Spanish)
Hsu, C.N., Lin, H.W., Pickard, A.S., Tain, Y.L.: EQ-5D-Y for the assessment of health-related quality of life among Taiwanese youth with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 30(4), 298–305 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzy011
Bergfors, S., Åström, M., Burström, K., Egmar, A.C.: Measuring health-related quality of life with the EQ-5D-Y instrument in children and adolescents with asthma. Acta Paediatr. 104(2), 167–173 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.12863
Wong, C.K.H., Cheung, P.W.H., Luo, N., Cheung, J.P.Y.: A head-to-head comparison of five-level (EQ-5D-5L-Y) and three-level EQ-5D-Y questionnaires in paediatric patients. Eur. J. Health Econ. 20, 647–656 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-018-1026-7
Fitriana, T.S., Purba, F.D., Rahmatika, R., Muhaimin, R., Sari, N.M., Bonsel, G., Stolk, E., Busschbach, J.J.V.: Comparing measurement properties of EQ-5D-Y-3L and EQ-5D-Y-5L in paediatric patients. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 19(1), 256 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-021-01889-4
Åström, M., Krig, S., Ryding, S., Cleland, N., Rolfson, O., Burström, K.: EQ-5D-Y-5L as a patient-reported outcome measure in psychiatric inpatient care for children and adolescents - a cross-sectional study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 18(1), 164 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-020-01366-4
Pei, W., Yue, S., Zhi-Hao, Y., Ruo-Yu, Z., Bin, W., Nan, L.: Testing measurement properties of two EQ-5D youth versions and KIDSCREEN-10 in China. Eur. J. Health Econ. 22(7), 1083–1093 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-021-01307-y
Verstraete, J., Marthinus, Z., Dix-Peek, S., Scott, D.: Measurement properties and responsiveness of the EQ-5D-Y-5L compared to the EQ-5D-Y-3L in children and adolescents receiving acute orthopaedic care. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 20(1), 28 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-022-01938-6
Gusi, N., Perez-Sousa, M.A., Gozalo-Delgado, M., Olivares, P.R.: Validez y fiabilidad de la versión proxy del EQ-5D-Y en español Validity and reliability of the Spanish EQ-5D-Y proxy version. An. Pediatr. (Barc.)Pediatr. (Barc) 81(4), 212–219 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anpedi.2013.11.028. (Spanish)
Bray, N., Noyes, J., Harris, N., Edwards, R.T.: Measuring the health-related quality of life of children with impaired mobility: examining correlation and agreement between children and parent proxies. BMC. Res. Notes 10(1), 377 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-017-2683-9
Matza, L.S., Secnik, K., Mannix, S., Sallee, F.R.: Parent-proxy EQ-5D ratings of children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in the US and the UK. Pharmacoeconomics 23(8), 777–790 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2165/00019053-200523080-00004
Shiroiwa, T., Fukuda, T., Shimozuma, K.: Psychometric properties of the Japanese version of the EQ-5D-Y by self-report and proxy-report: reliability and construct validity. Qual. Life Res. 28(11), 3093–3105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-019-02238-1
Fitriana, T.S., Purba, F.D., Stolk, E., Busschbach, J.J.V.: EQ-5D-Y-3L and EQ-5D-Y-5L proxy report: psychometric performance and agreement with self-report. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 20(1), 88 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-022-01996-w
Furlong, W., Rae, C., Feeny, D., Gelber, R.D., Laverdiere, C., Michon, B., Silverman, L., Sallan, S., Barr, R.: Health-related quality of life among children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 59(4), 717–724 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.24096
Oken, M.M., Creech, R.H., Tormey, D.C., Horton, J., Davis, T.E., McFadden, E.T., Carbone, P.P.: Toxicity and response criteria of the eastern cooperative oncology group. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 5(6), 649–655 (1982)
EuroQol Research Foundation.: EQ-5D-Y User Guide, 2020. https://euroqol.org/publications/user-guides. Accessed 23 Jan 2022
Idler, E.L., Benyamini, Y.: Self-rated health and mortality: a review of twenty-seven community studies. J. Health Soc. Behav. 38(1), 21–37 (1997)
Verstraete, J., Scott, D.: Comparison of the EQ-5D-Y-5L, EQ-5D-Y-3L and PedsQL in children and adolescents. J. Patient Rep. Outcomes. 6(1), 67 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41687-022-00480-9
Manor, O., Matthews, S., Power, C.: Dichotomous or categorical response? Analysing self-rated health and lifetime social class. Int. J. Epidemiol. 29(1), 149–157 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/29.1.149
Yang, Z., Jiang, J., Wang, P., Jin, X., Wu, J., Fang, Y., Feng, D., Xi, X., Li, S., Jing, M., Zheng, B., Huang, W., Luo, N.: Estimating an EQ-5D-Y-3L Value Set for China. Pharmacoeconomics 40(Suppl 2), 147–155 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-022-01216-9
Zhou, W., Shen, A., Yang, Z., Wang, P., Wu, B., Herdman, M., Luo, N.: Patient-caregiver agreement and test-retest reliability of the EQ-5D-Y-3L and EQ-5D-Y-5L in paediatric patients with haematological malignancies. Eur. J. Health Econ. 22(7), 1103–1113 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-021-01309-w
Perez-Sousa, M.A., Olivares, P.R., Gusi, N.: Psychometric properties of the spanish versions of EQ-5D-Y-3L and EQ-5D-Y-5L in children with cancer: a comparative study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19(18), 11420 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811420
Tan, R.L., Soh, S.Z.Y., Chen, L.A., Herdman, M., Luo, N.: Psychometric properties of generic preference-weighted measures for children and adolescents: a systematic review. Pharmacoeconomics 41(2), 155–174 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-022-01205-y
Sinlapamongkolkul, P., Surapolchai, P.: Health-related quality of life in Thai children with thalassemia as evaluated by PedsQL and EQ-5D-Y: a Single-Center Experience. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 12(1), e2020036 (2020). https://doi.org/10.4084/MJHID.2020.036
Willems, D.C., Joore, M.A., Nieman, F.H., Severens, J.L., Wouters, E.F., Hendriks, J.J.: Using EQ-5D in children with asthma, rheumatic disorders, diabetes, and speech/language and/or hearing disorders. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 25(3), 391–399 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266462309990171
Xu, R.H., Zhu, L., Sun, R., Tan, R.L., Luo, N., Zou, S., Dong, D.: Investigating the psychometric properties of the EQ-5D-Y-3L, EQ-5D-Y-5L, CHU-9D, and PedsQL in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur. J. Pediatr. 181(12), 4049–4058 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-022-04626-1
Lin, J., Wong, C.K.H., Cheung, J.P.Y., Cheung, P.W.H., Luo, N.: Psychometric performance of proxy-reported EQ-5D youth version 5-level (EQ-5D-Y-5L) in comparison with three-level (EQ-5D-Y-3L) in children and adolescents with scoliosis. Eur. J. Health Econ. 23(8), 1383–1395 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-022-01435-z
Wong, C.K.H., Cheung, P.W.H., Luo, N., Lin, J., Cheung, J.P.Y.: Responsiveness of EQ-5D Youth version 5-level (EQ-5D-5L-Y) and 3-level (EQ-5D-3L-Y) in Patients With Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 44(21), 1507–1514 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.000000000000
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the patients and their caregivers from Shanghai Children Medical Centre who participated in the study. Funding for this study was provided by the EuroQol Group (grant number EQ Project 20170330). This work was also sponsored by unrestricted grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 71728010).
Funding
Funding for this study was provided by the EuroQol Group (grant number EQ Project 20170330) and was sponsored by unrestricted grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 7172810).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NL, ZY, PW, BW, MH and JB conceived the study, participated in the design, and made substantial contribution to the intellectual content of the manuscript. WZ, AS and NL participated in the acquisition and interpretation of data, performed statistical analyses and writing of the manuscript. The first draft of the manuscript was written by WZ and AS and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Consent for publication
All of the authors read and approved to publish this article. No contents of this article have been published elsewhere.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Renji Hospital Ethics Committee (Project Identification Code: 2018087). The study protocol followed the tenets of the declaration of Helsinki. The participants were fully informed and informed consent was acquired in writing from all of the participating individuals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, W., Shen, A., Yang, Z. et al. Validity and responsiveness of EQ-5D-Y in children with haematological malignancies and their caregivers. Eur J Health Econ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-024-01669-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-024-01669-z