Abstract
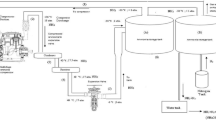
Various research has attempted to determine the proper treatment of sewage sludge, including thermal technologies. Efficient thermal technologies have been focused on because of their energy saving/energy recovery. Gasification technology can be considered one of these approaches. In this study, the characteristics of gasification reactions were investigated with the aim of finding fundamental data for utilizing sewage sludge as an energy source. For the experiments on sewage sludge gasification reaction characteristics, a laboratory-scale experimental apparatus was set up with a fluidizing bed reactor of 70-mm inner diameter and 600-mm total height using an electric muffle furnace. The experimental materials were prepared from a sewage treatment plant located in Seoul. The reaction temperature was varied from 630 to 860°C, and the equivalence ratio from 0.1 to 0.3. The gas yields, compositions of product gas, and cold gas efficiencies of product gas were analyzed by GC/TCD and GC/FID installed with a carboxen-1000 column. The experimental results indicated that 800°C, ER 0.2 was an optimum condition for sewage sludge gasification. The maximum yield of product gas was about 44%. Producer gas from experiments was mainly composed of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane. The cold gas efficiency of sewage sludge gasification was about 68%. The H2/CO ratio and CO/CO2 ratio were about 1.1 and 1.4, respectively, in optimum reaction conditions. Gaseous pollutants such as SO2, HCl, NH3, H2S, and NO2 were also analyzed at various gasification/combustion conditions, and their gaseous products were compared, showing significantly different oxidized product distributions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ministry of Environment of Korea (2009) Water and sewage statistics. pp 766–781
Yoon YS (2004) Hydrogen production technology by gasification. Korea Soc Energy Eng 13:1–11
Basu P (2006) Combustion and gasification in fluidized beds. CRC press, USA, pp 59–101
Shen LH (2007) Simulation of hydrogen production from biomass gasification in interconnected fluidized bed. Biomass Bioenergy 32:120–127
Kirkels AF, Verbong GPJ (2011) Biomass gasification: still promising? A 30-year global overview. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 15:471–481
Lv PM, Xiang ZH, Chang J, Wu CZ, Chen Y, Zhu JX (2004) An experimental study on biomass air-steam gasification in a fluidized bed. Bioresour Technol 95:95–101
Manya JJ, Sanchez JL, Abrego J, Gonzalo A, Arauzo J (2006) Influence of gas residence time and air ratio on the air gasification of dried sewage sludge in a bubbling fluidised bed. Fuel 85:2027–2033
National Institute of Environmental Research of Korea (2007) Standard method
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, SW., Dong, JI., Kim, JM. et al. Gasification and its emission characteristics for dried sewage sludge utilizing a fluidized bed gasifier. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 13, 180–185 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-011-0016-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-011-0016-y