Abstract
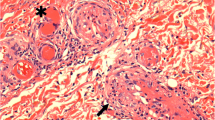
Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia is rare lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by the presence of a monoclonal IgM paraproteinemia. Cryoglobulinemia is a common sequela of Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia present in 8–18% of the patients. Cryoglobulinemia has also been described as occurring after treatment with rituximab. In the previous report, the cryoglobulinemia was a transient phenomenon and did not carry any adverse effect. We present a case of an 80-year-old male with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia in whom the rituximab-induced cryoglobulinemia resulted in acute renal failure and a vasculitic rash. Cryoglobulins level reached a peak of 63%. The patient was successfully treated with plasmapheresis, chlorambucil and prednisone, with near-complete recovery of renal function. As this case illustrates, the rituximab-induced cryoglobulin is not always benign. Pre- and post-treatment monitoring of the cryoglobulin level is advised in these patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brouet JC, Clauvel JP, Seligmann M. Cryoglobulinemias. Clinical and biological correlations. Ann Med Intern. 1975;126:563–7.
Dammacco F, Gnisci G, Silvestris F, Bonomo L. New clinical and immunological trends in cryoglobulinemia. Ric Clin Lab. 1980;10:51–7.
Mussini C, Mascia MT, Zanni G, Curci G, Bonacorsi G, Artusi T. A cytomorphological and immunohistochemical study of bone marrow in the diagnosis of essential mixed type II cryoglobulinemia. Haematologica. 1991;76:389–91.
Invernizzi F, Galli M, Serino G, Monti G, Meroni PL, Granatieri C, et al. Secondary and essential cryoglobulinemias. Frequency, nosological classification, and long-term follow-up. Acta Haematol. 1983;70:73–82.
Gobbi PG, Bettini R, Montecucco C, Cavanna L, Morandi S, Pieresca C, et al. Study of prognosis in Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia: a proposal for a simple binary classification with clinical and investigational utility. Blood. 1994;83:2939–45.
Dimopoulos MA, Alexanian R, Gika D, Anagnostopoulos A, Zervas C, Zomas A, et al. Treatment of Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia with rituximab: prognostic factors for response and progression. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004;45:2057–61.
Treon SP, Hansen M, Branagan AR, Verselis S, Emmanouilides C, Kimby E, et al. Polymorphisms in FcgammaRIIIA (CD16) receptor expression are associated with clinical response to rituximab in Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:474–81.
Treon SP, Emmanouilides C, Kimby E, Kelliher A, Preffer F, Branagan AR, et al. Extended rituximab therapy in Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. Ann Oncol. 2005;16:132–8.
Ghobrial IM, Uslan DZ, Call TG, Witzig TE, Gertz MA. Initial increase in the cryoglobulin level after rituximab therapy for type II cryoglobulinemia secondary to Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia does not indicate failure of response. Am J Hematol. 2004;77:329–30.
Gorevic PD, Kassab HJ, Levo Y, Kohn R, Meltzer M, Prose P, et al. Mixed cryoglobulinemia: clinical aspects and long-term follow-up of 40 patients. Am J Med. 1980;69:287–308.
Treon SP, Agus TB, Link B, Rodrigues G, Molina A, Lacy MQ, et al. CD20-directed antibody-mediated immunotherapy induces responses and facilitates hematologic recovery in patients with Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. J Immunother. 2001;24:272–9.
Kanelli S, Ansell SM, Habermann TM, Inwards DJ, Tuinstra N, Witzig TE. Rituximab toxicity in patients with peripheral blood malignant B-cell lymphocytosis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001;42:1329–37.
Zaja F, De Vita S, Mazzaro C, Sacco S, Damiani D, De Marchi G, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in type II mixed cryoglobulinemia. Blood. 2003;101:3827–34.
Roccatello D, Baldovino S, Rossi D, Mansouri M, Naretto C, Gennaro M, et al. Long-term effects of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment of cryoglobulinaemic glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19:3054–61.
Basse G, Ribes D, Kamar N, Mehrenberger M, Esposito L, Guitard J, et al. Rituximab therapy for de novo mixed cryoglobulinemia in renal transplant patients. Transplantation. 2005;80:1560–4.
Nehme-Schuster H, Korganow AS, Pasquali JL, Martin T. Rituximab inefficiency during type I cryoglobulinaemia. Rheumatology. 2005;44:410–1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Shaikh, A., Habermann, T.M., Fidler, M.E. et al. Acute renal failure secondary to severe type I cryoglobulinemia following rituximab therapy for Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Clin Exp Nephrol 12, 292–295 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-008-0042-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-008-0042-9