Abstract
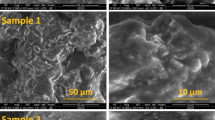
This article reports the operational results of the effective utilization of hospital waste molten slag produced using a high-temperature melting system, and being operated at a hospital in Selangor, Malaysia. The hospital waste is incinerated and subsequently melted at 1200°C. Scanning election microscope (SEM)/EDX results showed that the slag produced after melting contained amounts of SiO2, CaO, and Al2O3 in excess of 53%, 9%, and 16%, respectively. The results from a leaching analysis on the slag produced proved that the melting process had successfully stabilized the heavy metals. The use of this slag as an alternative material to replace conventional aggregates for road construction was studied. The results from aggregate and asphalt mix tests showed that the slag produced fulfills all the requirements of an alternative aggregate. The average asphalt content, or the optimum asphalt content to be mixed with hospital waste molten slag, was found to be about 5.53%.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azni, I., Katayon, S., Ratnasamy, M. et al. Stabilization and utilization of hospital waste as road and asphalt aggregate. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 7, 33–37 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-004-0123-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-004-0123-0